by Lisa Cooke | Feb 6, 2015 | 01 What's New, Canadian, Google Earth, History, Maps, Military, United States
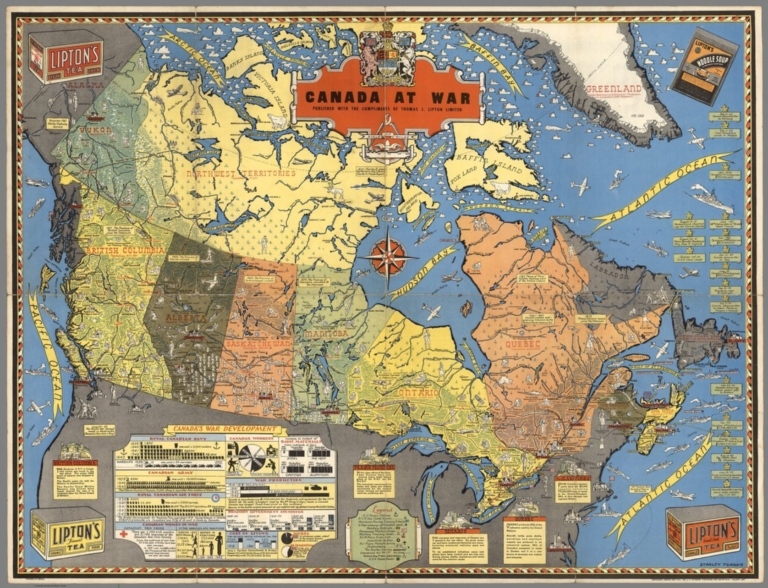
Canada at War by Stanley Turner, 1944. Online at the David Rumsey Map Collection. Click on image for full citation and to access image.
During World War II, millions of people anxiously followed the progress of battles and troop movements that affected their loved ones. Artists and map-makers stepped up to provide colorful, action-packed maps.
Toronto artist Stanley Turner was one of these. He created a series of maps between 1942 and 1945 that were printed and licensed as promotional giveaways to businesses in Canada and the U.S. Today you can find Turner’s maps digitized at the David Rumsey Map Collection.
Stanley wasn’t the only one making these beautiful maps. Read about Richard Eddes Harrison and the big changes in popular cartography during the war in my blog post, “World War II: A Revolution in Map-Making.”
Fast-forward 60 years in time, and the latest revolution in map-making and information-sharing is where? On Google Earth! Google Earth is packed with topography, but also shows us man-made features like roads and bridges, geographic boundaries, historical maps and photographs and so much more. These help us understand things like movements of our ancestors–whether they were troops in World War II or settlers in distant places.
 Want to learn more about using Google Earth for genealogy (or the Google Earth Pro version that was just released FREE to the public)? Become a Genealogy Gems Premium member. You’ll have access to video classes like these:
Want to learn more about using Google Earth for genealogy (or the Google Earth Pro version that was just released FREE to the public)? Become a Genealogy Gems Premium member. You’ll have access to video classes like these:
- Time Travel with Google Earth
- 5 Ways to Enhance Your Research with Old Maps (this class’ retail value alone is $39.95)
Premium Membership is a bargain at only $29.95 for an entire year’s access, plus right now you get the free bonus ebook Lisa Louise Cooke’s 84 Best Tips, Tricks & Tools from Family Tree Magazine. Click here to learn more about Premium Membership.
by Lisa Cooke | Aug 25, 2011 | Google
Podcast Listener Joan wrote me recently: “I get to spend a day at the National Archives. What should I do to prepare to take full advantage of the visit? I checked their website, but it was not as helpful as I hoped. Any suggestions?”
While this first resource is from the National Archives in the UK, it’s applicable to archives in other countries as well. Check out their video series called Quick Animated Guide.
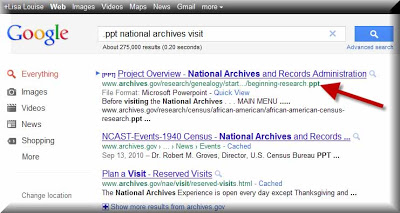
Another good approach is to search for presentations on archive visits using Google. By conducting a ‘file type search’ in Google you can uncover presentations posted on the Web that are geared to doing research at the National Archives.
I conducted the following search in Google:
.ppt national archives research and came up with a Powerpoint presentation called
Beginning Your Genealogical Research at the National Archives which comes from the US National Archives website. When you click the link above you’ll be prompted to RUN the presentation, and I found that it detected Powerpoint on my computer and opened the presentation in my Powerpoint program.
This little genealogy search gem can come in quite handy. Sometimes you know exactly what kind of file or document you are looking for online. By searching for the keywords of the subject and then adding .ppt (the file extension for Powerpoint presentations) Google will pull up only Powerpoint presentations that include those keywords.
You may not be able to get out to genealogy conferences very often, but some creative searching may bring up presentations that cover topics that interest you right from your home computer. That’s a little gem you need to add to your search toolbox for sure! For more search gems check out my book
The Genealogist’s Google Toolbox.

