by Lisa Cooke | Jun 27, 2019 | 01 What's New, Digital Archives, Photographs
Historical photos and images can bring depth and understanding to genealogical findings. In the case of sharing your family history with others in your family who don’t share your passion for genealogy, they are an essential part of bringing family history to life.
One of the best free online resources for historical photos is the Creative Commons at Flickr.
Flickr is a popular photo, image and video hosting and sharing service. It’s a great platform for sharing your favorite photos with family and friends. It’s also an excellent place to find images that fit into your family history.
An important part of the Flickr world is Creative Commons, which describes itself as part of a “worldwide movement for sharing historical and out-of-copyright images.”
Groups and individuals alike upload old images, tag and source them, and make them available to others through the Creative Commons. And when it comes to groups, the list of participants is impressive.
The British Library photostream features over a million images in its photostream! And a robust collection of historical photos and images can be found at the (U.S.) Library of Congress photostream, with over 34,000+ photos.
Searching the Creative Commons
When searching the Creative Commons, be sure to look for your favorite libraries and historical societies. If you don’t find them today, don’t worry. Check back regularly because new content is being added all the time.
Here’s another example of what you can find at the Creative Commons. The Netherlands Institute of Military History (Nederlands Instituut voor Militaire Historie) has a photostream.
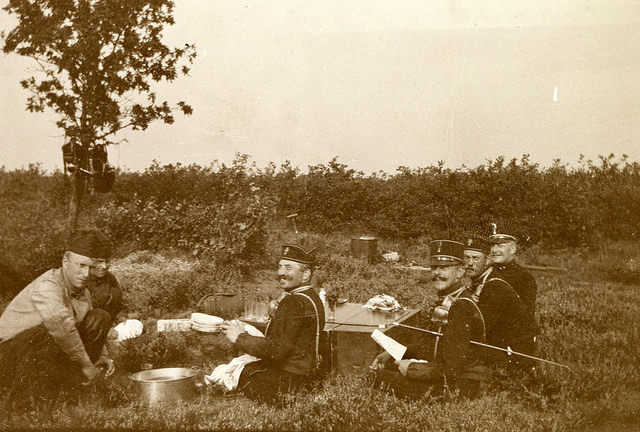

