The Incredible Story of the Public Records Office of Ireland
Dr. Brian Gurrin is a specialist on Irish censuses and census substitutes and author of such books as Pre-census sources for Irish demography and The Irish religious censuses of the 1760s.
In this week’s video premiere he joins me for a discussion of the incredible story of the repository that held early census records and much more: the Public Record Office of Ireland.
Dr. Gurrin will take us back through the history of the building and the surprising and ironic catastrophes that destroyed countless valuable records. Then he will share the truly inspiring ways that records are being restored, some of which will be available soon!
Watch Live: Thursday, June 9, 2022 at 11:00 am CT
(calculate your time zone)
Three ways to watch:
- Video Player (Live) – Watch video premiere at the appointed time in the video player above.
- On YouTube (Live) – Click the Watch on YouTube button to watch the YouTube premiere with Live Chat at the appointed time above at the Genealogy Gems YouTube channel. Log into YouTube with your free Google account to participate in the live chat.
- Video Player above (Replay) – Available immediately after the live premiere and chat.
Show Notes
Downloadable ad-free show notes PDF for Premium Members.
(This interview has been edited for clarity.)
If you’re looking for Irish records that were created prior to 1922, and you’re in the right place, today, we are talking about the Beyond 2020 to Ireland project, which may just be the best hope for Irish research in a long time.
Dr. Brian Gurrin is a specialist on Irish census records and substitutes. He’s also the author of the books Pre-census sources for Irish demography and The Irish religious censuses of the 1760s and he’s here today to tell us about this exciting project.
Lisa: What was held at the Public Records Office of Ireland prior to 1922? What kind of records would somebody have found there?
Dr. Gurrin: The Public Record Office (PRO) opened its doors in 1867. Prior to that the Irish records, the various state records, records of Parliament and so on, they were dispersed around in various repositories, around Dublin and around the country. Many of them were stored in locations that were unsuitable for maintaining records in good condition. The records were getting damaged, some records were getting damaged by damp and so on.
So, when the PRO opened, they started to take in records from these unsuitable repositories. There were a vast quantity of records available. Our earliest census records, our first census was held in 1813. That wasn’t a particularly successful census. And then are our next census was the first time that Ireland was fully enumerated by statutory census in 1821. And thereafter, we held censuses every 10 years on a year to terminal digit one. So, we held our census in 1821m 1831, 1841, 1851, and so on, right up to 1911, which was the last census that was held in Ireland, when Ireland was part of the United Kingdom.
And so, they were very important, very important for genealogists. And an interesting thing about the census: when the Public Record Office opened, and it just goes to show how research is changed, they published annual reports every year, the Deputy Keepers Reports. And when they opened, one of the earlier reports, I think it might have been the second report or the third report, made a comment about the census records. It talked about that the census records were just clutter taking up space and that they weren’t very important. And that they were just taking up taking up an enormous, inordinate amount of space in the Public Record Office. They didn’t want to receive any more census records because there were just basically clutter. And when you think about the census and how important the census is for genealogical research and family history research now, it just goes to show how historical research has changed, and how these records are vital records for historical research and historical study.
Overview of the background and contents of Public Record Office of Ireland:
- Public Record Office of Ireland opened to public in 1867.
- National repository for records:
- Census returns (1813-5, 1821, 1831, 1841 & 1851)
- State papers
- Parliamentary records (Ireland had its own parliament until 1800).
- County records; accounts, administration; grand juries.
- Charters, corporation records
- Maps
- Testamentary (wills), parish registers (Established Church)
- Tax records (poll taxes, hearth tax)
The building destroyed on 30 June 1922; and almost all records lost.
So it was a really vast collection and it built up from 1867 right up to 1922 when it was still receiving records into the record office.
Let’s just go back and talk about the 1821 census. Again, Ireland’s first census. When that census was held, the census recorded the names of all householders in the country, but also the act that initiated the census specified that at the each of the individual counties where to make a copy of the census as well to hold locally as their own local copy of the census. But then when the county records came in after 1891, after the fire, in the Cork courthouse, all those copies of the 1821 census also came into the Public Record Office as part of the county records collection. In 1922 the Civil War the civil war commenced, and the public record was on the north side of Dublin City in the Four Courts complex, just north of the River Liffey on the north bank.
The anti-treaty IRA occupied the Four Courts complex. We’re not sure what happened. There are two schools of thought. One is that the Anti-treaty IRA deliberately mined the building and blew up the building when they were evacuating it to destroy the records which were primarily records of British administration in Ireland. So, it was a great strike for Irish republicanism, destroying the records of the British administration in Ireland. The second thought on it is that when the anti-treaty IRA started shelling the Four Courts complex to drive out anti-treaty Republican forces there, a shell went in into the Public Record Office, exploding munitions that were stored in the Public Record Office.
Whatever happened, it was quite a disaster for Irish record keeping the beautiful fantastic archive was destroyed. It was explosions that occurred on the 30th of June 1922. It was a catastrophe for Irish history. The building was destroyed, this beautiful archive was destroyed. Records going back 800 years were blown up. The records were scattered around Dublin City. Records were blown on the wind over 10 miles out around Dublin. People were picking them up and handing them back in. There were very little handed back in. It was a catastrophe for Ireland and a really great tragedy. So that’s the backstory.