Available in the Genealogy Gems Store
And finally, when it comes to preparing for and making a trip to an archive or library Margery Bell of the Family History Centers offered some great ideas for preparing for a research trip, regardless of whether it is to the National Archives or the Family History Library. The interviews are episode 17, 18 & 19 in the
Family History: Genealogy Made Easy podcast.
Great question Joan and have a wonderful time! Happy hunting everyone!
by Lisa Cooke | Mar 6, 2015 | 01 What's New, Brick Wall, Canadian, Cemeteries, FamilySearch, Google, Maps, Records & databases, Research Skills, United States
Every week, we see so many new genealogy records posted online! We highlight major resources in individual blog posts. But sometimes smaller or  regional collections catch our eye, too. We’ll round these up for you in a post like this on Fridays.
regional collections catch our eye, too. We’ll round these up for you in a post like this on Fridays.
Watch for the genealogy records that your ancestors might appear in–but also watch for the kinds of records that may be out there for your kin, which might help you break down your family history “brick walls.”
PRISON RECORDS. Kingston, Canada, Penitentiary Inmate Ledgers, 1913-1916, are now available on Flickr. According to GenealogyCanada.blogspot.com, “The ledger includes frontal and profile mug shots, the inmate’s name, alias, age, place of birth, height, weight, complexion, eye colour, hair colour, distinctive physical marks, occupation, sentence, date of sentence, place of sentence, crime committed, and remarks of authorities.”
CEMETERY HEADSTONES. The Canadian Headstone Photo Project is now also searchable at FamilySearch.org. The original site with over a million headstone photos isn’t new. But some people don’t know about the site, and its search interface isn’t as pretty or flexible. So we think it’s nice that FamilySearch is hosting that data, too. According to FamilySearch, the collection is still growing. “This collection will include records from 1790-2013. The records include a name index of headstone inscriptions, courtesy of CanadianHeadstones.com, which is a family history database of records and images from Canada’s cemeteries.”
HISTORICAL PROPERTIES MAP INTERFACE. The state of Delaware in the United States has launched an updated version of its CHRIS (Cultural and Historical Resource Information System) GIS tool. Use this interface to explore houses, districts and National Historic Landmarks in your ancestor’s Delaware neighborhoods. Maybe a place they lived, worked, shopped, worshiped or attended is still standing!
 Not sure how to find record sets like these for YOUR family history? Here’s a tip! Use the “numrange” search operator in Google to locate records from a particular time period. Do this by typing the range of years to search (first and last year) into your Google search box, with two periods in between (no spaces). For example, the search “Kingston Penitentiary” 1900..1920 brings up the ledgers mentioned above.
Not sure how to find record sets like these for YOUR family history? Here’s a tip! Use the “numrange” search operator in Google to locate records from a particular time period. Do this by typing the range of years to search (first and last year) into your Google search box, with two periods in between (no spaces). For example, the search “Kingston Penitentiary” 1900..1920 brings up the ledgers mentioned above.
This tip comes to you courtesy of the book The Genealogist’s Google Toolbox, Second Edition by Lisa Louise Cooke–the fully-revised 2015 edition that’s packed with strategies that will dramatically improve your ability to find your family history online.
by Lisa Cooke | Mar 20, 2017 | 01 What's New, DNA |
Your DNA test results come with raw DNA data. This raw data is the next piece in your DNA puzzle. Your DNA Guide, Diahan Southard, shares some interesting facts about raw DNA data and its use. Dig in and learn why!
What is Raw DNA Data?
Raw DNA data is the actual output file created by the DNA testing company. You can access your raw data at each testing company, and I strongly encourage that you do. You will need to download and save your raw data results to your computer. For instructions on how to do this, head on over to this page on my Your DNA Guide website.
This file contains your little DNA values at over 700,000 locations tested by your testing company. Any company with the right set-up and analysis tools can help you find matches with other people, and make additional genealogical discoveries. They may also be able to tell you if you like cilantro and are likely to have high blood sugar!
Raw DNA Data Research Projects and Destinations
Raw DNA data has to have a place to go. There are several research projects underway that utilize your data from any of the big four testing companies (Family Tree DNA, 23andMe, MyHeritage DNA, and AncestryDNA) for various genealogical or genetic purposes.