“Exercise Field Artillery Corps” album, image AKL092038, Netherlands Institute of Military History uploads at Flickr Creative Commons, https://www.flickr.com/photos/nimhimages/16026248719/.
According to the Netherlands Institute of Military History blog, “The Institute exists to serve all those with an interest in the military past of the Netherlands. Its sphere of activities covers the Dutch armed forces on land, at sea and in the air, from the sixteenth century until now. The staff of the NIMH administer a unique military history collection containing approximately 2 million images, of which they will be uploading many to the site.”
Back in 2015 when we first wrote about their brand new photostream it only included a couple dozen images, like the one shown here. Today they have well over 3,300.
Tips for Finding and Using Historical Photos at the Creative Commons
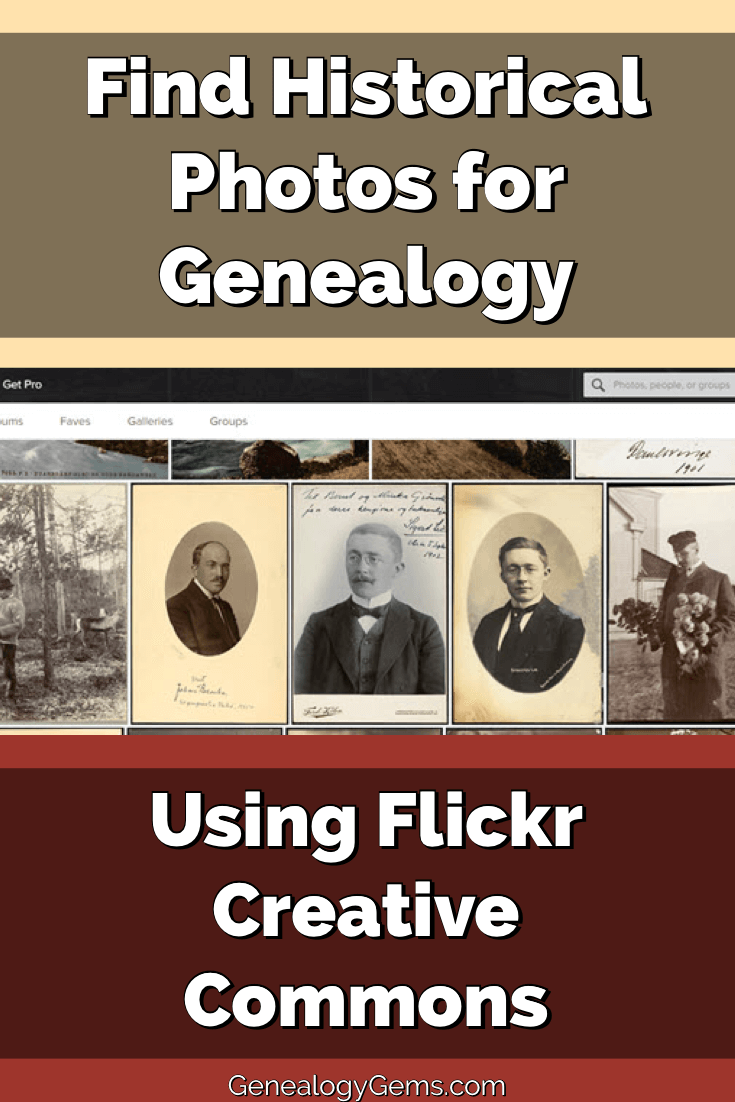
Searching for Historical Photos: On a photostream home page, click the search icon (magnifying glass) just above the first row of photos in the upper right corner. A search box will pop up at the top of the page. Enter Keywords to search for images within that photostream. (Image below)
Location isn’t Everything: Just like with brick and mortar libraries, don’t let the location of the library or archive hosting the photostream fool you! Their collections are not limited to only items in their area. If you’re in search of something specific, try the Flickr Advanced Search page here.
Understanding Downloading and Copyright: Those who post images to Flickr Creative Commons offer different rights to those who want to download and use their images. Described here (and searchable here by the kinds of rights you want), those rights may include the ability to use a photo as long as it’s for noncommercial purposes and proper credit is given. Perfect for a responsible, source-citing genealogist!
10 Favorite Flickr Photostreams with Historical Focus
It would be impossible to list all of the potential photostreams at Flickr’s Creative Commons that feature historical photos, so I won’t even try. However, I’m happy to provide this list of favorites, which illustrates the breath and depth of possibilities. I hope it inspires you to search out your favorite library or archive at the Creative Commons.
(Organized by number of photos)
Internet Archive Book Images
5,240,000+ Photos
Though not currently organized by Albums or Galleries, there is something here for absolutely everybody! Use the search feature to zero in on what you want. (See tips section below)
The British Library
1,000,000+ Photos
A gloriously eclectic mix of images. Just one example: World War I: The Canadian Experience. This photo album covers 1895 and 1924, and contain depictions of Canadians’ experiences of the First World War. From the British Library: “Either produced by photographers on home soil or individuals in Europe employed by Lord Beaverbrook’s ‘Canadian War Records Office’ the photographs provide a wide ranging account of the many Canadians involved in and impacted by the war.”
