by Lisa Cooke | Oct 2, 2014 | 01 What's New, Digital Archives, images
Digital archives are getting so much better! They’re not just about reproducing historical documents anymore. Multimedia add-ons–from searchable statistics to animated timelines–fill in the gaps not explained by the map keys.
Atlas of the Historical Geography of the United States, http://dsl.richmond.edu/historicalatlas/.
Recently, Slate.com writer Rebecca posted on some of her favorite digital archives. Four of the five are of interest to genealogists! Read the article to learn more about them:

Want to learn more about using maps in your research? Watch my FREE class on Google Earth for Genealogy. Genealogy Gems Premium members can also watch my NEW video class online, 5 Ways to Enhance Your Genealogy Research with Old Maps. (Not a Premium member? Learn more here.)
by Lisa Cooke | Aug 8, 2014 | 01 What's New, Digital Archives, Google, Maps
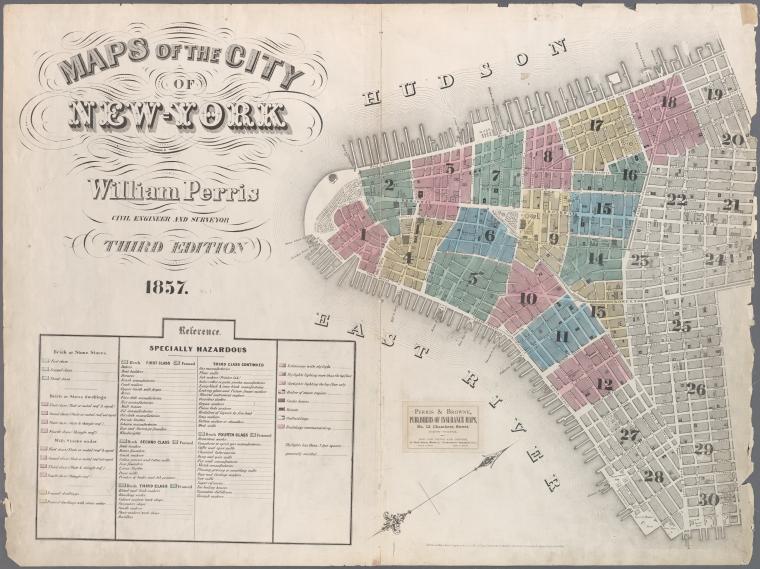
Map of New York City, 1857. Click for full citation information.
Thousands of historical maps of New York City, the mid-Atlantic states and even the Austro-Hungarian empire (yes, really!) are now online–and they’re free.
The New York Public Library has published more than 20,000 historical maps dating from 1660-1922. They are free for public use, downloading, manipulating and publishing! A lot of the maps are from New York City neighborhoods, like the one shown here.
The author of a news item about the collection said this: “We can’t imagine too many people wanting to remix Gangs of New York-era property charts, but it’s hard to object to getting more geographic knowledge at no charge.” Well, we genealogists may not “remix” these old property maps, but we can certainly see the value in them!
Do you use maps in your research? Have you tried overlaying a historical map showing an ancestor’s home with a modern one on Google Earth? Learn more about using Google Earth in your genealogy research in this FREE video.
And if this post is interesting to you, you should also read this blog post about interactive historical maps of major cities (like New York City).
by Diahan Southard | Jul 24, 2014 | 01 What's New, Beginner, Newspaper
 Recently I decided to learn more about my great-uncle Paul McClellan, my grandfather’s brother. After World War II, Paul left his Idaho hometown for Pennsylvania. Surviving relatives know hardly anything of his life or family.
Recently I decided to learn more about my great-uncle Paul McClellan, my grandfather’s brother. After World War II, Paul left his Idaho hometown for Pennsylvania. Surviving relatives know hardly anything of his life or family.
The census only takes me through 1940 and he lived through the 1970s. Pennsylvania vital records are pretty tight-lipped. So almost immediately, I found myself looking for obituaries.
Our online community tree at FamilySearch told me when and where he died. I emailed the local history and genealogy contact at the public library in that town. I heard back within a day and had this obituary within a week.
I’ve seen a lot of detailed obituaries. But perhaps because I’m so thirsty for information on Paul, the level of detail in this obituary made me especially happy. I see his:
- Age
- Street address
- Hospital where he died and length of stay there
- Birthplace and age
- Parents’ names, including mother’s maiden name
- Employer and retirement date
- Membership in local civic organizations
- WWII Army veteran status
- Surviving widow’s name, including maiden name
- Names, spouses and residences of surviving siblings
- Name of funeral home and officiator of funeral
- Cemetery name
Wow! Some of these details confirmed that I had the right guy: his age, birth data, relatives’ names. Others open new avenues of research for me. I’ve already started following leads to the civic organizations, funeral home and cemetery.
