by Lisa Cooke | Oct 3, 2016 | 01 What's New, Google
You can use Google Slides for genealogy to create one-of-a-kind presentations, a virtual scrapbook, or a virtual library list…and it’s free! Here’s how to take advantage of yet another awesome Google tool.

I was recently asked if there was a software program or app, something free perhaps, to share a slideshow or create a visual presentation. There is! It’s called Google Slides. Here’s how Lisa Louise Cooke, author of The Genealogist’s Google Toolbox, explains it:
Google Slides is an online presentation application, much like Microsoft’s Powerpoint. It’s part of Google’s free office suite of tools. As a genealogist, it provides the opportunity to create and visually share your family history.
It’s a Cloud-based service and that means you can access your presentations wherever you are and on any computing device. You will sign-in to Google Slides with your personal Google account. That means you will be able to keep everything private unless you decide to share it. Although it’s Cloud-based, you can use it offline too. Any new presentations you create or changes you make will be automatically updated when you get back online. You can show your presentation at the next family reunion or genealogy society meeting even if there’s no Internet access.
There’s a lot of potential for using this powerful tool for genealogy!
With that great introduction, I’d like to share a few unique examples of how a genealogist or a genealogy society could use Google Slides.
Google Slides for the Genealogist
Google Slides is an easy way to create a fun slide show of your ancestor photos. This can be shared at family gatherings or reunions right from your laptop. You can also share the presentation with a click-able link.
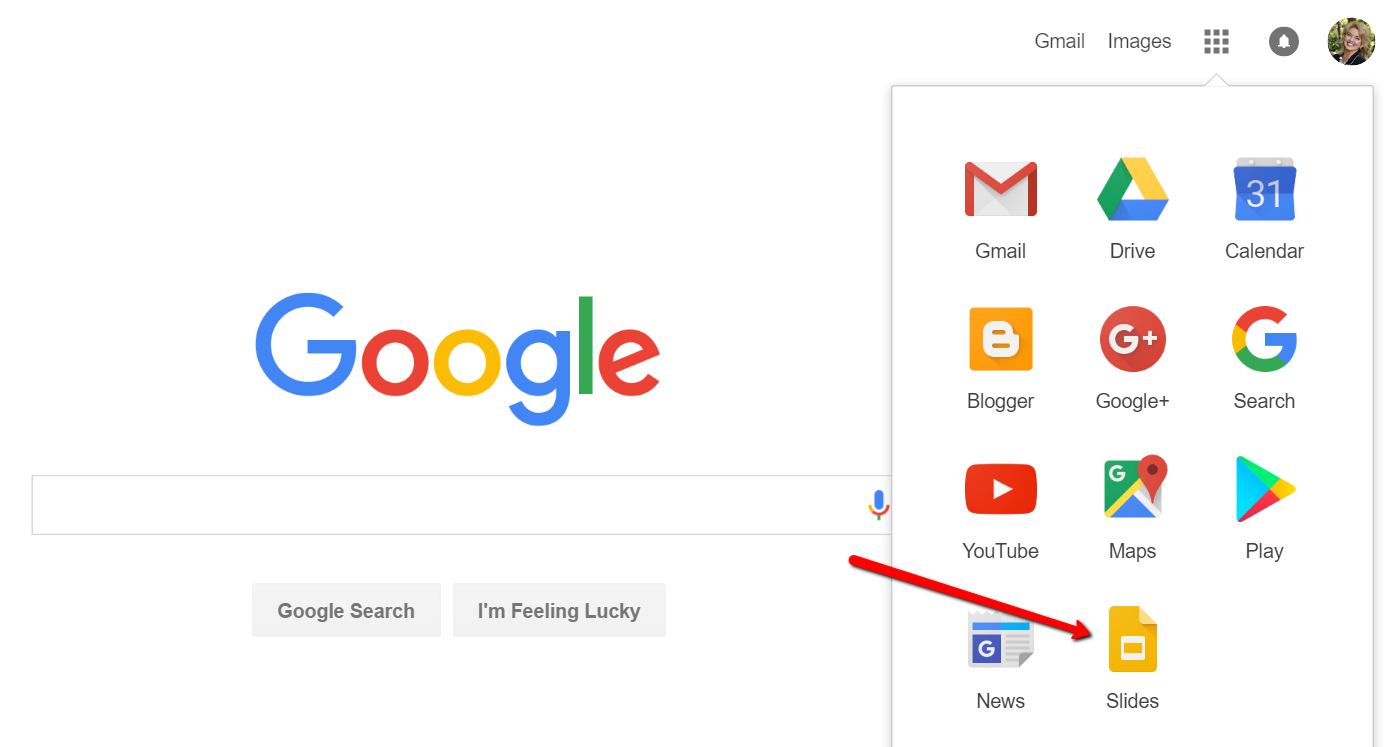
To begin, find Google Slides by going to Google.com and sign-in to your free Google account (or sign up if you don’t have one.) Click on the grid to the left of your sign-in avatar. This will bring down several options. If you don’t see Google Slides as an option, click More at the bottom.