Home page of the DNA Land website
Let’s look at four examples of places you might upload your raw DNA data.
1. Family Tree DNA. If you have tested at 23andMe or AncestryDNA, you can transfer your raw data file to Family Tree DNA for free! You can access all of your matches and use the matching tools. For an additional $19, you can get access to the ethnicity features and other tools.
2. DNA Land. The not-for-profit DNA Land has over 26,000 individuals who have voluntarily uploaded their autosomal DNA test results into their website to be used for research purposes. Their self-stated goal is to “make genetic discoveries for the benefit of humanity.”
3. MyHeritage. MyHeritage also accepts your raw DNA data for incorporation into their genealogical database. You can upload your results for free and receive access to matches along with the ability to contact them. For a one-time fee of $29, you can unlock access to all of MyHeritage DNA’s features and tools as well. Learn more and upload your data here.
4. Geni.com. Geni.com (a family tree collaboration tool) jumped on the DNA bandwagon and announced they too would be integrating DNA into their family tree tool. Utilizing a partnership with Family Tree DNA, Geni.com is utilizing all three kinds of DNA (autosomal, YDNA, and mDNA) in their offering. The interface looks much like what you would see at your testing company: a list of matches with some family tree information.
The biggest takeaway from the recent influx of destinations for your raw DNA data shows us that the integration of DNA into genealogy is in full swing. I estimate every genealogy company and every major genealogy software will offer some kind of DNA integration within the next five years. DNA has certainly earned a permanent spot as a genealogical record type!
A Word of Caution
With all of these options available, and surely more to come, you will want to be careful about who you are giving your raw data to. Make sure you are comfortable with the company and its goals. Be sure you understand what role your DNA will be playing in their research, as well. These are exciting times in the world of genealogy.
Take the Next Steps in Your DNA Journey
 Wherever you are in your DNA journey, we can help!
Wherever you are in your DNA journey, we can help!
Take your very first steps and learn how to get started using DNA testing for family history.
If you have already taken the plunge, learn how to harness the power of DNA matching.
For the most help in understanding DNA for family history, take a look at the ten different DNA guides in both print and digital form from Your DNA Guide, Diahan Southard.
by Lisa Cooke | Jul 27, 2013 | 01 What's New, Findmypast, Research Skills
 If you’ve ever used the Periodical Source Index (PERSI), you know what a genealogy gem it is. PERSI is a master index to thousands of genealogical and historical periodicals, published by the Allen County Public Library’s Genealogy Center (ACPL). According to the Journal Gazette, PERSI contains about 2.5 million citation and adds another 100,000 a year. This is where you go to see if someone’s written about your family or ancestral hometown in state, regional, ethnic, local and other journals and newsletters.
If you’ve ever used the Periodical Source Index (PERSI), you know what a genealogy gem it is. PERSI is a master index to thousands of genealogical and historical periodicals, published by the Allen County Public Library’s Genealogy Center (ACPL). According to the Journal Gazette, PERSI contains about 2.5 million citation and adds another 100,000 a year. This is where you go to see if someone’s written about your family or ancestral hometown in state, regional, ethnic, local and other journals and newsletters.
You can currently search PERSI through the HeritageQuest Online databases at your local library and with your Ancestry.com membership. But the trick is accessing those articles once you find them. The best way right now is to order them directly from ACPL (click on Article Fulfillment Form). It costs $7.50 USD to order up to 6 articles at a time, plus $.20 per page and you get the articles in the mail.
Now findmypast.com has big plans to make PERSI easier to use. Findmypast.com is becoming the new online host of PERSI, and they plan to link digital images of as many articles as possible to the index. “PERSI unearths hidden gems for genealogy researchers,” says D. Joshua Taylor, lead genealogist for findmypast.com. “We look forward to working with various societies and publications to get permission to digitize their articles.”
That sounds like an enormous undertaking, but certainly one that’s long overdue and will pay off for family history researchers. I’ll keep you posted on their progress!

 Want to learn more about using Google Earth for genealogy (or the Google Earth Pro version that was just released FREE to the public)? Become a Genealogy Gems Premium member. You’ll have access to video classes like these:
Want to learn more about using Google Earth for genealogy (or the Google Earth Pro version that was just released FREE to the public)? Become a Genealogy Gems Premium member. You’ll have access to video classes like these:

 regional collections catch our eye, too. We’ll round these up for you in a post like this on Fridays.
regional collections catch our eye, too. We’ll round these up for you in a post like this on Fridays. Not sure how to find record sets like these for YOUR family history? Here’s a tip! Use the “numrange” search operator in Google to locate records from a particular time period. Do this by typing the range of years to search (first and last year) into your Google search box, with two periods in between (no spaces). For example, the search “Kingston Penitentiary” 1900..1920 brings up the ledgers mentioned above.
Not sure how to find record sets like these for YOUR family history? Here’s a tip! Use the “numrange” search operator in Google to locate records from a particular time period. Do this by typing the range of years to search (first and last year) into your Google search box, with two periods in between (no spaces). For example, the search “Kingston Penitentiary” 1900..1920 brings up the ledgers mentioned above.

 Wherever you are in your DNA journey, we can help!
Wherever you are in your DNA journey, we can help!