The National Archives UK
20,000+ Photos
the UK government’s official archive contains more than 1,000 years of history, so their photostream is not to be missed! Nicely organized into Albums focused on location, the images offer a sampling of their massive holdings.
The U.S. National Archives
16,500+ Photos
Nicely organized into a vast array of albums, these photos represent only a small sampling of the photographs in their collection which totals more than 25 million photos and 20,000 graphic images. Early on they focused on uploading photos from the Women’s Bureau, the Environmental Protection Agency, and a few staff favorites. According to the National Archives, “These photographs, most taken by agents of Federal agencies over the years, cover a wide range of subjects and themes documented in the work of the United States government. Higher resolution versions of many of these images can be obtained from the U.S. National Archives by following the links located below each image.”
SMU Libraries Digital Collections
10,000+ Photos
Southern Methodist University Digital Collections includes the digital libraries and online digital collections from the six SMU Libraries. You’ll find an emphasis on digital collections of Mexican photographs, locomotives, Texas history, art, and currency notes, and more.
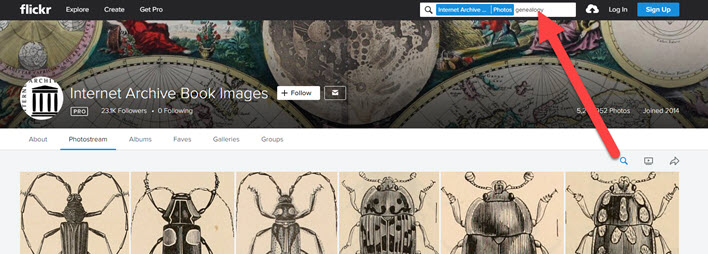
National Library of Norway
3600+ Photos
These images either fall in the public domain or the copyright belongs to the library and has been wavered. You’ll find photos, postcards, stereograph cards and other ephemera depicting life in Norway. With all of the portraits you may just spot an ancestor!
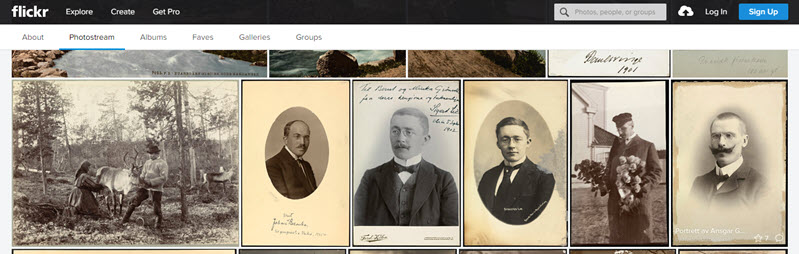
National Library of Norway photostream
The New York Public Library
2500+ Photos
Considering how many Americans passed through New York, this photostream is definitely worth a visit.
National Library of Ireland on The Commons
2500+ Photos
Here you’ll find a range of items from the Ephemera Collections of the National Library of Ireland. They provide a snapshot of different periods in Ireland’s social, political, economic and cultural history. They’ve also added items from their Manuscript collections, Prints and Drawings, Exhibitions, as well as photos from Library Events.
UBC Library Digitization Centre
of the University of British Columbia
2400+ Photos
Just one of many Canadian library photostreams, the UBC Library shows off it’s diverse image collection in well organized albums. My personal odd-ball favorite is the Tremaine Arkley Croquet Collection!
Library Company of Philadelphia
1280+ Photos
They’ve organized their current photo collection into more than 50 albums, making it easy to quickly spot the historical collections. Notable albums feature unique historical images from the Civil War era.
by Lisa Cooke | May 10, 2017 | 01 What's New, Adoption, Canadian, Census, DNA, Genealogy Gems Podcast
The Genealogy Gems Podcast
with Lisa Louise Cooke
Episode #203