There was two parts to the records office. In designing this, they were really careful to try to ensure that nothing, no catastrophe, could happen that these records could be destroyed. There were two parts to the building. There was a squarish type building (on the left in the photo).
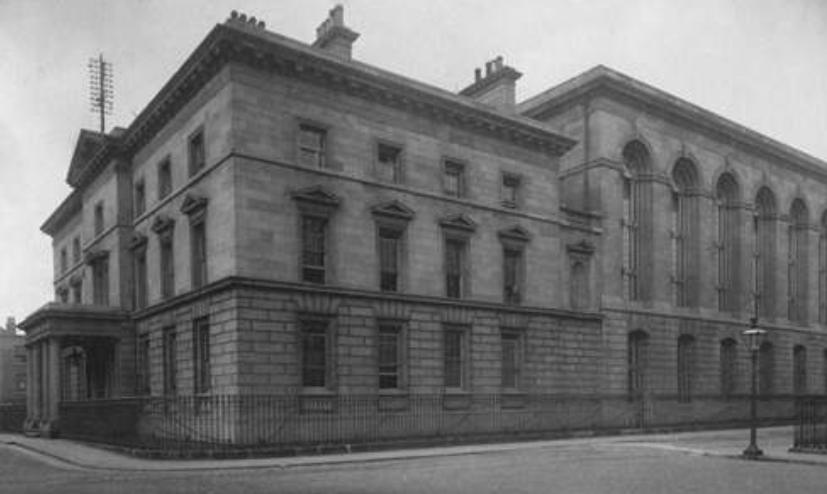

Ireland Public Records Office
That’s called the Record House. That’s where the researchers went. If you want to access records, you went into the Record House, (it was like the Reading Room of the archive) and you filled out a form. You filled out the details of the record you wanted.
The building on the right was called the Record Treasury. It was called the Treasury because these were Ireland’s treasures. This was where Ireland’s treasures were store. It was a beautiful archive containing beautiful records of Irish history over 800 years.
If you look up towards the roof, between the two buildings, you can see a gap. This was a fire break that was that was installed because it was thought that if any fire broke out, it wasn’t going to break out in the Record Treasury, it was going to break out in the record house where the where the public came in and where the heating systems were. So, they wanted to ensure all the collections of records that were in the Record Treasury were going to be protected from fire. So that building isn’t actually joined together. That’s a false wall there. That firebreak gap between the two buildings was to ensure that there was no possibility that a fire could spread from the Record House into the Record Treasury and destroy the records.
The great irony is that when the fire broke out, when the explosions occurred, the explosions occurred in the Record Treasury. That meant that the firebreak operated in reverse protecting the Record House from the Treasury. And by coincidence, whoever was working on records on the day that the record office was occupied, those records were moved from the Treasury to the Record House for them to access. Those records remained in the Record House. So, a small quantity of records survived just by pure accident because people were using them in the Record House at the time. So, the firebreak operated in reverse, protecting the Record House from the fire that was in the Record Treasury even though it was designed with the idea that it would protect the Treasury from any fire that was going to occur in the Record house.
Lisa: Did you say that there was actually munitions stored there?
Dr. Gurrin: Just to take up on the first question that yes, they did. They were really careful to ensure that no damage could come to the records. It wasn’t just that they installed a firebreak, but they also made sure that there was no wood in the Record Treasury to ensure that there was no possibility. So everything was metal. Initially there were wooden shelves in there. But then, maybe 10, 15 years in, the Deputy Keepers annual report says, that’s it, there’s no wood left in here, We have it perfectly protected, so there is no possibility of fire occurring in here.
