by Lisa Cooke | Mar 18, 2014 | 01 What's New, Certification, Family History Podcast, Research Skills, Source Citation
Listen to the Family History: Genealogy Made Easy podcast by Lisa Louise Cooke. It’s a great series for learning the research ropes and well as refreshing your skills.
Originally published 2009
Republished March 18, 2014
https://lisalouisecooke.com/familyhistorypodcast/audio/fh23.mp3
Download the Show Notes for this Episode
Welcome to this step-by-step series for beginning genealogists—and more experienced ones who want to brush up or learn something new. I first ran this series in 2008-2009. So many people have asked about it, I’m bringing it back in weekly segments.
Episode 23: The GPS in Action: Using the Genealogical Proof Standard
In episode 20, we talked about using the Genealogical Proof Standard (GPS), the powerful research process used by the professionals. This process ensures the quality, accuracy and success of our research. Researching by these standards now may save you going back and re-doing some of your hard work later down the road.
In today’s episode I’m going to help you put the GPS into concrete action with an example from my own research. And I have some downloadable free tools that will help you do the job! In this episode we also follow up with a listener question on how to export your family tree from Ancestry.com—see below for an updated link.
The GPS in Action
Wouldn’t it be nice to have a worksheet that prompts you through the GPS process and helps you keep track of everything and stay organized? Well, I wanted something like that myself. I think we need more than just a blank form: we need and want a detailed worksheet that not only gives the area to record our findings, but also buy medication online usa incorporates all the key areas of the Genealogical Proof Standard so that we can be sure we aren’t missing anything.
I didn’t find something like this online so I created it myself. Click on the Research Worksheets, under Links below, for both a filled-out sample version and a blank version that you can save to your computer.
According to the Board of Certification of Genealogists the 5 keys elements of the Genealogical Proof Standard are:
- a reasonably exhaustive search
- complete and accurate source citations
- analysis and correlation of the collected information
- resolution of any conflicting evidence
- a soundly reasoned, coherently written conclusion
I’ve incorporated these elements while keep in mind Mark Tucker’s process map worksheet (see Links section below) into my Research Worksheet.
The Research Worksheet is divided into the following sections:
- Research Objective
- Known Facts
- Working Hypothesis
- Research Strategy
- Identified Sources
- Final Conclusions
In your conclusion which is called a Proof Argument you should:
- Explain the problem
- Review the known sources which you identified on your worksheet
- Present the evidence with source citations and the analysis of those sources
- Discuss any conflicting evidence. This important because it may generate another search that needs to occur, or put to rest questions about evidence that on first glance looks conflicting.
- And finally summarize the main points of your research and state your conclusion.
Updates and Links
How to download your GEDCOM from Ancestry.com
Research Worksheet: Example
Research Worksheet: Blank Form
Correspondence Log
Mark Tucker’s GPS Flowchart
by Lisa Cooke | May 23, 2014 | 01 What's New, MyHeritage
 MyHeritage has signed on to sponsor The Genealogy Gems Podcast! Their support helps us to continue to bring you free multimedia content to inspire and inform your genealogy journey.
MyHeritage has signed on to sponsor The Genealogy Gems Podcast! Their support helps us to continue to bring you free multimedia content to inspire and inform your genealogy journey.
Our editorial team has spent several months getting to know MyHeritage.com. We think you’ll love their…
International membership. MyHeritage serves over 70 million members worldwide in 40 languages. Did your English-speaking ancestors originate in the British Isles? Are you discovering Sephardic roots in Spain? MyHeritage members may be your cousins—or know something about them. Check out their world membership map here.
24/7 record searching technology. MyHeritage uses a unique and powerful search system called Record Matches to constantly cull 5 billion historical records for your family. It’s the only family history interface out there using semantic analysis to search newspaper articles, books, and other free-text documents. It is also the first to translate names between languages. I personally like that matches from MyHeritage’s historical newspaper collections show up toward the top. It’s a great way to find obituaries!
Millions of trees. MyHeritage can search over 1.5 billion records in their own 27 million trees and recently-acquired Geni.com’s unified tree. From a single screen, members can search all those trees plus WikiTree and other trees. But you don’t even have to search. MyHeritage’s unique Smart Matching technology intelligently matches each family tree to hundreds of millions of profiles in other family trees. Members are alerted when new matches appear on the site.
Offline software companion. Family Tree Builder 7.0 is free software that allows you to keep a master copy of your family tree offline. Read my blog post on that topic here.
Great app. The MyHeritage app for iPhone, iPad and Android 2.2 helps you research, record and share your family history on the go. You can browse records, photo-share, and show off your tree in its beautiful display.
Genealogy Gems will continue to bring you news and gems on a wide range of genealogy topics and companies, not just MyHeritage. But we do encourage you to get to know MyHeritage.com. We choose our advertisers carefully and are very proud to partner with them!
by Lisa Cooke | Apr 6, 2020 | 01 What's New, Legacy Tree Genealogists, Research Skills |
The Genealogical Proof Standard tells us that we need to conduct reasonably exhaustive research in order for our work to be credible. If you’ve ever wondered just what constitutes “reasonable” (and if your family tree is up to snuff) my guest author Kate Eakman, professional genealogist at Legacy Tree Genealogists, has answers.

Professional Genealogist Kate Eakman explains evidence on the Genealogy Gems blog.
Genealogical Evidence: Have You Got What It Takes?
How do we know when we have compiled enough evidence to constitute proof?
Is a birth certificate or an autosomal DNA test result sufficient to declare this person is the child of that person?
Must we collect every record regarding an individual – the deeds, the tax lists, the newspaper clippings, the census reports – before we can declare a familial connection?
The Genealogical Proof Standard (GPS)
The Genealogy Proof Standard (GPS) directs us to perform reasonably exhaustive research, which requires that we identify and review all available records related to an individual.[1] This is being as thorough and accurate as possible and is a goal toward which we should all aspire in our genealogical research.
But, let’s be honest: most of us do not want to spend weeks or months (or even years) documenting one person before moving on to the next individual. We don’t want to know every detail of grandpa’s life before we turn to grandma.
We want to build a family tree which accurately provides us with the names of our ancestors so that we can identify our immigrant ancestor, or join a lineage society, or enjoy the satisfaction that comes from a balanced tree extending back a hundred years or more.
We want to be thorough and accurate, but we also want to make some progress. How do we balance the need for accuracy with the desire for results? How do we determine the necessary quality and quantity of evidence for our research?
Below are some guidelines to demonstrate how we can go about compiling the necessary information to say with confidence “this person is my ancestor.”
Genealogical Evidence Guidelines
1. One record/source is never enough.
Any one piece of data can say anything. A mother might lie on her child’s birth certificate for a number of reasons. A grieving spouse might not correctly recall the information for a husband or wife’s death certificate. There are typos and omissions and messy handwriting with which to contend. Even a lone DNA test is not sufficient evidence to prove a family connection.
We need multiple sources, and different kinds of sources, which corroborate the details of the others.

A single source is not enough. A marriage license does not guarantee that John and Griselda married. Photo courtesy https://newspapers.com.
A census report and autosomal DNA test results.
A deed and a will.
A birth certificate and an obituary.
Or, better still, a birth certificate, a census report, a deed, a will, an obituary, and autosomal DNA test results.
2. The more contemporary the source is to the person or event in question, the better.
Records of events made immediately after the event tend to be more accurate, and provide better details, than records created months or years later. As time passes, details become fuzzy, two events can be confused with each other, and our memories fade.
The passage of time between an event and the record of the event also allows for some revisionist history to creep in.
Here are some examples:
A birth year is adjusted to make someone appear older or younger in order to avoid the draft, enlist in the military, mask a dramatic age difference between spouses, or conceal an out-of-wedlock birth.
An obituary ignores the deceased’s first marriage because of some embarrassment associated with that marriage.
A census report enumerates everyone in the household as natives of Stepney, London, when they really were born in Stepney, and Hackney, and Whitechapel, which explains why the baptismal records can’t be found in Stepney.

According to this obituary for Griselda, she was the widow of Willis Tenney, not John Wise. It appears Griselda and John did not marry after all. Photo courtesy https://newspapers.com.
According to this obituary for Griselda, she was the widow of Willis Tenney, not John Wise. It appears Griselda and John did not marry after all. Photo courtesy https://newspapers.com.
This is particularly true when it comes to autosomal DNA testing. My autosomal DNA is more useful for identifying my ancestors than is my son’s because I am one generation closer to those ancestors. This is the reason we encourage people to test the oldest members of their family first: their DNA has the potential to be the most useful simply because they are from an earlier generation (or two).
3. It is okay to make appropriate assumptions, but be careful!
In genealogical research we must sometimes make assumptions. When research theories are based on logical reasoning, it is perfectly acceptable to make those appropriate suppositions.
Determining which assumptions are appropriate can be simple: the two-year-old child enumerated in the home of a 90-year-old woman in the 1850 census can safely be eliminated as a biological child of that woman; the man born in 1745 could not have been buried in 1739; the person with whom I share 3150 cM of DNA is my sibling.
The challenge is to avoid making what seems like an appropriate assumption but is really based on faulty reasoning or bias. For instance, we presume that every child listed in a household in the 1860 U.S. Census is son or daughter of the two adults listed first. However, the household could include step-children, cousins, or individuals not even related to the family who were erroneously assigned the same surname.
Other inappropriate assumptions can include:
- the notion that a baby was born within a week of his baptismal date;
- a woman’s reported surname on her marriage certificate is her maiden name;
- there is only one person in any village, town, or city with the name of your ancestor;
- someone who shares 2000 cM of DNA with you must be your grandparent, aunt or uncle, niece or nephew, half sibling, or grandchild (they could be a ¾ sibling, the child of one of your parents and the sibling of the other parent).
4. All of the data from the various sources must correlate, and there can be no unresolved contradictions.
When the birth certificate says Richard was born in 1914, the 1938 newspaper article about his wedding reports Richard was 24 years old and the 1942 World War II Draft Registration card notes Richard’s date of birth occurred in 1914, we can confidently declare Richard was born in 1914.
If the wedding article declared the groom was 23 years old the contradiction could be explained by the time of year in which the wedding occurred – before or after Richard’s birthday.
But if his birth certificate reported a 1914 birth, and the newspaper article noted Richard was 32 years old, while the World War II Draft Registration listed his year of birth as 1920, we have some important contradictions. It is most likely the records are for three different men with the same name.
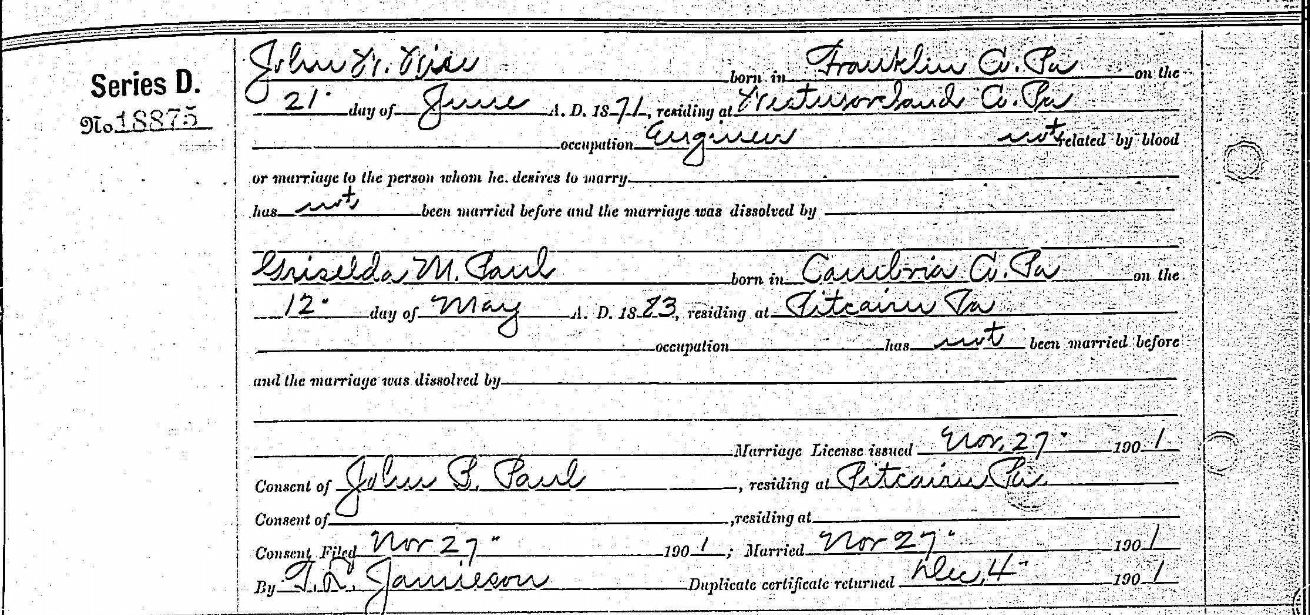
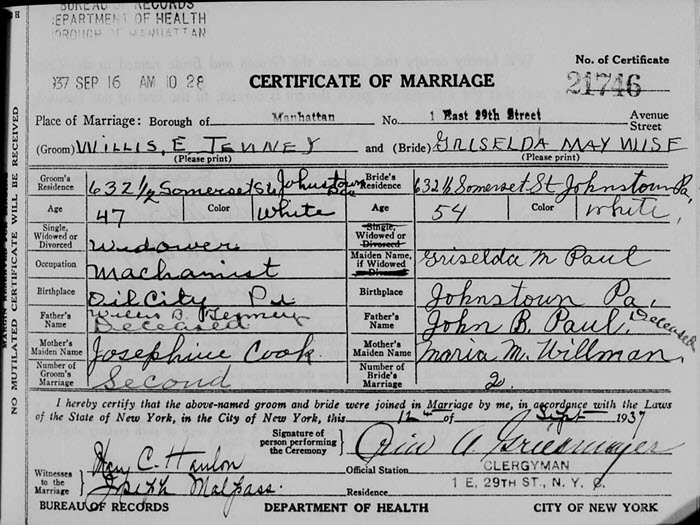
By collecting additional evidence, we finally learn that Griselda and John Wise did marry, and after his death Griselda married Willis Tenney. If we had collected only one of these four records we would not have had the most accurate information regarding Griselda Paul. Photos courtesy https://familysearch.org.
It’s important to remember that once we have accomplished that initial goal of building out our tree a few generations (or identifying our immigrant ancestor, or determining if we are related to that historical person) we can – and should – go back and collect other sources related to that person. This will result in uncovering a more complete story of their lives in the process.
As we can see from the four documents regarding Griselda Paul’s marriages, her story is much more than a simple list of birth, marriage, and death dates. As we identify, review, and analyze the other available sources, Griselda’s story will come alive with the facts and details we uncover.
A Fresh Set of Eyes on Your Genealogy Brick Wall
Sometimes the wrong evidence or assumptions can push us into a brick wall. A fresh set of expert eyes can help you identify the problem, and recommend the sources you need to pursue in order to compile trustworthy evidence.
If you are looking for some assistance in your genealogical research, Legacy Tree Genealogists can help. Our affordable ($100 USD) Genealogist-on-DemandTM Virtual Consultation service provides you with the opportunity for a 45 minute one-on-one discussion of your research with one of our expert genealogists. We can help guide you in evaluating evidence and determining research strategies to move forward with your research confidently.

About the Author: Kate Eckman
Legacy Tree guest blogger Kate Eakman grew up hearing Civil War stories at her father’s knee and fell in love with history and genealogy at an early age. With a master’s degree in history and over 20 years experience as a genealogist, Kate has worked her magic on hundreds of family trees and narratives.

Professional Genealogists Kate Eakman
[1] “Genealogical Proof Standard (GPS),” Board for Certification of Genealogists, https://bcgcertification.org/ethics-standards, accessed March 2020.
by Lisa Cooke | Jan 9, 2015 | 01 What's New, Ancestry, Newspaper, Research Skills
 Recently Sue from Elk Grove, Illinois wrote in with a question about what to do when records were lost due to fire (or war, or disasters, etc.):
Recently Sue from Elk Grove, Illinois wrote in with a question about what to do when records were lost due to fire (or war, or disasters, etc.):
“We have been trying to locate information on my great great grandparents Hugh and Mae Sullivan. I have never been able to find marriage or birth records and have realized that it was mainly due to the Great Chicago Fire of 1871. Interestingly, through a directory from 1866, they may have lived only blocks from the origin of the fire. I have them in 1880 with 4 sons, the first of which was born just 10 months following the fire.
“I suspect that they may have lost other children in the tragedy. I am unsure which direction to go to find more of their story and any suggestions would be helpful. Several newspapers are reported to have lists of the missing but I have either been unable to read them or to locate them. Sam Fink’s list [an index of Cook County marriages and deaths] did not provide any information. I suspect that my ancestors were among the very poor immigrants that flooded into Chicago. There were relief societies and I have wondered if records were kept of those who were rehoused.”
Here’s my response to Sue:
 I think you are on the right track with newspapers. Newspapers.com (owned by Ancestry) carries the Chicago Daily from 1871. Here is a screen shot of the List of Missing from Oct. 11, 1871. It might be worth a subscription to Newspapers.com to be able to really comb through all the issues.
I think you are on the right track with newspapers. Newspapers.com (owned by Ancestry) carries the Chicago Daily from 1871. Here is a screen shot of the List of Missing from Oct. 11, 1871. It might be worth a subscription to Newspapers.com to be able to really comb through all the issues.
 Here’s a tip on working with less-than-the best digital images of historical newspapers. You can “invert” the actual image (have it read white-on-black instead of black-on-white), then darken it and add a little more contrast to get the most readable copy possible. This can be done right from the Newpapers.com viewer.
Here’s a tip on working with less-than-the best digital images of historical newspapers. You can “invert” the actual image (have it read white-on-black instead of black-on-white), then darken it and add a little more contrast to get the most readable copy possible. This can be done right from the Newpapers.com viewer.
Also, in Family History podcast episode #37 I discussed a book specifically on Chicago research: Finding Your Chicago Ancestors: A Beginners Guide To Family History In The City Of Chicago by Grace DuMelle. As I recall, it was a very comprehensive book and could give you good leads on where to look.
by Grace DuMelle. As I recall, it was a very comprehensive book and could give you good leads on where to look.

For more tips like these, read my book How to Find Your Family History in Newspapers. Inside you’ll find:
- Step-by-Step Instructions
- Worksheets and Checklists
- Tech Tools You Probably Aren’t Using But Should
- A Massive Amount of Location Specific Websites and a Case Study that Puts It Al Together
by Lisa Cooke | Apr 11, 2015 | 01 What's New, Humor, images, Trees

“STWink Eye” by Source. Licensed under Fair use via Wikipedia – https://lisalouisecooke.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/04/FileSTWink_Eye.jpg.
After the passing of beloved actor Leonard Nimoy last month, MyHeritage.com took a closer look at his ancestry. Through resources on the world tree site Geni.com, MyHeritage discovered that this star of the Star Trek universe is related to another of its stars, though in the show they portray characters from different worlds.
According to a MyHeritage blog post, “Leonard Nimoy is William Shatner’s second cousin once removed’s wife’s first cousin once removed’s husband’s great niece’s husband’s fourth cousin’s ex-husband.”
Okay, so they’re very distantly and circuitously related! But they are, just like many of us. Click on the blog post above to see a chart showing their family relationship.
 Celebrity genealogy aside, do you want to chart your own topsy-turvy family relationships? Click here to find out about relationship calculators and how they help relatives figure out how they are related to each other.
Celebrity genealogy aside, do you want to chart your own topsy-turvy family relationships? Click here to find out about relationship calculators and how they help relatives figure out how they are related to each other.











 I think you are on the right track with newspapers.
I think you are on the right track with newspapers. 