This episode features a special interview with renowned Canadian expert Dave Obee. He shares his favorite tips on researching the Canadian census?his insights are fascinating whether you have Canadian ancestors or not!
Also in this episode: an inspiring adoption discovery, DNA testing news at 23andMe, a tip for incorporating family history into a wedding, and a brand-new resource that can finally help you solve one of genealogy’s most perplexing questions.
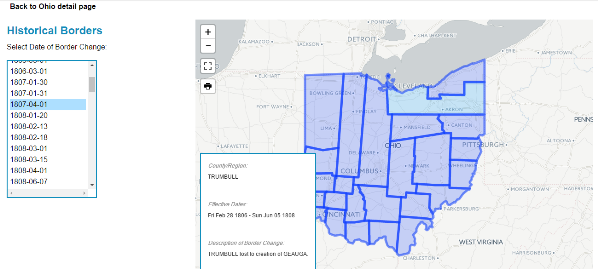
NEWS: ATLAS OF HISTORICAL COUNTY BOUNDARIES UPDATE
Atlas of Historical County Boundaries
Google Earth for Genealogy (and more on Google Earth Pro)

LINK: https://lisalouisecooke.com/free-google-earth-for-genealogy-video-class-by-lisa-louise-cooke/
NEWS: 23andME DNA TEST UPDATES
Click here for the full news and Diahan’s comments
MORE recent DNA news:
Family Tree DNA enhancements:Click here for the full story, with comments and step-by-step instructions on updated myOrigins tool
Get help with DNA testing at both these sites with these quick reference guides by Diahan Southard:
Understanding 23andMe
Understanding Family Tree DNA


NEW! GENEALOGY GIANTS GUIDE
by Genealogy Gems Editor Sunny Morton
Click here to watch the presentation that inspired this guide: a popular RootsTech 2017 lecture comparing the four major genealogy records websites: Ancestry.com, FamilySearch.org, Findmypast.com and MyHeritage.com.
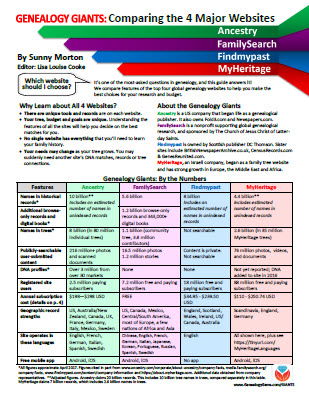
LINK: https://www.shopgenealogygems.com/collections/genealogy-guides/products/genealogy-giants-quick-guide
Available in print or digital format
This comprehensive quick reference guide explains:
How knowing about all four websites can improve your family history research
How the sites stack up when it comes to the numbers of historical records, names in trees, DNA profiles, site users, site languages and subscription costs
Unique strengths of each website and cautions for using each
What to keep in mind as you evaluate record content between sites
Geographic record strengths: A unique table has an at-a-glance comparison for 30+ countries
How to see what kinds of records are on each site without subscribing
How family trees are structured differently at these websites?and why it matters
Privacy, collaboration and security options at each site
How DNA testing features differ at the two websites that offer it
What you can do with free guest accounts at each website
Subscription and free access options
MAILBOX: LIZ ON FINDING CHUCK’S BIRTH FAMILY
Click here to learn more about Diahan Southard’s genetic genealogy video tutorials?and a special discount price for Genealogy Gems fans.

LINK TO: https://www.yourdnaguide.com/genealogy-gems-dna-tutorial

Lisa Louise Cooke uses and recommends RootsMagic family history software. From within RootsMagic, you can search historical records on FamilySearch.org, Findmypast.com and MyHeritage.com. In the works: soon RootsMagic will be fully integrated with Ancestry.com, too: you’ll be able to sync your RootsMagic trees with your Ancestry.com trees and search records on the site.

Keep your family history research, photos, tree software files, videos and all other computer files safely backed up with Backblaze, the official cloud-based computer backup system for Lisa Louise Cooke’s Genealogy Gems. Learn more at http://www.backblaze.com/Lisa
MAILBOX: THANKS FOR 1940 CENSUS TIPS