A view inside the Record Treasury:
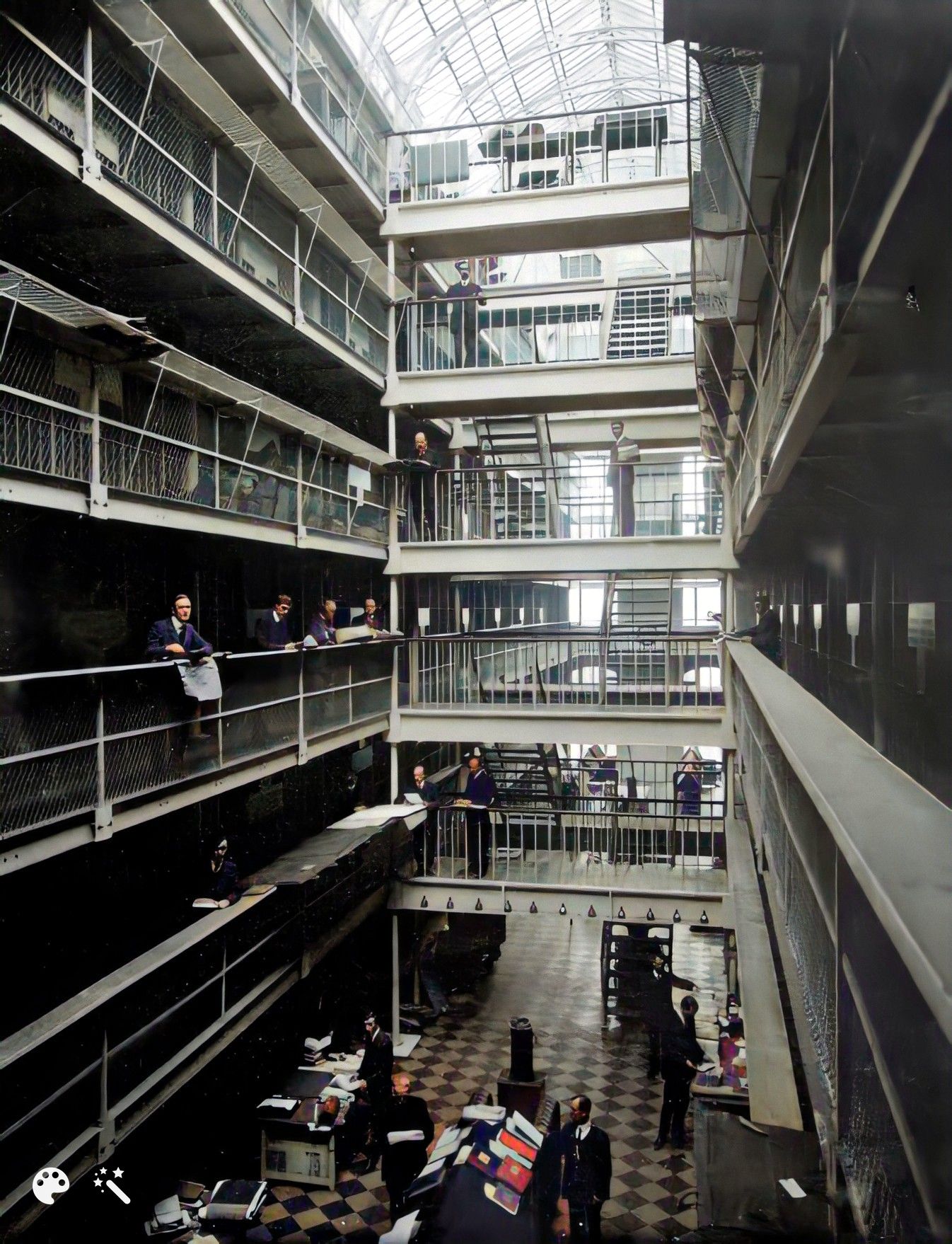

(enhanced and colorized photo)
There were six floors in that building. You won’t see any wood at all.
These people are called searchers. So, you go into the Record House:

The Record House
You’d sit down in one of those benches down the back, you’d fill out your document, and you’d hand it up to the clerk behind the desk. They give it to one of the searchers who then goes in through those double doors. That’s the way in between the firebreak and the link into the Record Treasury. They wander up to the steps to whichever floor the record was on and find the record, and bring it back down into the Record House for you.
Now we do have a great knowledge of what was in the Record House.
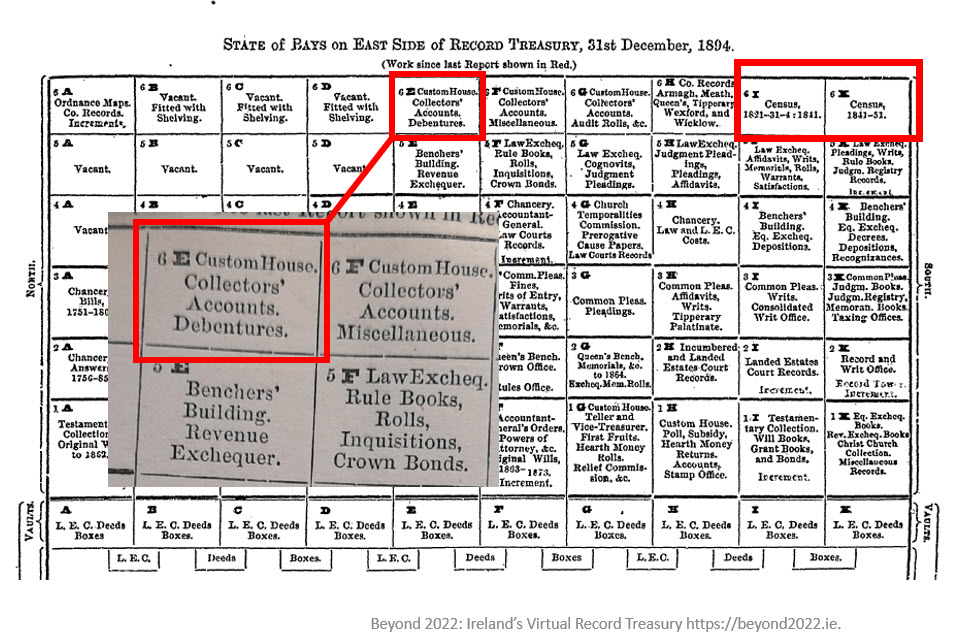
record treasury chart
There was a kind of a central aisle down. On either side there were what were called “bays”. There were six floors to it. This chart is giving you an indication of what was in the Record Treasury and what type of records were in the bays.