You know, what is NOT said in this obituary may also prove important as I continue my research on Paul. First, there are no surviving children or grandchildren listed. This disappoints me as I was told he did have children by at least one previous marriage. If he did have children, the informant (his widow?) either didn’t know about them or didn’t choose to mention them. Second, the informant did know a lot about Paul’s kin. Maybe Paul and his wife didn’t totally lose touch with the folks back home–it just seems so years later.
Have you worked much with obituaries? Do you know how to find them? Learn more in Lisa’s book How to Find Your Family History in Newspapers, available in print or as an e-book. There’s an entire chapter on online digitized newspaper collections, and one on online resources for finding newspapers (either online or offline). Yet another chapter is devoted to African American newspapers. This book will teach you to find all those elusive obituaries–and plenty more mentions of your family in old newspapers.
by Lisa Cooke | Feb 17, 2014
Join Lisa at an upcoming event near you! Genealogy conferences, seminars, workshops, webinars, and more! Lisa speaks to audiences all over the world with dynamic, education, and entertaining presentations on the hottest topics in genealogy. Be enthralled and inspired...
by Lisa Cooke | Feb 16, 2014 | 01 What's New, Adoption, Beginner, History
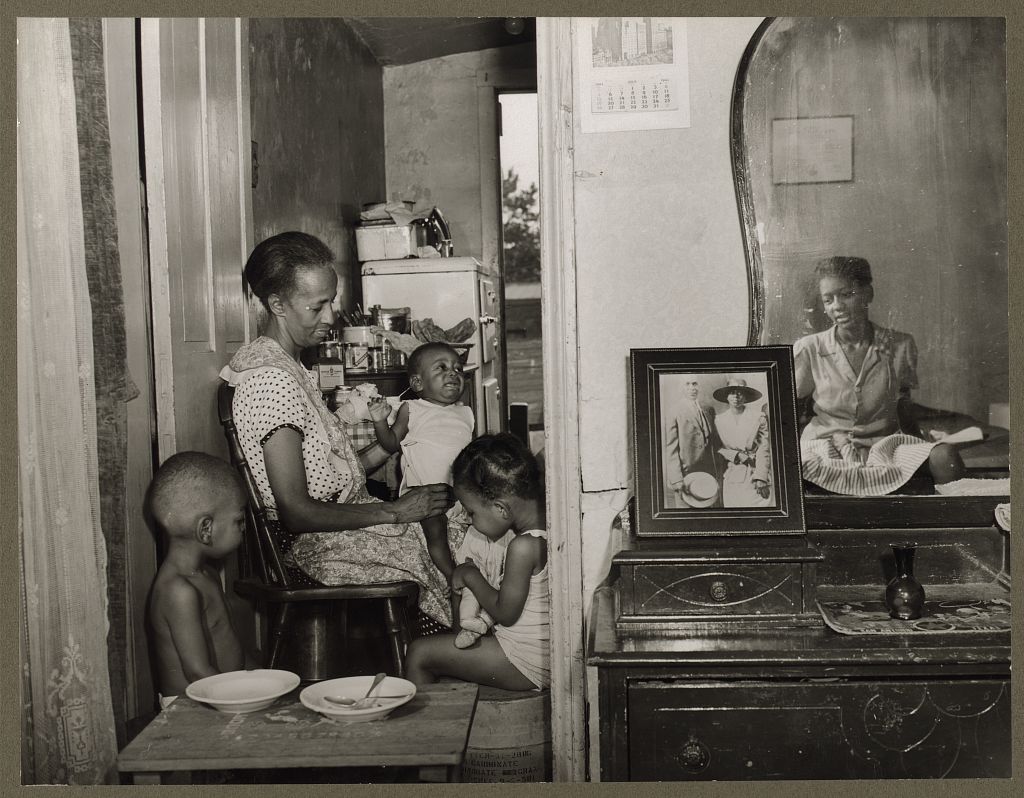

Mrs. Ella Watson, a government charwoman, with three grandchildren and her adopted daughter [reflected in the mirror]. Image from The Gordon Parks Archives in the Library of Congress.
Formal, legal adoption wasn’t common in the U.S. until the late 1800s. (State adoption laws didn’t even exist until after Massachusetts passed the first one in 1851.) Before that, if mom and dad couldn’t take care of a child, a relative, neighbor or friend took that child in, or the child was sent to a county orphanage or poor home. In even earlier days, orphaned or poverty-stricken children were also sold by their towns into indentures.
The Adoption History Project at the University of Oregon has a great timeline of adoption history in the U.S. Check it out to see what was going on when your family member was adopted.
To learn more about adoption and genealogy research, check out these links:
FamilySearch Wiki U.S. Adoption Research
All About Adoption Research by Maureen Taylor
RootsWeb’s Guide to Tracing Family Trees: Adoption