Kate Eakman shares tips for understanding the 1940: click here to read them or click here to listen to them on Genealogy Gems Podcast episode 201
MAILBOX: WEDDING TIP
Before a wedding: start an online family tree and invite each family member to add what they know!
Share family history this summer: Reunions, weddings, BBQs, etc
Genealogy Gems Pinterest Page: Incorporating Family History Ideas into Your Wedding
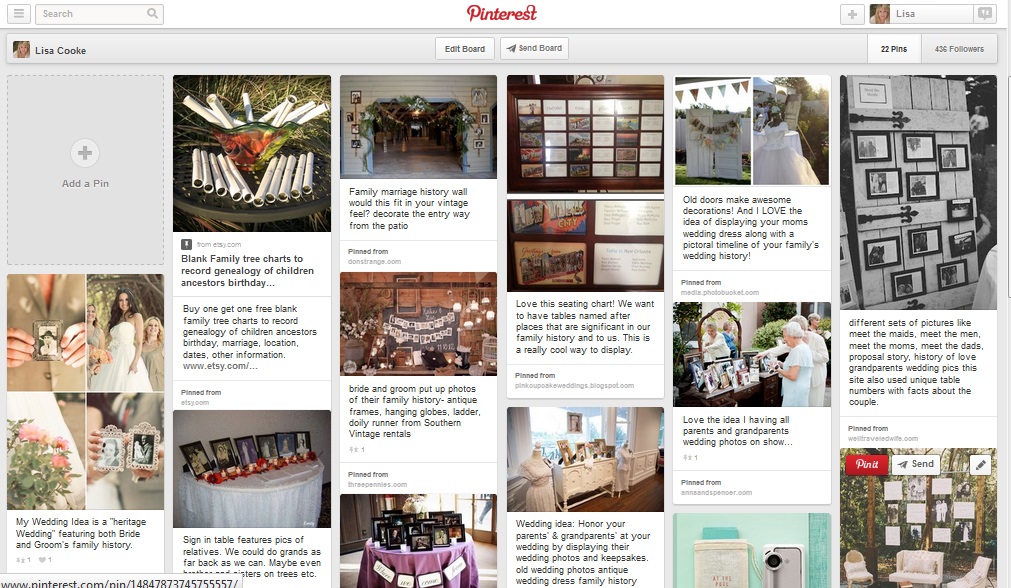
Go to: https://www.pinterest.com/lisalouisecooke/incorporating-family-history-into-your-wedding/
Our sponsor for this episode: StoryWorth
Give Mom the gift of StoryWorth this Mother’s Day
Visit www.StoryWorth.com/Lisa to get $20 off

Visit: www.StoryWorth.com/Lisa
INTERVIEW: DAVE OBEE


Continuing our celebration of Canada’s 150th birthday!
Dave Obee is an internationally-renowned Canadian journalist, historian and genealogist. Dave is a columnist for Internet Genealogy and Your Genealogy Today (formerly Family Chronicle). Dave has also written about family history for Canada’s History and Your Family Tree in the United Kingdom.

Put Dave’s books on your shelf:
Finding Your Canadian Ancestors: A Beginner’s Guide
Counting Canada: A Genealogical Guide to the Canadian Census
Destination Canada: A Genealogical Guide to Immigration Records
Making the News: A Times Columnist Look at 150 Years of History
Canadian census tips from Dave Obee:
The 1901 census is his favorite because it says for the first time where people had come from
He starts his searches on Ancestry.ca but census databases are free to search on Library and Archives Canada website
Marital status may not have been totally accurate. They only captured single or married or windowed. Divorced was not captured.
There are two different types of enumerations: de facto and de jure, and the rules were different.
This means your ancestor could be enumerated in multiple locations
Lisa Louise Cooke Googled the Canadian Census Enumerator Instructions for 1901:
At Library & Archives Canada
Original instructions digitized at Archive.org

More on Canada genealogy research:
Claire Banton in Genealogy Gems Podcast episode #199
Blog post on Canadian Censuses 1825-1921
Search Canadian Passenger Lists for Free at Library and Archives Canada
Canadiana: Canadian Digital Archive and Portal to the Past
Google Earth for Canada and Genealogy
Our Sponsors:

Start creating fabulous, irresistible videos about your family history with Animoto.com. You don’t need special video-editing skills: just drag and drop your photos and videos, pick a layout and music, add a little text and voila! You’ve got an awesome video! Try this out for yourself at Animoto.com.