Public Record Office inspection document:

Tennyson Groves was a great hero of mine. He was a genealogist who sat in the Public Record Office and transcribed vast amounts of information from various census records. A lot of what we have surviving now are transcripts that were transcribed by Tennyson Groves.
Lisa: You mentioned the copies of records that were often made. We see that in genealogical records around the world that sometimes copies get made, and then the original set may go to a central location, and then they would keep a set locally. You mentioned that with some of the census records they actually sent the second set into the public records office as well. Do you have a sense of how many duplicates are out there? I mean, how much hope is there that there are copies of some of the things that were in the building and lost that day?
Dr. Gurrin: That’s a really good question.
Once the fire occurred in the courthouse in 1891 in Cork, they said, ‘right, we cannot have, we can’t have a situation where local records are stored in unsuitable accommodation like this. They can’t be destroyed. We have a perfectly fireproof location here. So, we’re going to take them all in.’
So, whatever records counties produced, like as I said, the 1821 census, they were required to make copies. Not all counties produced copies, and not all counties produced complete copies for their county, but many counties did. And many counties produced partial copies. All of those went into the Public Record Office after 1891 as per instructions of the Public Record Office. They all went in except for one county, which is county Cavan. About 40% of the census records survive for Cavan. They were the only county that didn’t send in their local copies into the record office. All the others transferred.
If the fire hadn’t occurred in Cork, maybe the Public Record Office would have let the records stay locally, and they would have survived. In terms of survival of records, Cavan is the only county that copies of the 1821 census survived. Now there are four volumes of 1821 census original volumes that survived. Some bits of partial sets of records have survived. That’s four out of 480 original volumes that existed. So, it’s like 1% of the original volumes from 1821 to survive. But for Cavan 40% of the county is covered by copies that were made under the terms of the census act.
Then there are transcripts for various parts from genealogists and local historians. Prior to 1922, they made copies. But in terms of survival there’s probably about, I suppose, 50 or 60,000 names surviving from 1821 and transcripts. Now that’s 50 or 60,000 names out of the 6.8 million names that were enumerated in 1821. So it’s really, really tragic.
And it’s even worse as you go as you go to the next census for 1831, the survival rate is even lower. And for 1841, it’s very low as well. And there are about two and a half thousand civil parishes in Ireland. And for 1841, there is only one parish that the original record survived. The scale of the losses is just catastrophic.
We are very lucky in that we do have census substitutes. In some instances, we have a wonderful land value taxation valuation that was conducted in the 1860s or in the 1850s called Griffiths Valuation, which is effectively a census substitute. But that’s what we’re down to as Irish genealogy. We’re down to using census substitutes in a lot of instances because unfortunately, this wonderful census records were lost.
There was one other very interesting census that was conducted in Ireland in 1766, a religious census. And that’s a real focus of our project now. It’s a magnificent survey that was conducted that is in the second book of mine that you mentioned. Some original records survive from that as well. So, that’s a really interesting focus of our project, which I could talk for hours!
Lisa: How has this loss of records been coped with over the last 100 years? Were there efforts to try to reconstruct them and fill it back in?
Dr. Gurrin: There were. As soon as the Record Office was reconstructed they did put out calls for records or records transcripts that were taken before 1922. Those came back in and were donated back into the facility. They did make efforts to recover them.
A lot of the records like the charred remains of records that were picked up around the streets of Dublin and in the vicinity of the Four Courts were collected and boxed and cataloged. Many of those records weren’t accessed again until our project started.
The National Archives has been cataloging those records that were picked up almost 100 years ago on the streets of Dublin, and they’ve been cataloging them they’ve been trying to recover them to try to treat them to make them accessible again.
There were various efforts made and donations came in from genealogists like we had a lot of genealogists who transcribed records previous to 1922. If genealogical transcripts came up in auctions the government was very active in trying to secure those. They did as much as they could do, I think, to try to recover the losses, but it was only going to be a drop in the ocean in comparison with what was there.
Lisa: Now you’ve got a brand new project called Beyond 2022. Tell us how this gets started. And what’s your end goal?
Dr. Gurrin: It’s part of the decade of the decade of Centenaries in Ireland. There were a lot of things happening around 1916, with an Easter Rising around 1918, with a general election, which saw Sinn Fein’s win the majority of the seats. It saw the War of Independence, the Civil War, and then the government of Ireland enacted the partition of Ireland. So, it was a lot of things happening around there.
Beyond 2022 really fits into that as a part of the Decade of Centenaries. It’s a two year project that’s been going on with the intention of identifying material that still exists in archives around the world and local archives here in Ireland. It’s an effort to recover it to make it freely available digitally online. They’re being digitally imaged as high-quality digital images. They are being transcribed as much as possible. And that’s not being hand transcribed. This is a transcription package, which is reading the handwriting and trying to transcribe that handwriting into searchable text.
At the end of it, it is the intention of the project to make 50 million words available and searchable through the Beyond 2022 website. So you will be able to enter a name, enter a name, enter a townland name, enter a place name, enter free text and search these documents and come back with whatever we have. The launch date is June 30, 2022.