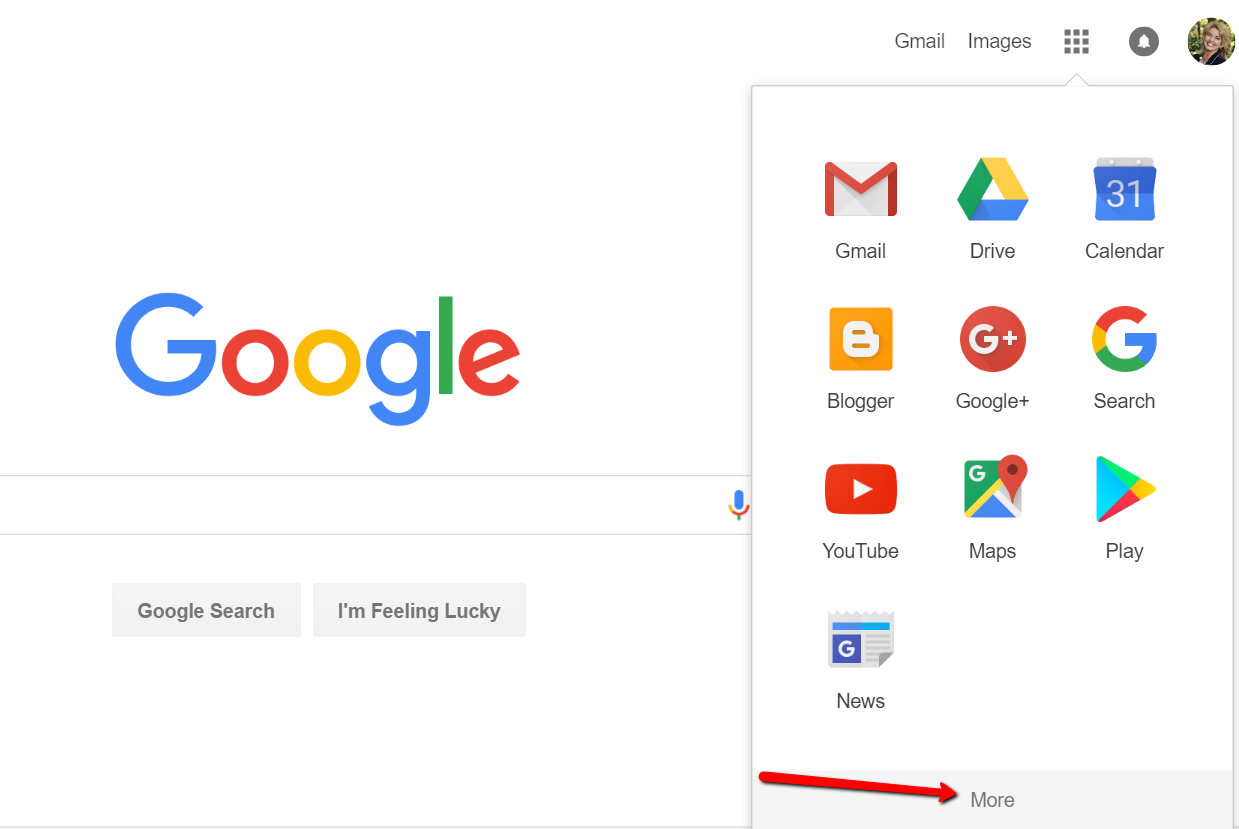
If you still don’t see Google Slides as an option, click on Even More from Google. This will take you to another screen of all sorts of Google goodies! Scroll down until you find Google Slides and click on it.
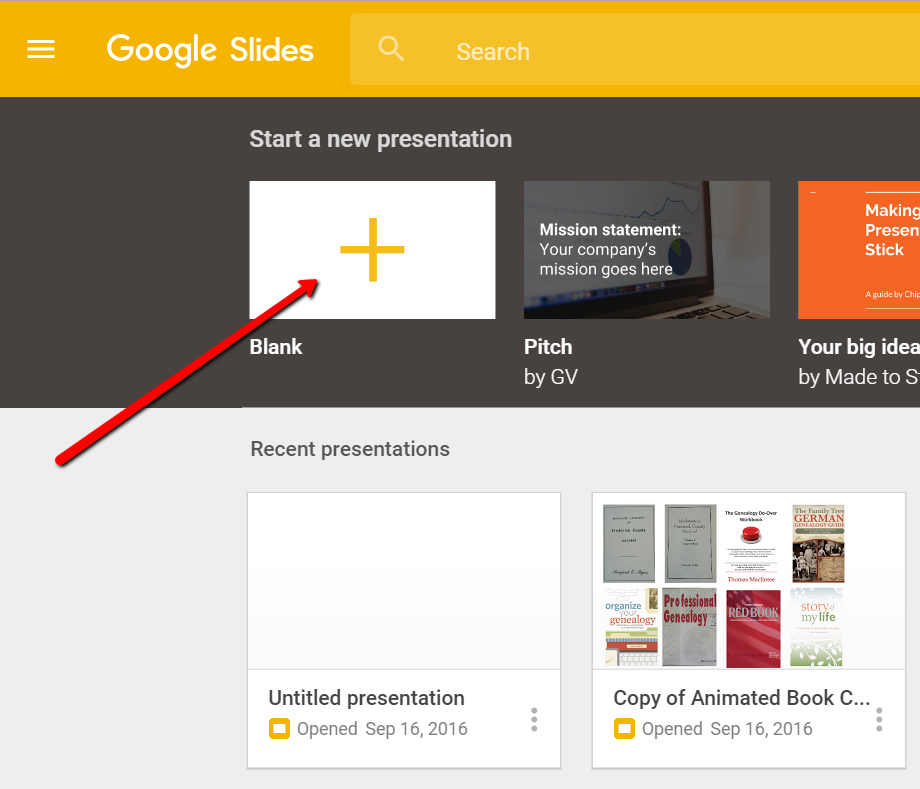
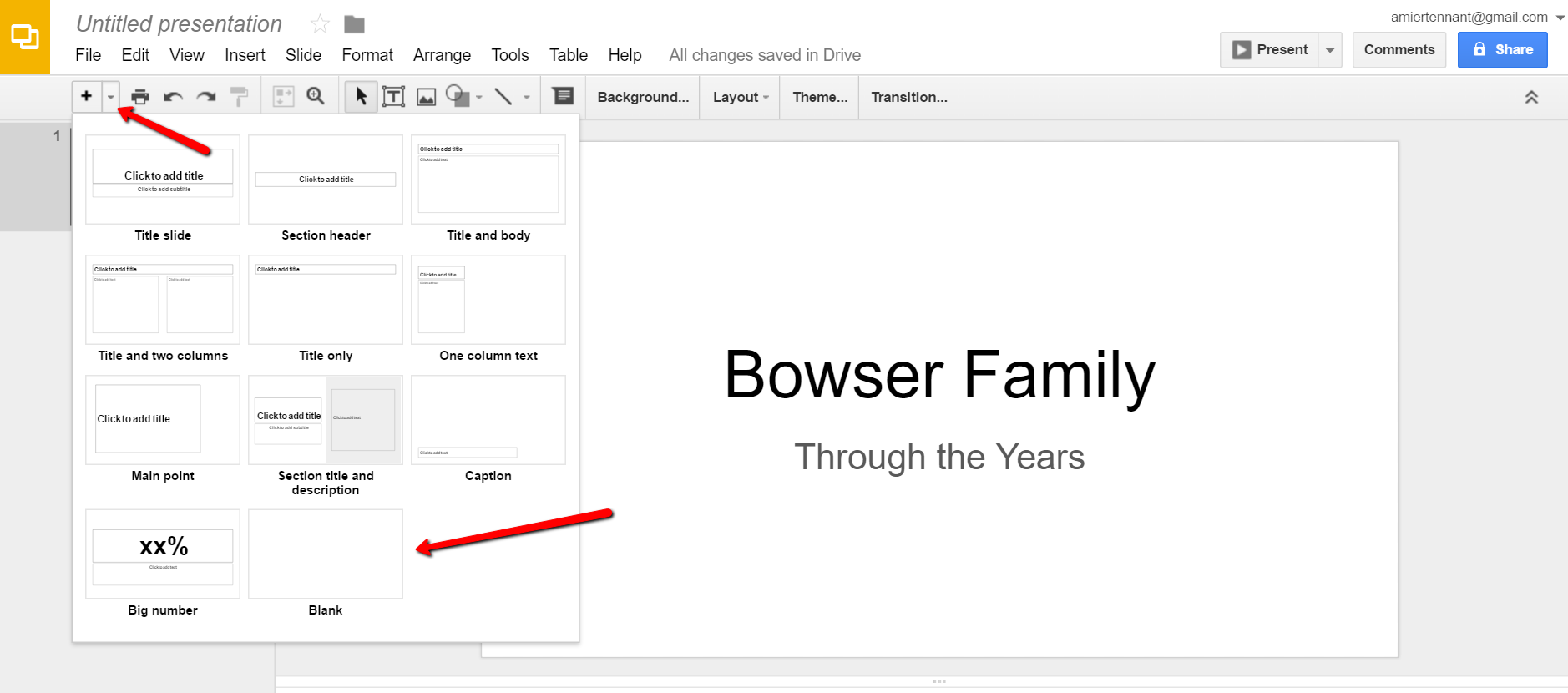
Once you have opened Google Slides, click the plus sign to begin.
I added a title and then clicked the tiny arrow to the right of the plus sign to add a new blank slide.
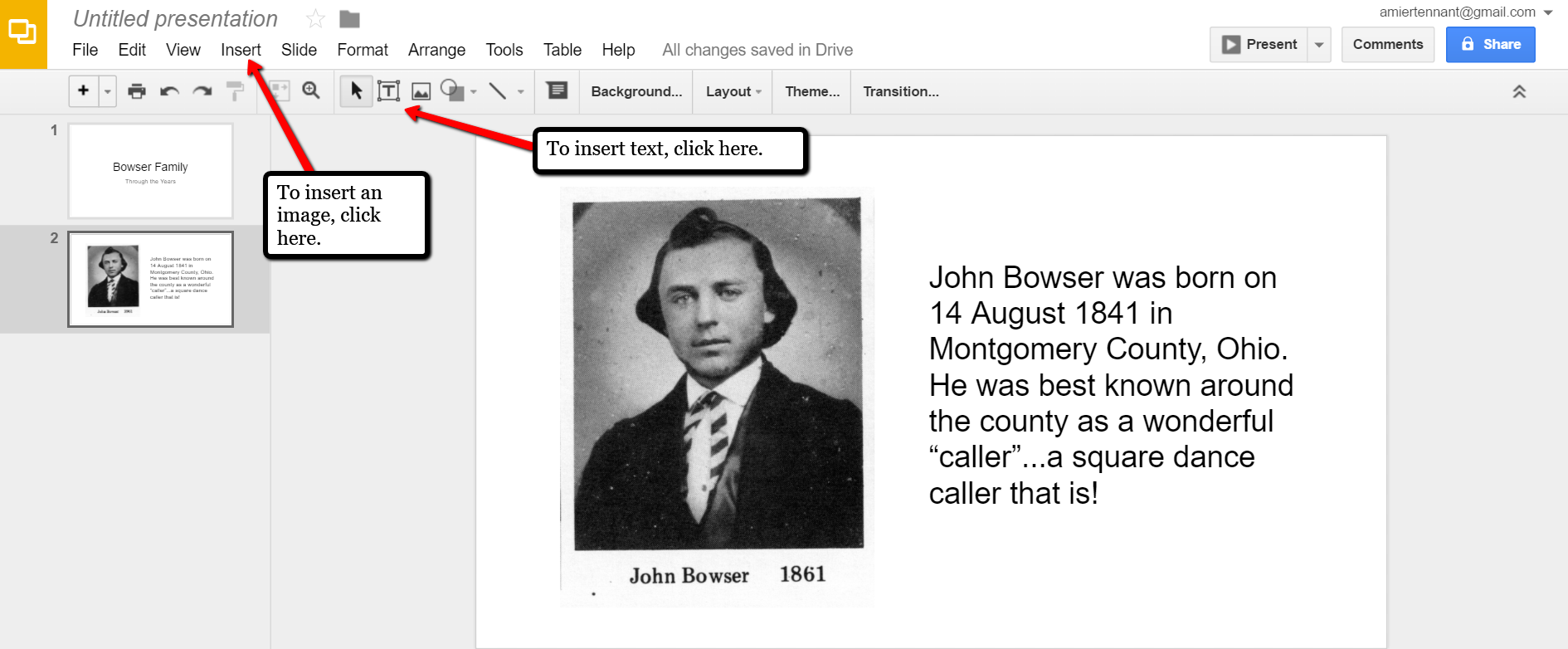
At the new slide and each additional slide, you can add a picture by first clicking Insert from the labels listed across the top, then choose Image. A pop-up window will appear and allow you to Choose an Image to Upload. You will then find the image you have saved on your computer and click Open.
Keep adding your slides until you have all of them created.
Sharing Your Google Slides Presentation
Like many of us, I like to share my ancestor photos with my family and friends. While at a family gathering of a small group, I just set my laptop up on the coffee table and we huddle around. Bring up your Google Slides presentation on your laptop or mobile device and click on Present at the top right of the screen. The computer does the rest and presents a slideshow for your viewers.
You might also wish to share your slides with family and friends far away. You can do this by sharing a link. To create a shareable link, click Share at the top right corner.
A pop-up window will appear. Click the little drop-down menu next to the words “can view.” This option allows you to choose whether you wish people to be able to edit, comment, or view only. I typically choose the “view only” option. Then, a shareable link is created for you. Click Copy link and paste that into an email directly to a family member, to your family history blog, in a Tweet, or in a Facebook post. Wa-la! You have shared your Google Slides presentation.
Create a Virtual Book Cover List with Google Slides
Another stellar way to use Google Slides for genealogy is to create a convenient virtual library list. A recent article found online gave me the idea of creating a library list using images of the covers of books.
For example, if you enjoy attending genealogy conferences and buying books for your society, you may get stuck wondering, “Do we already have that in our collection?” By creating a virtual book cover list, you won’t have to wonder anymore!
You will first need to begin this project by taking a picture of the covers of each of your books and saving the images to your computer or laptop. I took pictures, cropped them, and sharpened them up a bit with my smartphone. Then, I saved them to a file folder on my computer named Book Covers. [Tip: It would be an even better idea to save the Book Covers folder to your Google Drive!]
For something quick and easy, use the virtual book cover template here:
Virtual Book Cover List Template. If you choose to use this link, when it opens, click
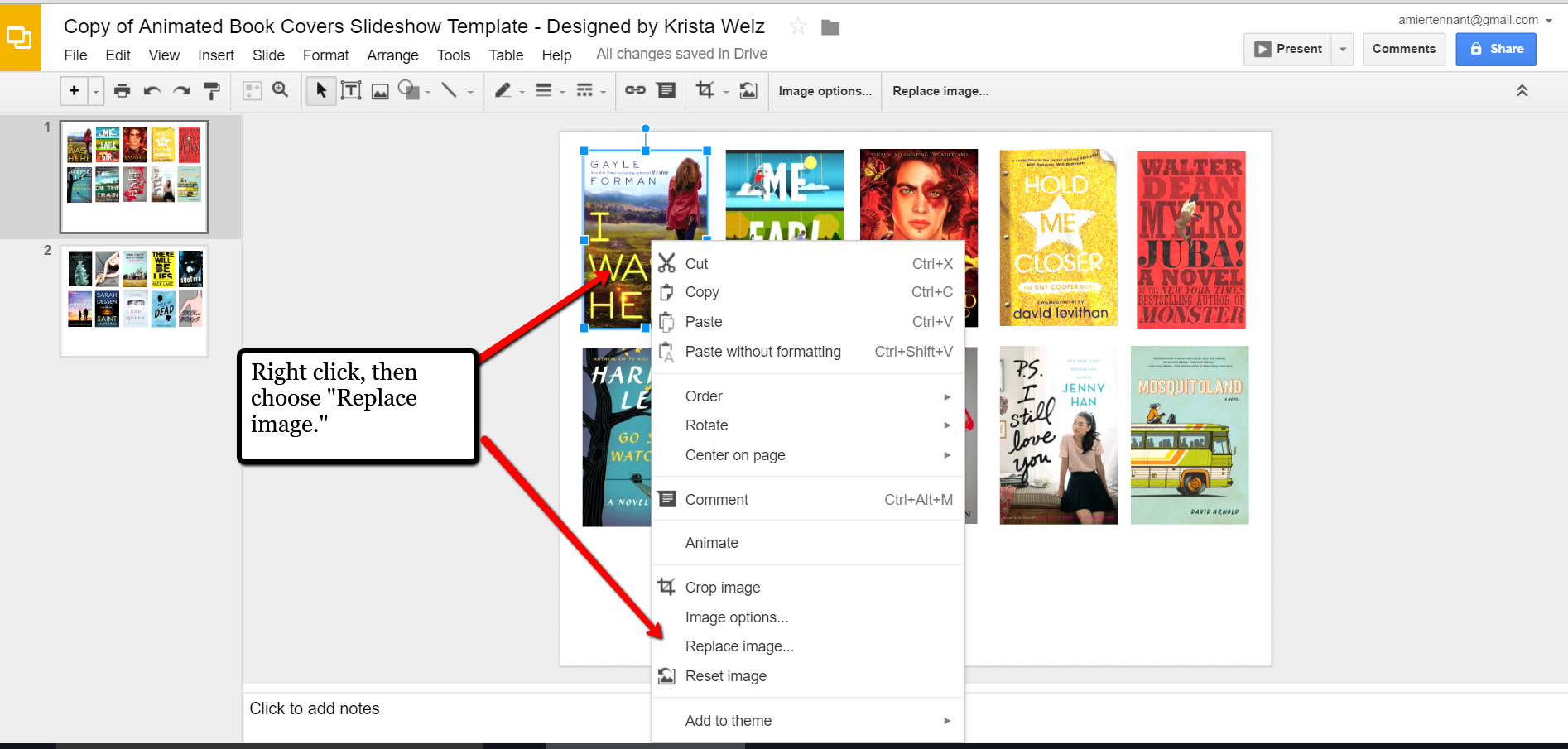
Make a copy and Google Slides will open. Right click on any of the book cover images you see, a pop-up window appears. Choose
Replace image and then find an image of one of your own book covers.
Once you have replaced each of the book covers with ones of your own, you can rearrange them with the click-and-drag method. You might want to put them in alphabetical order or perhaps categorize them by subject or place.
When you have finished, don’t forget to title it. There is no need to save it because Google Slides automatically saves for you. Google Slides is accessible from any of your devices and can even be viewed on-the-go from your mobile device. You’ll love this feature when you are trying to decide what books to add to your genealogy library.
How Can You Use Google Slides for Genealogy?
We are sure there are dozens of ways to use Google Slides for genealogy. Give Google Slides a try and if you think of another use for this wonderful tool, let us know about it in the comments below! Thanks for reading, friends.
More Gems on Google for Genealogy
by Lisa Cooke | Feb 17, 2020 | 01 What's New, Records & databases
There are a wide range of genealogical records newly available online. Here are new and updated collections as of this week. We’ve included important information about each collection that will help you determine whether it is suitable for your genealogical research. We include affiliate links for which we may be compensated, at no expense to you. Thank you for supporting free article like this by using our links.

The latest genealogy records from Genealogy Gems.
NEW: HALL COUNTY NEBRASKA NEWSPAPER DIGITIZATION PROJECT
About the collection:
“The Hall County Newspaper Digitization Project is a collaborative project supported by the historical and genealogical societies, newspapers, public libraries, and museums in Hall County. This project will digitize the 28 historic newspapers published in Hall County since 1870. The Grand Island Independent (up to 1924) is included in this project.”
Newspapers included in the first completed phase of digitization include:
- Platte Valley Independent (1870-1884);
- Grand Island Times (1873-1892);
- Grand Island Independent (1884-1900);
- Wood River Gazette (1884-1892);
- Doniphan Eagle (1892-1895);
- Staats-Anzeiger und Herald (1894-1918);
- Wood River Interests (1894-1919);
- Wood River Sunbeam (1906-2003).
Search the collection here.
DIGITAL LIBRARY OF GEORGIA
Sanborn Fire Insurance Maps (Select Georgia towns and cities. 1923-1941)

Sanborn Fire Insurance Maps at the Digital Library of Georgia
About the collection:
“The Digital Library of Georgia has just made Sanborn fire insurance maps produced between 1923-1941 for 39 Georgia towns and cities in 35 counties freely available online. The maps, which are now in the public domain, can be retrieved at dlg.usg.edu/collection/dlg_sanb, and complement the DLG’s existing collection of the University of Georgia Map and Government Information Library’s 539 Sanborn maps dating from 1884-1922 that have been available since 2005. The DLG has also upgraded its image viewer, which will allow better access and improved navigation to the new and older Sanborn images from this collection.”
Search the collection here.
MYHERITAGE
Search the following collections here at MyHeritage.
NEW: New York, Birth Index, 1881-1942
About the collection:
“This collection consists of indexes of births from the state of New York between the years 1881 and 1942. The State of New York began statewide registration of births in 1881, supervised by the local board of health. A record may include the following information when it is available: given name and surname, birth date, town of birth, and gender. The images in this collection have been obtained through the outstanding work and efforts of Reclaim the Records.
This index does not contain lists of births from New York City. New York City is considered to be a separate vital records jurisdiction from the rest of New York state, and consequently the city has its own birth indices. However, a small number of New York City birth listings are found throughout this index. This is due to the births happening in towns that were previously independent before the consolidation of the city in 1898 (for example, a pre-1898 birth in a place like Canarsie [Brooklyn] or Flushing [Queens] might be listed here) or because there was a late birth registration.”
NEW: Minnesota, Death Index, 1904-2001
About this collection:
“This collection includes an index of death records from Minnesota, between 1904-2001. Information may include the deceased name, date of death, county of death, date of birth, county of birth and certificate number. It may also include the mother’s maiden name when available.
Information for the years 1908-2001 is recorded from death certificates as recorded by a physician or a mortician. Information in this collection for years prior to 1908 is taken from death cards. Unlike death certificates, many death cards were filled out very incompletely. Cards, especially for the cities of Minneapolis and St. Paul, frequently contain little more information than the name of the decedent, date of death, sex, marital status, birthplace, cause of death, and person reporting the death.”
Number of records: 4,460,579
NEW: Minnesota, Birth Index, 1900-1934
About this collection:
“This collection contains an index to birth records from Minnesota between 1900-1934. Information may include: first name, middle name, and last name of the child. It may also include the date and county of birth, certificate number. It may also include the mother’s maiden name when available.
Birth certificates were used to record birth information beginning in 1907. When a child was born, a physician or midwife compiled information about the child on a birth certificate. The certificate was registered with the local county registrar. Birth cards were used to collect birth information from 1900 to 1907. Unlike birth certificates, many birth cards were not completely filled out. 80% of this collection takes place between 1907-1937, 19% is from 1900-1907 and 1% is from before 1900.”
Number of records: 3,406,802
Updated: MyHeritage Photos and Docs
About this collection:
“This collection includes public photos, videos and documents posted by MyHeritage members on their family sites. You may contact a member who submitted a photo to get in touch or request additional information.”
Number of records: 141,129,707
ANCESTRY
U.S. City Directories, 1822-1995
About the collection: “This database is a collection of directories for U.S. cities and counties in various years. The database currently contains directories for all states except Alaska.
Generally a city directory will contain an alphabetical list of citizens, listing the names of the heads of households, their addresses, and occupational information. Sometimes a wife’s name will be listed in parentheses or italics following the husband’s. Other helpful information might include death dates for individuals who had been listed in the previous year’s directory, names of partners in firms, and forwarding addresses or post offices for people who had moved to another town.”
Search the collection here.
NEW: New York State, Address Notification and Absentee Ballot Application Cards, 1944
About the collection:
“This collection consists of notices received in 1944 by the War Ballot Commission from members of the United States Armed Forces, American Red Cross, and other service organizations serving in World War II that resided in New York requesting absentee ballots or notifying the office of a change in address. For more information on this collection, please visit the Finding Aid page on the New York State Archives site. There are two main forms present in this collection – pre-printed applications for war ballot, and postcards with change of address information.”
Information contained varies, and may include:
- soldier’s name
- soldier’s rank or rating and service number
- soldier’s birth date
- soldier’s residence at time of request
Search the collection here.
Updated: 1860 U.S. Federal Census – Slave Schedules
About the collection:
“The slave schedule was used in the following states: Alabama, Arkansas, Delaware, Florida, Georgia, Kentucky, Louisiana, Maryland, Mississippi, Missouri, New Jersey, North Carolina, South Carolina, Tennessee, Texas, Virginia.”
Search the collection here.
Updated: 1850 U.S. Federal Census – Slave Schedules
About the collection:
“The slave schedule was used in the following states: Alabama, Arkansas, Delaware, Florida, Georgia, Kentucky, Louisiana, Maryland, Mississippi, Missouri, New Jersey, North Carolina, South Carolina, Tennessee, Texas, Virginia.”
Search the collection here.
Updated: New Zealand, Cemetery Records, 1800-2007
About the collection:
“These transcriptions of headstones from cemeteries in New Zealand typically include details such as name, birth date, death date, and the cemetery name and plot location. But they may also provide family relationships with name and other details about a spouse, cause of death, military dates, an epitaph, or even a description of the headstone.”
378,207 new records were added.
Search the collection here.
Updated: U.S. Virgin Islands, Danish West Indies Slave Records, 1672-1917
About the collection:
“This database contains Danish records relating to slavery in what became the U.S. Virgin Islands.
During Danish rule, officials kept voluminous records, including the slave-related records found in this database. They include the following:
- case papers concerning contested slave ownership
- emancipation records
- registers of free men, women, and children of color
- lists of baptisms, marriages, and burials
- lists of slave owners and former slaves
- mortgages and loans
- slave lists and censuses
- records of Royal Blacks
- compensation agreements
- courts martial
The records can be a valuable source of names, dates, places, and other details. These records have not yet been indexed, but they can be browsed by record type. Most of the records are in Danish.
This collection was previously published as image only. The collection has since been indexed and this update adds 80,184 new records.”
Search the collection here.
Updated: California, Voter Registrations, 1900-1968
About the collection: “This database consists primarily of the voter indexes published every two years, including indexes to the Great Registers, to affidavits for registration, and to precinct registers.
Voter registrations were kept on the county level by the county clerk. Indexes to these records are organized according to county and voting wards and/or precincts. Within each precinct voters are listed alphabetically according to surname.”
Information may include:
- Name
- Age
- Address
- Occupation
- Political Affiliation
Search the collection here.
UNIVERSITY OF NEVADA, RENO – CITY DIRECTORIES
The University Libraries has recently digitized early city directories of Reno, Sparks, and the surrounding areas, which date from 1900.
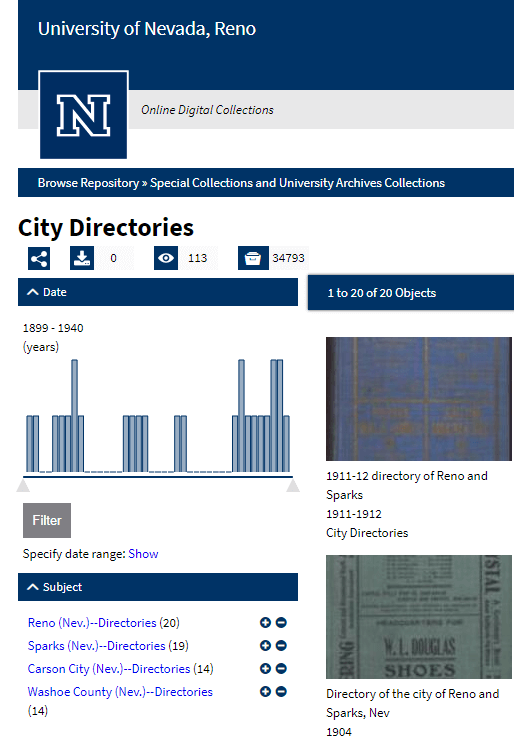
Nevada City Directories at the University of Nevada
Search the collection here.
FINDMYPAST
NEW: Canadian Directories & Almanacs
Findmypast has launched brand new collection with records from the province of Prince Edward Island. According to the company, more will be added from across Canada over the coming months.
About the collection:
“The eclectic mix of five directories cover the late 19th century from 1880 to 1899.”
The titles included are:
- Frederick’s Prince Edward Island Directory
- McMillian’s Agricultural and Nautical Almanac
- McMullan’s Almanac
- Teare’s Directory & Hand Book Of The Province of Prince Edward Island
- The Prince Edward Island Almanac
Search the collection here.
Updated: PERiodical Source Index (PERSI)
About the collection:
“Over 7,000 images have been added covering a variety of PERSI publications, perfect for fleshing out family stories. The new periodical titles that have been added are:
- Vermont Quarterly Gazetteer: A Historical Magazine / Bound With New Title: Vermont Historical Gazetteer
- Recherches Historiques
- Cambridge Historical Society Publications/proceedings
- Archivium Hibernicum / Irish Historical Records
- Queen City Heritage / Ohio Valley History
- Connecticut Historical Society Collections
Simply filter by periodical to get to the latest additions.”
Search the collection here.




 The Genealogist’s Google Toolbox
The Genealogist’s Google Toolbox