MyHeritage.com is the place to make connections with relatives overseas, particularly with those who may still live in your ancestral homeland. Click here to see what MyHeritage can do for you: it’s free to get started.
BONUS CONTENT for Genealogy Gems App Users

If you’re listening through the Genealogy Gems app, your bonus content for this episode is EXTRA special! It’s an exclusive conversation between Your DNA Guide and Cece Moore of DNA Detectives on researching adoption or unknown parentage. Don’t miss it! The Genealogy Gems app is FREE in Google Play and is only $2.99 for Windows, iPhone and iPad users.
GENEALOGY GEMS BOOK CLUB
Our featured genealogy book club author this month is Miss Fannie Flagg!

The Whole Town’s Talking by Fannie Flagg
Read more tips on discovering the historical context of your ancestor’s lives:
Tell Your Ancestor’s Story: Use Social History for Genealogy
Social History for Genealogy and the Colored Farmer’s Alliance

PRODUCTION CREDITS
Lisa Louise Cooke, Host and Producer
Sunny Morton, Editor
Diahan Southard, Your DNA Guide, Content Contributor
Lacey Cooke, Service Manager
Vienna Thomas, Associate Producer
Check out this new episode!
by Lisa Cooke | Sep 16, 2017 | 01 What's New, Book Club, Libraries, Listeners & Readers, Mobile
Your local library may offer free genealogy magazines and ebooks. Why choose them over print? So many reasons! No more late fees. Read on the go. Choose your font size. So go ahead: check out digital versions of that Genealogy Gems Book Club title you’ve been meaning to read, or the current issue of Family Tree Magazine. Here’s how.