Learn more about Beyond 2022
- Web address: https://beyond2022.ie
- Twitter: @VirtualTreasury
- Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/Beyond2022/
- Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/beyond2022/
Resources
Downloadable ad-free show notes PDF for Premium Members.

Click to learn more about Genealogy Gems Premium Membership.
Getting Started on Ancestry.com
Getting started on Ancestry.com can be a little daunting. As one of the world’s top genealogy websites, it’s packed with information about millions of people–perhaps including your ancestors. These step-by-step instructions will help you start...Free Genealogy Records from Around the World: Newly Online!
Free genealogy records, newly available online, may be able to take you around your ancestor’s world! This week’s record destinations include Australia, Belgium, Brazil, Bolivia, Canada, Chile, Dominican Republic, France, Italy, Netherlands, Nicaragua, Russia, and South Africa.

Civil registration records–key genealogical resources–from several countries are among the free new family history records online in recent days and weeks. But you’ll also find probate records, church records, military personnel records, and even a digital archive meant to preserve ancient aboriginal languages. Which might mention your ancestors?
Argentina
Over 100,000 indexed names have been added to FamilySearch’s free collection, Argentina, Entre Ríos, Catholic Church Records, 1764-1983. According to a collection description, it includes “baptisms, confirmations, marriages and burials for cities in the province of Entre Ríos.”
Australia
An exciting new Australian website houses a digital archive of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander language materials. It includes texts, audio, video, and ebooks about Australia’s First Nations languages. The hope of the site is to be a digital repository for gathering, preserving, and sharing materials that in effect preserve these languages and revitalize their use. The site managers will continue to work with partners to bring more content to the site. Click here to read more about the site’s launch, and click here to access it directly.
Belgium
Two free Belgian civil registration collections at FamilySearch.org have been updated:
Both of these collections are comprised of civil registration of births, marriages, and deaths from the Belgium National Archives, as well as marriage proclamations, marriage supplements, and some original indexes. Additional images will be added as they become available.
Brazil
Several free Brazilian genealogy records collections have been updated at FamilySearch.org. Among them are the following:
- Pernambuco, Civil Registration, 1804-2014 (more than 300,000 newly indexed records)
- Piauí, Civil Registration, 1875-2013 (nearly 150,000 newly indexed records)
- Brazil, São Paulo, Immigration Cards, 1902-1980 (over 20,000 newly indexed records)
Bolivia
Over 300,000 indexed names have been added to FamilySearch.org’s enormous free collection of Bolivia Catholic Church Records, 1566-1996. The collection hosts over 1.5 million digitized images of Catholic Church records created by parishes in Bolivia. “These records include: baptisms, confirmations, marriages, pre-marriage investigations, deaths, indexes and other records. Some of these records have been indexed and are searchable as part of this collection. Additional indexed records will be published as they become available.”
Canada
Library and Archives Canada continues to update its free Personnel Records of the First World War database. So far, the database includes “digitized files for many individuals of the Canadian Expeditionary Force and the Royal Newfoundland Regiment and Newfoundland Forestry Corps (courtesy of the Rooms Provincial Archives).”
Newly digitized CEF files are added to the references every two weeks, states the collection’s landing page. To date, over 461,000 of an expected 640,000 files have been added. “Library and Archives Canada is digitizing the service files systematically, from box 1 to box 10686, which roughly corresponds to alphabetical order,” explains a blog post. “Please note that over the years, the content of some boxes has had to be moved and, you might find that the file you want, with a surname that is supposed to have been digitized, is now located in another box that has not yet been digitized.”
Chile
FamilySearch.org has updated its free collection, Chile Civil Registration, 1885-1903. These include “births, marriages, and deaths for various localities in Chile from 1885 to 1903. For a complete list of all the provincias and comunas included in this collection, see the Provinces of Chile – Civil Registration coverage table. Only records from a few localities have been indexed. More records and images will be added as they become available.” Need help reading these? FamilySearch suggests using this Spanish Genealogical Word List, which also links to other translation tools.
Dominican Republic
Over 175,00 indexed names have been added to FamilySearch’s free collection, Dominican Republic Civil Registration, 1801-2010. Spanning over 200 years, the collection includes images of births, marriages, and deaths as well as some divorces and indexes. “Some of these records have been indexed and are searchable as part of this collection,” states the collection description. “Additional images and indexed records will be published as they become available. These records were obtained from public access sources in the Dominican Republic.”
France
FamilySearch has updated its collection of indexed Catholic parish record images for Coutances et d’Avranche Diocese, 1533-1894. Baptisms, marriages, and burials are all included. “Parishes within this diocese are within the boundaries of the department of Manche,” states a collection description. “French commission for Informatics and Liberties (CNIL) does not allow publication of sensitive data below 150 years.”
Italy
FamilySearch continues to publish more Italian civil registration records! These are some of the latest:
- Asti, 1803-1814, 1911-1935. Over 50,000 indexed records have been added to this existing collection.
- Bergamo, 1866-1901. Over 25,000 indexed names have been added to this database.
- Chieti, 1866-1930. Over a half million browsable images comprise this new collection.
- Macerata, 1808-1814. Over 90,000 browsable images are in this new collection.
Netherlands
Just shy of a million records have been added recently to FamilySearch’s free collection, Netherlands, Archival Indexes, Miscellaneous Records. “Archives around the Netherlands have contributed indexes which cover many record sources, such as civil registration, church records, emigration lists, military registers, and land and tax records,” says the collection description. “These records cover events like birth, marriage, death, burial, emigration and immigration, military enrollment and more. These indexes were originally collected, combined and published by OpenArchives.”
Nicaragua
There are now over two century’s worth of records in the free FamilySearch collection, Nicaragua Civil Registration, 1809-2013. It includes “births, marriages, deaths, and other records created by civil registration offices in various departments of Nicaragua.” Civil registration in Nicaragua didn’t begin until 1879, and it appears that most records in this collection date from that year or later.
Paraguay
Nearly 125,000 browse-only images have been added to FamilySearch.org’s free collection, Paraguay Miscellaneous Records, 1509-1977. According to the site, “These records include two complete collections: Sección Nueva Encuadernación (Rebinding Section) and Sección Propiedades y Testamentos (Properties and Wills Section). Copies of the original records are housed at the Archivo Nacional in Asunción, Paraguay. The “Propiedades y Testamentos” section can give a brief look at the personal wealth of clerics, economic bases of resident foreigners in Paraguay, or the fortunes of a given family over a period of time.”
Russia
FamilySearch.org has updated its free collection, Russia, Samara Church Books, 1779-1923. It includes “images and partial index to records of births and baptisms, marriages, deaths and burials performed by priests of the Russian Orthodox Church in the province of Samara. These records were acquired from the state archive in that province.” Another brief statement in the collection description illustrates the incremental and ongoing nature of record additions to FamilySearch: “Currently this collection is 4% complete. Additional records will be added as they are completed.”
South Africa
Over 40,000 indexed records have been added to the free FamilySearch.org collection, South Africa, Transvaal, Probate Records from the Master of the Supreme Court, 1869-1958. The records are described simply as “probate records from the Master of the Supreme Court, Transvaal, South Africa. Original records are located in the Transvaal Archives Depot, Pretoria, Republic of South Africa.
Spotlight on probate records
 Probate records detailed the final settling of our ancestors’ financial assets. They often contain rich genealogical information and interesting insights into a person’s life. They are among the many records you might find at courthouses and government archives. More U.S. probate records are coming online (click here to learn more), but even if you have to visit a courthouse yourself or hire someone to do it for you, it’s often worth it. Click here to read why.
Probate records detailed the final settling of our ancestors’ financial assets. They often contain rich genealogical information and interesting insights into a person’s life. They are among the many records you might find at courthouses and government archives. More U.S. probate records are coming online (click here to learn more), but even if you have to visit a courthouse yourself or hire someone to do it for you, it’s often worth it. Click here to read why.
Thanks for sharing this post with those who will want to know about these free genealogy records online!

Early Virginia Genealogy
Show Notes: Learn how to trace your ancestors back to Virginia just prior to the Revolutionary War. Professional genealogist Jeri Satterwhite-Dearing specializes in early Virginia research in her work as a professional genealogist with Legacy Tree Genealogists. She explains some of the biggest challenges you’ll face when researching early Virginian ancestors, the records you should be looking for, and some of the best resources.
Early Virginia Genealogy Video and show notes
Watch the Video
Resource
Download the ad-free show notes including a BONUS Virginia checklist cheat sheet. (Premium Membership required)
Show Notes
Lisa: A while back, we did a video on Finding early American Ancestors in New England and we got tons of comments on it. We also received a lot of requests to dig into early American genealogical research. In this video and article, we are going to do just that for Virginia.
Guest: Jeri Satterwhite-Deering, professional genealogist at Legacy Tree Genealogists.
Exclusive Discounts
Learn more at https://www.legacytree.com/GenealogyGems This is our affiliate link and includes special discount coupon codes just for you.
Virginia Genealogy Research Challenges
What are some of the unique challenges that face people who are trying to research ancestors in Virginia?
Jeri: I think the main thing is that the further back you go, the different record types that you would expect to find and use. You won’t have census records before 1790, and you won’t necessarily have marriage records, or death certificates, because that didn’t come till much later. But those records are there, and then you just have to really know where to dig and what to look for.
I rely more on land records, tax records, court records, and those types of record. As I said, census records go back to 1790, maybe 1783, when they have county type census. Then at that point you need to rely on tax records more and look for your ancestors in land records. Land records are full of all kinds of genealogical clues about your family as you as you dig in deep.
Lisa: And it can be a bit of a challenge for folks who might be researching Virginia for the first time. We hear about things, like you mentioned the land records and tax records, and that could be very new territory for us. It can be a little intimidating to jump into a record collection you haven’t worked before.
Jeri: Right, especially because then you’re relying on original documents, which means reading the handwriting of the time. That takes practice. It’s like when you first learn to write cursive in school. It’s not that hard, it just takes a little bit of time. It’s kind of fun, because they write different, and their terminology is different. But that’s where your dictionary comes in. Practice makes perfect. The more you do, the easier it gets.
Most of those records are going to be at county level. If you have a burned county, then you may have to rely on state records. The Virginia state library may have more than what is left in a burned county. There are all kinds of records there. It’s just a matter of knowing where to go.
Learn More About the County in Virginia
My first recommendation would be to learn more about the county you’re going to be dealing with. First go to the FamilySearch Wiki for the county. Read what they have to say about which records are available for that particular county and start there. Make a research plan. Make notes and determine exactly what to look for.
I know that you’ve done a couple of past episodes, especially I think it was episode 64, where you talked about how to do research using FamilySearch. I think those are things you need to learn a little bit before you jump right in. I think that would be a really good start if they’re not familiar with FamilySearch. It’s one of the best places to go to look at records when you’re starting out.
Lisa: And it’s free, which is great.
Jeri: That’s right, so it’s definitely a good place to start along with learning about the county. Learning about the formation of the county, that’s almost a genealogical research adventure in itself because you need to know how the counties changed so quickly over time. And you do need to get back to what that parent county was. It’s important to know the genealogy of the counties and know where to look for those records, because they’re not all just going to be in today’s county. You may have to go back to multiple counties to find those records.
Lisa: Typically, when a record was created in a particular county, and then that county maybe splits out or changes we should be looking in the county that it was at the time our ancestors were there, right?
Jeri: Exactly. You might think, “that’s it, I’m done. I can’t find anything else.” When you feel that way, step back, review the various forms the county has taken. Check all of them. You’d be surprised where those records will be in many different places. They might even be in the courthouse basement. I’ve come across that many times as well.
In Virginia, not all deed records are going to be online. For example, here in North Carolina our counties have so many records available online. But in Virginia, they might not be on FamilySearch. You may have to go to a courthouse to actually see those records. However, they are getting better about getting them filmed.
If you’ve exhausted some of that, like I mentioned before, check out tax records. These put your person in their place in time, and that’s what you’re looking for. You always want to remember that a man by one name is not necessarily that man. Always remember that because there are so many same named people throughout history, and you have to be careful which one you’re chasing and get the right one.
Lisa: I love your idea about the genealogy of a county! Getting to know the history county at the same time as you’re getting to know the history of your family.
Virginia Burned Counties
You mentioned burned counties. Seasoned genealogists have heard that many times. But there are those who are new to genealogy, or they’ve been researching other parts of the country, and now they’re finding that their family line takes them into the South where burned counties are more common. Tell us a little bit about what you mean by a “burned county” and what does that mean to the records?
Jeri: Generally burned counties have a lot to do with war. That’s especially true during the Civil War. For the South, many courthouses burned down. But it happens even in today’s time. We see floods, we see fires. Again, look at your county history on the FamilySearch Wiki. It will tell you which counties were burned. Then you can determine where else to look for records.
I had a project recently that was in Washington County, Arkansas. The county was totally burned, and there was nothing really left. But at the state level, I was able to find the tax records. So, for the client’s ancestor, we were able to place him in that county in the time that we needed to place him there even though there was no information about him anywhere in the county. Those records were burned at two different times. Once in the 1800s, and then again later on.
When your ancestor got a deed, they would take it into the courthouse to get it recorded. This means that when you’re looking at a deed book, you’re not looking at the original record because they didn’t keep the original deed. They just recorded it, and then they handed it back. Folks then took it home to keep it in a safe place. I was very fortunate in one of my research projects that when we had burned counties, they had all the people bring their deeds back in and they recorded them again. And so that’s how we ended up with still having deeds that were probably burned the first go around in the clerk’s books.
I inherited deeds from my great grandmother that were in a trunk. That is probably what started this whole journey for me 30 years ago. One of the deeds was from 1812. It was just amazing! They had kept those deeds. The courthouse over in Orange County did not have that deed, so I took it over there, and they got to copy it into the deed book. And then they had it. There’s a lot of ways to get around the burned counties, and there’s reason for hope.
Lisa: That’s very encouraging that they brought records back in and entered them again.
State Level Records for Virginia
How do records end up at the state level? You mentioned a couple of times to check with the State Archives. Was there a process where every so often the counties were supposed to send copies of books to the state? Or did that happen much later?
Jeri: Well, I think it did, like, are in North Carolina, particularly. So many of our marriage records have gone to the state. So, they’re at our archives now. And so, they came out of the county’s hands, I don’t know, maybe because they just kept getting burned to the ground. They, and so they ended up, you know, at the at the state level at the State Archives for most of them. And so, your state archives is a good place for your research. State libraries are good, like the Library of Virginia (state library), as the just you couldn’t ask for better. And online and offline. It’s a great, it’s a great resource for learning and looking for records as well.
Important Types of Records for Early Virginia Genealogy
Lisa: You’ve mentioned a couple of different types of records. We talked about tax records. Would we find tax records for somebody who doesn’t own property?
Personal Property and Planned Tax Records
That would be your personal property tax records, and then you had planned tax records. So, there are two different ones and you want to look for each. There may only be just one white pole, which means that one person is over the right age to be taxable. It might be a horse, it might be a silver watch, things like that.
Land Tax Records
Then there’s the land tax where they’re going to tax you on how much property that you own.
Included in the property tax would be enslaved persons. So, if you’re doing African American research, especially for Virginia, these are helpful. If the person you are researching was an enslaver, they would have these people listed by their names, typically their first names because that’s generally all they had. Some of them were sorted out by age. Not necessarily every county would be the same. But you would have perhaps age under 15 or 16, and then over 16. And while that’s a broad range, you’re looking for every little thing you can when you’re doing that type of research. Those are the kinds of things that you would see in the tax records.
Chancery Records
Another great resource is chancery records, which I love. They’re court records which you can find at the Virginia Library. You can search by plaintiff or defendant or just a surname. I usually just do the surname when I search. You go to each county so choose your county, and then choose your name. It’ll bring up folders of court records. Everybody sued everybody just like they do now. Everybody was in court all the time. Sometimes it’ll just be maybe a lawsuit over land, or it could be a lawsuit over a horse or an enslaved person as well. But a lot of times you would find records that would involve state records, probate records, and every now and then you will really get lucky and you could find a whole family’s history in some of these files that explain the parents and the grandparents, the grandchildren. I’ve had them go many generations in one file and even include the neighbors. It puts your person in their place and time and helps you not confuse them with someone else

Virginia Chancery Record, courtesy of Jeri Satterwhite-Dearing
I would say that if you don’t look at those you’re missing out, totally! They are refilming a lot of the records right now. So, when you search your file might not come up. You would be able to see the file folder, but you might not be able to see the contents of it. But then you could take that information and go to your county level court records. Again, I would go through FamilySearch and do your search in the catalog by the county, not just a record search. By doing that, you can actually find those folders are still going to be within the county. You’ll have to dig a little deeper. But it’s always rewarding to do that.
Colonial Tithables
Lisa: You’ve mentioned several really important types of records, chancery court records, deeds, wills and estate records. What other types are there? You have on your list colonial tithables. What are those?
Jeri: Those were really early. They’re like taxing, and it has to do with who the person by the age, and if they’re old enough to be taxed. It’s another form of the tax record. Those are the really early lists that you would be back quite far. You might not need those for a while, but if you get lucky, and you’re really getting back pretty far, then those are good.
Understand Virginia Law
Lisa: I imagined to be able to really use these records, we have to really understand things like geography and the law. What are your recommendations to a genealogist on really getting to understand the law? What’s a good way to go about that?
Jeri: Reading, taking classes, I mean, there are so many classes available online nowadays, just from the comfort of your home to be able to learn a lot. That would be the best thing to get familiar with the law. Learning the law is a little bit more complex but it is important. For example, it helps you determine if someone would have been the right age to get married. It’s a good way to separate the person out that might be the same name. It would help you know if your ancestor was able to buy and sell land, whether they could be a witness, all those ages change frequently. Then you know whether to go look for those records.
Understand Virginia Geography
Lisa: Are there any other resources that you think should really be on the forefront of the minds of people who are going to be digging into their Virginia roots?
Jeri: Land and maps are really my favorite! The David Rumsey collection is free and it’s excellent. I think you did a video episode on finding and using David Rumsey maps, too. Oh, my gosh, it was great!
And I definitely look for maps with Google. (Resource: The Genealogist’s Google Toolbox by Lisa Louise Cooke.) You can Google historical maps for Roanoke County, Virginia, for example. Some of those older maps have the landowners on them. I’ve got a huge map collection. You can find them from the formation of the county. They will have the landowner’s names written where their land was. Maybe your person did not own land, maybe they were just tenant farmers, but you found the name of the landowner, or you find them in another record. Look to see who they were living around. You can then find where they were, when they were in that particular county. That also gives you a way to look for more records that might involve your ancestor, as well.
Lisa: Well, that makes great sense. Maps are such an important part of it’s all location and timeframe, right?
Jeri: Yeah, because everything was about land. It still is, but it always has been about the land, and you don’t want to bypass that. You don’t want to just look at census, marriage, and death records, and that’s it. You really need to understand the context of their life and everything that was going on around them in the area that they lived. You then know more about who they are. Say their name, know who they were, and make them come back. They can be alive.
Getting Help from a Professional Genealogist Specializing in Virginia
Lisa: That’s a great way to look at it. Jeri, if people get really stuck, and they just feel like I need help with a professional genealogist, how could they get in touch with you? And what do you guys do at Legacy tree genealogist?
Jeri: They can contact us, and we can steer them to the right professional genealogist for their project. We have a wonderful team, and they do really good work! If you get stuck or if you don’t feel like you have the years to go and take the time to take classes and do everything, come join us and we’ll be happy to get you on the right track and help you find your ancestors.
Exclusive Discounts: Learn more at https://www.legacytree.com/GenealogyGems This is our affiliate link and includes special discount coupon codes just for you.
Lisa: It’s a good feeling to be able to take a big leap forward and professionals can help you do it. Jeri, this has been terrific. Thank you for giving us a jumpstart into our Virginia genealogy.
(This interview was edited minimally for clarity.)
Resources
Download the ad-free show notes including a BONUS Virginia checklist cheat sheet. (Premium Membership required)