Here in the U.S., it’s my favorite time of year: back-to-school! The weather slowly cools. My children shake off summer’s mental lethargy. My own schedule resumes a more predictable, productive rhythm. And after months spent outdoors, I rediscover my local library. Top on my library list this fall: free genealogy ebooks and magazines I can check out on my mobile device. It’s on-the-go reading for my favorite hobby–with no searching under my bed when items come due to avoid those pesky late fees.
Free Genealogy eBooks and Magazines
Genealogy Gems Premium Member Autumn feels the same way about free genealogy gems at her local library. Here’s a letter she wrote to Lisa Louise Cooke:
“I’m really enjoying both the Premium and free podcasts. I also like the addition of the Genealogy Gems Book Club. I haven’t read all the books yet but am adding them all to my wishlist on Overdrive, a free app that allows you to check out digital books for free from your local library. They don’t have every book but they have many, many books including some from the book club. Most libraries have a lot of biographies and histories available through Overdrive for free that are of interest to genealogists as well. Some libraries are adding video to their Overdrive offerings too.
Many of these same libraries offer magazines free as well. My library…use[s] Zinio, a magazine app. I only subscribe to a couple of magazines now because I can get so many for free through my library (not to mention keeping my home neater by not having them laying everywhere).”
 It makes me happy that Autumn is enjoying the Genealogy Gems Book Club. We hear from many avid readers who love browsing our list of mainstream fiction and nonfiction picks for family history lovers. As part of our book club, we interview every book club author, too–from beloved novelists like Fannie Flagg to acclaimed journalists, memoir writers, and historians who take their own unique approaches to family history themes. Hear excerpts of these interviews on the free Genealogy Gems Podcast; full interviews run on the Genealogy Gems Premium Podcast, available by subscription.
It makes me happy that Autumn is enjoying the Genealogy Gems Book Club. We hear from many avid readers who love browsing our list of mainstream fiction and nonfiction picks for family history lovers. As part of our book club, we interview every book club author, too–from beloved novelists like Fannie Flagg to acclaimed journalists, memoir writers, and historians who take their own unique approaches to family history themes. Hear excerpts of these interviews on the free Genealogy Gems Podcast; full interviews run on the Genealogy Gems Premium Podcast, available by subscription.
Overdrive and Zinio
At Autumn’s recommendation, I started using Overdrive through my local library. I love it! I’ve listened to several digital audiobooks on the road and at the gym through Overdrive and have read several ebooks, too. (I’m always on the hunt for the next Genealogy Gems Book Club title.) The books just disappear at the end of the lending period (hence the “no late fees” bonus).
 Genealogy Gems Service Manager Lacey Cooke loves Overdrive, too. She sent me these four reasons why:
Genealogy Gems Service Manager Lacey Cooke loves Overdrive, too. She sent me these four reasons why:
1. Download for Offline Listening: “You can download the ebooks, audiobooks, magazines etc. to your device so that you can enjoy them offline (great for traveling). They’ll still disappear once your lending period expires, but having them available offline is awesome. You don’t have to worry about data charges or slow internet connections.
2. The Wishlist: Autumn briefly mentioned the Wishlist feature. I love this feature because it gives me somewhere to save book titles that I’m interested in reading at some point, but I’m not ready to check out just yet.
3. Bookmark/Syncing: You can bookmark a page, then pick up where you left off. If you have the Overdrive app on multiple devices, the app syncs. I can start reading on one device, and pick up on another right where I left off.
4. Format Adjustments: You can adjust the font style, size, and color to make it easier for you to read. I like to pick a nice, clean font in a big size so there’s no strain on my eyes.”
It’s worth noting that if you don’t already have a library card with your local library, you may be required to sign up in person to get a card, even if you only plan on using the Overdrive app to request items online. New releases or popular titles may have a wait list to check out the ebook or audiobook (especially if the library only possesses one copy). If you do have to place an ebook on hold, you will be notified via email when it becomes available to you, so if you don’t check your email regularly, keep that in mind when you place a hold. Each library system is different, so of course, your experience may vary.
Another helpful tip: not every library offers Overdrive ebook checkouts. But sometimes you can use another library’s Overdrive privileges. Autumn sent a link to these instructions on how to do so. (Thanks, Autumn!)
Autumn also mentioned the Zinio app. My library doesn’t offer Zinio yet, so I spent a little time on its public search portal. That doesn’t have a browsable genealogy category, and searches for the terms family history, genealogy and ancestry came up empty. But I did finally find these titles:
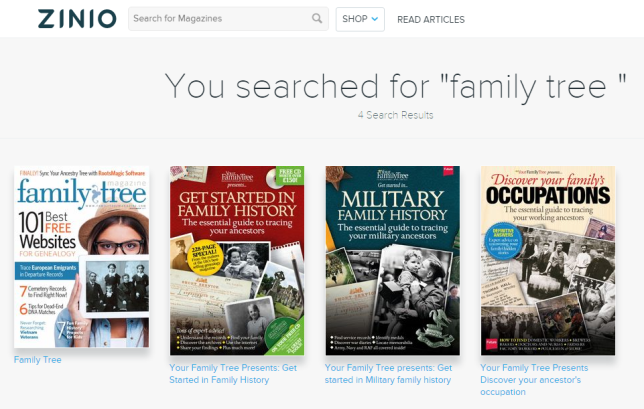
Lisa Louise Cooke, Genealogy Gems DNA expert Diahan Southard, and I are all frequent contributors to Family Tree Magazine, which we {heart} and recommend for its easy-reading research tips, hands-on tech and DNA tutorials, and the eye-candy layout.
More Free Genealogy Resources at Your Local Library
Of course, your local library may offer many additional free genealogy research and reading materials. Of tremendous value is access to Library editions of popular genealogy databases such as Ancestry, Findmypast, Fold3, and MyHeritage, along with institutional versions of historical newspaper databases. (Click here to learn more about the differences between the major genealogy websites.) Call your library or browse its website to see what resources may be available with your library card on site or even remotely from your own home or mobile device. And remember to watch for your library’s e-media options like those recommended by Autumn.
 As a special shout-out to all the free genealogy resources at your library, Lisa Louise Cooke has granted free access for everyone to Genealogy Gems Premium Podcast episode #125. In this episode, Lisa has a full discussion about more free genealogy gems at public libraries with Cheryl McClellan. Cheryl is not only my awesome mom, she rocks professionally as the Geauga County, Ohio public library system staff genealogist!
As a special shout-out to all the free genealogy resources at your library, Lisa Louise Cooke has granted free access for everyone to Genealogy Gems Premium Podcast episode #125. In this episode, Lisa has a full discussion about more free genealogy gems at public libraries with Cheryl McClellan. Cheryl is not only my awesome mom, she rocks professionally as the Geauga County, Ohio public library system staff genealogist!
This Premium episode is usually exclusively for Genealogy Gems Premium members. If you love it, and you’re not already a member, consider gifting yourself a “back to school” subscription. It’s the most fun, energizing, apply-it-now genealogy learning experience you may ever have.
by Sunny | May 25, 2018 | 01 What's New, British, Church, Genealogy Giants Websites |
English parish records top this week’s list of new online genealogy records. More new or updated family history collections: British newspapers, pensions and India records; records for Brazil, Germany, The Netherlands, Peru, and Poland; UK images and deaths; US...
by Lisa Cooke | Jul 8, 2015 | 01 What's New, Church, Irish, Libraries, Records & databases

Writer James Joyce’s baptismal certificate; click to link to Wikipedia image.
As of today, the National Library of Ireland expects to launch a free, digitized collection of ALL its Catholic parish registers on its website (this link takes you to the English version; it’s also available in Irish). Nearly 400,000 digital images of microfilmed parish records comprise this collection.
According to a press release, “The parish register records are considered the single most important source of information on Irish family history prior to the 1901 Census. Dating from the 1740s to the 1880s, they cover 1,091 parishes throughout the island of Ireland, and consist primarily of baptismal and marriage records….Their digitisation means that, for the first time, anyone who likes will be able to access these registers without having to travel to Dublin.”
Catholic parish registers are a vital genealogical resource. In addition to the names of those baptized or married, they usually include those event dates, names of parents of baptized children, godparents and witnesses (who may also be relatives).
NOTE: This is a browsable-only collection. There are currently no plans to index or transcribe the records. However, the press release included a great suggestion for accessing indexes: look to local family history centers for that parish or neighborhood. “The buy diet medication online nationwide network of local family history centres holds indexes and transcripts of parish registers for their local areas,” it says.
 Those unfamiliar with Ireland research may assume this means local FamilySearch Family History Centers, but a map shows only a few of these in Ireland. I would start first with the network of county genealogy centers, accessible online at Roots Ireland. According to that site, “The county genealogy centres are based in local communities, working with volunteers, local historical societies, local clergy, local authorities, county libraries and government agencies to build a database of genealogical records for their county. By using this website you are supporting that work and the communities from which your ancestors originated.” Several counties actually already have online records you can access through the Roots Ireland link above. Ancestry also has several databases of Irish Catholic parish registers.
Those unfamiliar with Ireland research may assume this means local FamilySearch Family History Centers, but a map shows only a few of these in Ireland. I would start first with the network of county genealogy centers, accessible online at Roots Ireland. According to that site, “The county genealogy centres are based in local communities, working with volunteers, local historical societies, local clergy, local authorities, county libraries and government agencies to build a database of genealogical records for their county. By using this website you are supporting that work and the communities from which your ancestors originated.” Several counties actually already have online records you can access through the Roots Ireland link above. Ancestry also has several databases of Irish Catholic parish registers.
For more tips on researching your Irish relatives, listen to the FREE Family History Made Easy podcast episode 21, in which we interviewed Irish expert Judith Wight. You’ll hear her tips on finding Church of Ireland records, civil registrations, estate records and how history helps us understand gaps in the records.
Thank you for sharing this post with those who will LOVE to know about these Irish genealogy resources!




























 Genealogy Gems Service Manager Lacey Cooke loves Overdrive, too. She sent me these four reasons why:
Genealogy Gems Service Manager Lacey Cooke loves Overdrive, too. She sent me these four reasons why:


