Using Wills and Probate Records in Genealogy Research
Using wills and probate records for genealogy can lead to unexpected “inheritances” of your own: clues about relatives’ identities, wealth, personal belongings, and family relationships. Wills can reveal great family stories, too: researcher Margaret Linford entertains her mother with them during trips to the courthouse. Here’s how wills can help your family history—and Margaret’s tips for finding and using them.
Using Wills and Probate Records in Genealogy Research
“Where there’s a will, there’s a way” to find out more about your family’s history.
Wills are legal records created to direct the settlement of a person’s property and other final affairs after his or her death. Probate (or estate) records are created after an individual’s death as part of the legal distribution of the estate and payment of debts. You’ll often find wills as one of many kinds of the documents included in probate records.
Wills and other probate records are valuable research tools, but are frequently neglected as sources of genealogical information. People often focus strictly on birth, marriage, and death records when searching out their family histories. If you rely solely on those records, your research will encounter many brick walls in the early 1800’s.
Probate records and land records were often the only official documents left behind to tell the stories of ancestors who lived prior to the legal requirement for the registry of births and deaths.
Wills of slaveholders can also be valuable tools in conducting African-American genealogical research. Before the Civil War, enslaved people were listed in wills because they were valuable property of slaveholders.
For instance, in the 1863 Smyth County property tax records, it is noted that Abijah Thomas owned 56 slaves, which were valued at $53,800. Some were given their freedom within wills, while others were transferred to other members of the family or sold. For instance, one of the first wills recorded in Smyth County is that of Hugh Cole.
Within his will, he says the following: “I bequeath to my beloved wife Martha Cole a negro girl named Amanda which she is to hold during her natural life.” The mention of an enslaved person in a will—along with any personal description of him or her—may be the only surviving document to mention that person by name.
Within another Smyth County will, recorded on February 20, 1835, a woman named Elizabeth Blessing left the following directive: “I will and desire that my negro woman Betty be free at my decease, and must see to her own support during her life, as I shall not make any provision for her out of any part of my estate.”
Information Found in Wills Varies
You can find just about anything in a will!
One organ, one compass, chain and plotting instruments, two chests, one hat rack, one music rack, one old United States map. These are some of the items found in the appraisement bill of the personal property belonging to the estate of Abijah Thomas, who lived in the well-known Octagon House in Marion, Virginia.
Here is a photo of that home, now in a dilapidated state, from a Wikipedia file image (click image for attribution.)
Also included in his personal property is a church bell. The story behind the bell is intriguing and illustrates the significance of the probate process.
Abijah Thomas utilized the bell at his foundry works in Marion, Virginia, to indicate shift changes. For decades, the oral history surrounding the bell indicated that he had donated it to the Wytheville Presbyterian Church before he died. The court documents reveal a different story.

Court document regarding the church bell
Since Abijah died intestate, the court appointed three men to appraise his personal property. During this process, the bell was valued at $75. It was sold on September 1, 1877, to the Presbyterian Church in the town of Wytheville, Virginia, as shown in the above list of items sold from his estate.
This document dispels the family myth surrounding the church bell. This is just one of many examples of the types of stories you find in probate records in courthouses all across the United States.
Genealogical Information May be Found in a Will or Probate Records
Wills and probate records can pass along unexpected genealogical wealth to you. You may find the following information in them: date of death (or approximate date of death), name of spouse, children, parents, siblings and their place of residence, adoption or guardianship of minor children, ancestor’s previous residence, occupation, land ownership, and household items.
Probate records also contain such interesting stories that they can even be read for entertainment!
Whenever I go on a research trip, I usually drag some poor, unsuspecting soul along with me. That person is usually my Mom. While she enjoys the scenery on our drive to different courthouses, she rarely enjoys the time spent at the courthouse.
Some of the research I do requires me to stay at the courthouse for several hours. That has posed a problem in the past since I haven’t known how to keep Mom occupied. But I have found the perfect solution. When we arrive at the courthouse, I find an old will book and let her start reading.
My mom enjoys reading the stories in these old—and sometimes tattered—books. One of her favorite stories came from a will in Henry County, Virginia. It is the will of Addie T. Thornton and reads as follows:
“I also give to my nephew Thomas T. Earles, fifty ($50) in cash to be deposited in some safe Banking Institution, on interest until he arrives at the age of twenty-one (21) years old and then the principal to be invested in a watch and I request that a monogram with both his and my name, one on inside and the other on outside of watch.”
Obviously, Addie Thornton cared deeply for her nephew, Thomas, and wanted to make sure he remembered her for the rest of his life.
Here’s part of Addie’s will, followed by a closeup image of the lines about the watch:
Stories like these are so much more meaningful than just a date of birth, marriage or death. Wills can help us know who these people were, how they lived and what was important to them during their sojourn here on earth. We can learn of their struggles and their successes. We can tell what their lives were like by reading through the lists of household items included in the inventories that are recorded.
And with stories like Addie’s bequest of the watch, we can also learn about ancestors’ personalities and how they expressed (or occasionally withheld) love for others through the final disposition of their belongings.
How a Will is Created
Before beginning probate record research, it is important to be familiar with the probate process and legal terminology associated with these records. It is estimated that, prior to 1900, about half of the population either left a will or was mentioned in one. Those who died having left a will are said to have died “testate.” Those who died without leaving a valid will died “intestate.”
A typical, legally-recognized will contains certain critical elements. It should be in written form and it must have signatures of the person leaving the will (“testator”) and witnesses, who attest to the validity of the document. A codicil is a document created by the testator to amend the will.
Once the testator dies, the will is presented to the judicial authority by a family member or executor/executrix (person appointed by the testator to see that his/her wishes are carried out), accompanied by a written application or petition for probate.
These petitions include names and addresses of the closest living relatives. The court then admits the will to probate and sets a hearing, providing an opportunity for interested parties to contest the will. The will is then recorded and the executor is given the authority to settle the estate. During this process, an inventory of the estate is made.
Some wills contain detailed information, regarding the testator’s final wishes. At times, these requests will shed light on relationships that might not otherwise be discovered. This was the case for a will on file at my local courthouse. Due to the nature of the requests made by the testator, I have changed the last name of the family to Smith. This wife was, obviously, upset with her husband and the circumstances of their marriage, providing clear details of her grievances for future generations.
“Since my husband has never made me a part of his family and has completely cut me out of ever living in Chihowie, Virginia [the husband’s hometown], or never provided me with a home or paid any of my bills and has broken all marriage contracts that we agreed to—I hereby decree that I be buried in Round Hill Cemetery at Marion, Virginia, where I own a lot—that my body or anything I own or possess will never be taken into Chilhowie or the Smith household.
My husband has never taken me into his own home, and furthermore stated, backed up by his nephew and his wife, whom he turned everything over to shortly after our marriage—that I would never own or live on a foot of the Smith ground, even though I have tried to build or buy or remodel a home in Chilhowie, Virginia, at my own expense.
“I give all books and material things pertaining to books to the Smyth County Library, Marion, Virginia, as I am sure that my family would not want anything to fall into the hands of anyone who has mistreated me.
“My husband has kept our marriage strictly on a time clock basis since his nephew and his wife moved back to Smyth County, and under their influence he comes at 6:30 or 7:00 p.m. (whichever is convenient to them) or later, and leaves promptly in the morning by 8:00 or 8:30 a.m., never calling during the day or show[ing] any sign of caring. He changed completely after they returned to Chilhowie to break up the marriage. Therefore, if I am still his wife, or otherwise, see that my wishes are carried out and that my remains and possessions remain in Marion.”
Where to Find Wills and Probate Records
The best place to search for a will is at the courthouse where your ancestor lived, if you can reasonably go there yourself.
Since the probate process is a function of state governments, the laws governing the maintenance of these records and their location will vary by state and should be researched before making a trip to the courthouse.
For example, in Virginia, probate records are maintained within the Circuit Courts and independent cities. In Massachusetts, probate records are found in county Probate Courts.
A useful resource for figuring out how U.S. probate records are organized state-by-state is free on the Ancestry.com wiki: Red Book: American State, County and Town Sources. Scroll down to click on the name of the state in question. Then go to the right side and click on the probate records link for that state to read about these records.
Once you have determined where the wills for your state/county are housed, the next step in the research process is to locate the Index for Wills. Even–perhaps especially–if you are unsure of the date of death for one of your ancestors, you may want to look through the index of wills (an example is shown here). Even when no specific death record exists, you may be surprised to find probate records that reveal the date of death, a list of heirs and more.
There will, most likely, be several index books, organized by year spans. These books serve as a compass, pointing you to any available probate records that may include your ancestors. The index is divided by devisor (the person making the will) and devisee (any person who is named in the will, as the recipient of property).
The research process will be incomplete if you do not conduct a search for your ancestors among the list of devisees. Even if you fail to find their names among the devisors, they could have inherited property from someone else.
Probate records include more than just the will of an individual. You may find letters of administration, lists of heirs, inventories, bills of appraisement, guardianships and other documents related to the settlement of an estate. In some counties, all these documents are found in the same collection. Other counties maintain these records in separate collections. It is important to understand the manner in which probate records are organized for your particular county.
The probate research process should not be rushed. Valuable records may be overlooked when time dictates the quality of your research. For this reason, it is important that you set aside ample time to comb through the probate records. If you find yourself confused about abbreviations or the location of records within the courthouse, there is usually someone in the records vault who would be happy to assist you. Never be afraid (or embarrassed) to ask for help.

Fortunately for many of us who can’t easily get to every ancestor’s courthouse, there are some wills available online on genealogy websites, including two of the genealogy giants, FamilySearch and Ancestry.com.
For example:
- Subscription website Ancestry.com has made it a priority to curate an enormous collection of wills and probate records from all 50 states. At last count, this collection has more than 170 million records—and they keep adding to it.
- The free FamilySearch.org hosts millions of probate records from the U.S. and around the world (click here to browse their probate and court record collections). Many of these collections are marked “browse-only,” which means they are not yet searchable by name online. You just have to page through them. Click here for instructions on reading browse-only records on the site (it’s not that difficult—and did I mention they’re free?).
Additionally, libraries or genealogical societies in your ancestor’s hometown or county may have books with abstracts from local wills or other resources related to local probate record research.
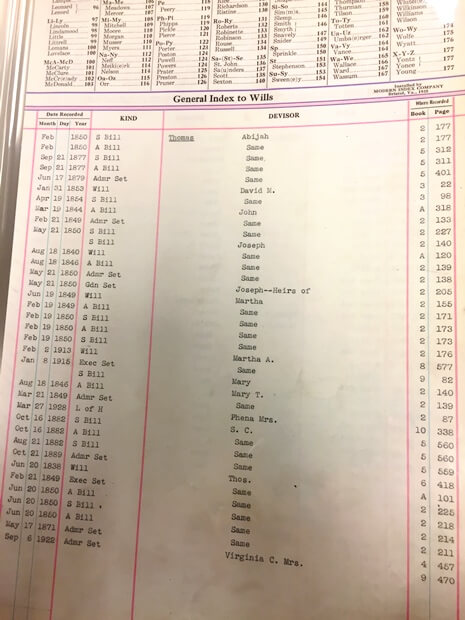
General Index to Wills
Well Worth the Effort
Finding the will of one of your ancestors is an amazing experience. Walking into the vault of a courthouse sometimes feels like walking into a time machine. As you read through the pages that tell of people who lived so long ago, you feel like for even just a small moment that you have gone back in time. You are sitting with them and hearing their stories whispered through the aging and brittle pages that have been left behind. They are all there just waiting to tell their stories. So take the opportunity to go to the courthouse and “meet” your ancestors through the one of the last—and perhaps one of the most revealing—documents they may ever have written: their wills.
Researching Wills and Probate Records: Your Next Steps
Take your genealogy research to the next level by planning a trip to a courthouse to retrieve records like wills and probate records. These articles and podcast episodes will help you get ready:
- Why you should be researching court records
- Success story: Genealogy research trip produced amazing family history find
- Premium Podcast Episode 128: Courthouse research tips (for Genealogy Gems Premium subscribers)
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links and Genealogy Gems will be compensated if you make a purchase after clicking on these links (at no additional cost to you). Thank you for supporting Genealogy Gems!

Margaret Linford is a professional genealogist who specializes in the Mid-South Region of United States research and has logged over 20,000 research hours. Born and raised in Virginia, she has enjoyed traveling the world, and now lives in her childhood hometown with her husband and children. She enjoys teaching her children about heritage, taking them along on research trips and serving as President of the Smyth County Genealogical Society.
Family History Episode 27 – Find Your Family History in Newspapers, Part 1
Listen to the Family History: Genealogy Made Easy podcast by Lisa Louise Cooke. It’s a great series for learning the research ropes and well as refreshing your skills.
Family History: Genealogy Made Easy Podcast
with Lisa Louise Cooke
Republished April 15, 2014
https://lisalouisecooke.com/familyhistorypodcast/audio/fh27.mp3
Download the Show Notes for this Episode
Welcome to this step-by-step series for beginning genealogists—and more experienced ones who want to brush up or learn something new. I first ran this series in 2008-09. So many people have asked about it, I’m bringing it back in weekly segments.
Episode 27: Find Your Family History in Newspapers, Part 1
Newspapers offer such a unique perspective on history in general, and our ancestors specifically. You can find everything from birth, marriage and death announcements, to school and club event, crime stories, land transactions, sports activities and just about any other activity that your ancestors were part of that made the news. So let’s get started and “Read all about it!”
In this episode, you’ll hear from Jane Knowles Lindsey at the California Genealogical Society. She is currently the president there and often teaches on this subject. Our conversation on newspaper research continues in next week’s episode!
Here are some take-away thoughts from this episode, along with some updates:
- Determine which newspapers existed for your ancestor’s hometown and time period. Look for ethnic and neighborhood papers, too. The most comprehensive U.S. newspaper directory is at Chronicling America. This site does let you search by language, ethnic background, labor group and more.
- Look for these newspapers at digitized newspaper sites, starting with the free ones. In the U.S., this means starting with Chronicling America and state digital newspaper project sites (search on the state name and “digital newspapers”). These sites came out of the government digitizing program mentioned in the show.
- Digitized newspaper searching is done with OCR (optical character recognition), which doesn’t pick up everything in tough-to-read historical print. Try searching with different spellings, a first name in a particular timeframe, or other people or terms that may have been mentioned.
- Ancestry has put lots of newspapers on their website—but not everything, and for only limited time periods. Notice what time period is covered for a specific newspaper. Ancestry has since launched Newspapers.com.
- If you’ve found the name of a newspaper that probably covered your family, but you haven’t found it digitized, search the name of the newspaper in your favorite web browsers. Most newspapers are on microfilm somewhere and web directories will likely list holdings. Also, some newspapers have also been indexed on USGenWeb or other sites.
- State archives and libraries are often a great resource for newspapers. Local libraries may have unique clippings files or scrapbooks.
- Several websites and databases now focus on obituary content. You can target a search for these.

Available at the Genealogy Gems Store
I loved this topic so much I ended up writing a book on it! How to Find Your Family History in Newspapers walks you through the process of finding and researching old newspapers. You’ll find step-by-step instructions, worksheets and checklists, tons of free online resources, websites worth paying for, location-based newspaper websites and a case study that shows you how it’s done.
6 Top Newspaper Research Resources
Some of the digital newspaper collections mentioned in the episode are available by library subscription, like The Early American Newspapers collection the and 19th century Newspaper Collection from The Gale Group. Check with your local library.
New England Historic Genealogical Society (by subscription only)
Episode 192
Genealogy Gems Podcast
Episode #192
with Lisa Louise Cooke
 Highlights from this episode:
Highlights from this episode:
- How to use Animoto, my favorite new tech tool for creating professional-looking slide shows and videos
- New Genealogy Gems team member Amie Tennant shares insights as she prepares for professional certification
- A listener shares a favorite genealogy database for finding recent relatives
- A listener uses DNA to connect adoptive and biological relatives?who were closer than she thought
- A segment from the Genealogy Gems Book Club interview with author Helen Simonson on The Summer Before the War
- News from Dropbox and a new initiative to capture the family histories of remote, indigenous populations
NEWS: Dropbox Improvement
New on Dropbox: Now when you share Dropbox content with someone, shared links will stay active even if you move or rename the file or folder.
Dropbox file-sharing tip: “If you ever want to unshare something you’ve already sent out (like to remove access to a sensitive document), it’s easy to disable an active link.” Just sign in to dropbox.com. “Click the link icon next to the file or folder, and click ‘remove link’ in the top right corner of the box that appears. You can also remove the link by visiting dropbox.com/links and clicking ‘x’ next to the file or folder.”
How to share folders on Dropbox
NEWS: MyHeritage and Tribal Quest
- TribalQuest.org
- FamilySearch Helping Preserve and Provide Access to African Records and Family Histories
- Ghana Oral Genealogy Project (on FamilySearch.org)
NEWS: New Premium Video
 Getting Started in Genetic Genealogy: a new video available to Genealogy Gems Premium website members by Your DNA Guide Diahan Southard
Getting Started in Genetic Genealogy: a new video available to Genealogy Gems Premium website members by Your DNA Guide Diahan Southard
Genealogy Gems Premium website membership: Click here to learn more
Click here to watch a free video preview
MAILBOX: Russ Recommends the U.S. Public Records Index
 Russ blogs at https://worthy2be.wordpress.com/
Russ blogs at https://worthy2be.wordpress.com/
Genealogy Gems Podcast episode 181: What to use while waiting for the 1950 census
Russ recommends the “U.S., Public Record Index, 1950-1993, Volume 1 and 2.”
“Volume 1 is far more interesting with more data. A search will return a Name AND Birth date, along with more than one ADDRESS, Zip Code and sometimes phone numbers.”
Ancestry’s description of its online database for Volume 1 says original data comes from public records spanning all 50 states, such as voter registration lists, public record filings, historical residential records and other household database listings.
- U.S. Public Records Index on Ancestry.com: Volume 1 and Volume 2
- Free partial version (1970-2009) at FamilySearch.org
- Another partial version (1970-2010) at MyHeritage
Thoughts about using the U.S. Public Records Index (some of these points come from the FamilySearch wiki):
Not everyone who lived in the U.S. appears in the index, and you’re more likely to find birth information for those born between 1900 and 1990. What you’ll find is primarily where someone lived, and often when they lived there.
It’s rarely possible to positively identify a relative in this index, since there’s limited information and it spans the entire country for up to a half century, and you can’t follow up on the record it comes from because the index doesn’t say where individual records come from. As Russ says, this is a great resource to use in combination with other records. It’s a similar concept to the way you might consult uncited family trees: great hints to go on and follow up with further research into verifiable sources.
When you find more recent listings, you can sometimes find telephone numbers for living distant relatives. The Family History Made Easy podcast has a 2-episode series (episodes 14 and 15) about cold-calling techniques for reaching out to distant relatives you don’t know.
MAILBOX: Katie on Cold-calling and Adoption and DNA
Katie blogs her family history adventures at McKinnon Ancestry.
Click here to read a blog post with her story and see more pictures that go with it.

INTERVIEW: Amie Tennant
 Amie Tennant is the newest member of the Genealogy Gems team. She contributes to the blog at www.genealogygems.com. She is also preparing to become a certified genealogist, which is a professional credential offered by the Board for Certification of Genealogists (BCG).
Amie Tennant is the newest member of the Genealogy Gems team. She contributes to the blog at www.genealogygems.com. She is also preparing to become a certified genealogist, which is a professional credential offered by the Board for Certification of Genealogists (BCG).
What have you learned in the process of preparing for certification?
“I think the biggest thing I have learned is the meaning of true exhaustive research. We talk a lot about that in our genealogy standards, but essentially, it is looking EVERYWHERE for EVERYTHING that might shed light on your research question.”
Why do you want to become certified?
I want a way to determine how well I am doing. A measuring stick of sorts.
What is the process like?
The process is the same for everyone. Once you have decided to become certified, you apply to the BCG. They send you a packet of information and you are “on the clock.” The clock is up in one year unless you ask for an extension. The portfolio you create consists of:
- Signing the Code of Ethics
- Listing your development activities (like formal coursework or enrichment activities);
- Transcribe, abstract, create a genealogy research question, analyze the data, and then write the research plan for a document that is supplied to you;
- Do those same 5 things for a document of your choosing;
- A research report prepared for another person.
- A case study with conflicting, indirect or negative evidence;
- A kinship determination project (a narrative genealogy that covers at least 3 generations)
- There is a lot of great free content on the BCG website: articles, examples, and skill-building activities.
GEM: How to Create Family History Videos Quickly and Easily
Visit our page on how to create family history videos which includes video tutorials and inspirational examples.
 BOOK CLUB: Interview excerpt with Helen Simonson,
BOOK CLUB: Interview excerpt with Helen Simonson,
author of
The Summer Before the War


Beatrice Nash is a bright, cosmopolitan young lady who has grown up traveling the world with her father. Now he’s gone, and she’s landed in the small village of East Sussex, England, where the locals aren’t entirely thrilled about engaging her as a female Latin instructor for their schoolchildren. She spends a summer fighting for her job, meeting a local cast of engaging eccentric characters (both gentry and gypsy) and trying not to fall for handsome Hugh. Then the Great War breaks out.
This novel follows Helen’s popular debut novel, Major Pettigrew’s Last Stand, which became a New York Times bestseller and has been translated into 21 languages. Genealogy Gems Premium website members can join us in June to hear our exclusive and fun interview with Helen Simonson.
GENEALOGY GEMS PODCAST PRODUCTION CREDITS:
Lisa Louise Cooke, Host and Producer
Sunny Morton, Contributing Editor
Vienna Thomas, Audio Editor
Additional content by Lacey Cooke, Amie Tennant
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links and Genealogy Gems will be compensated if you make a purchase after clicking on these links (at no additional cost to you). Thank you for supporting Genealogy Gems!
The Secret to Pairing FamilySearch and Pinterest for Family History
FamilySearch Family Tree plus Pinterest for family history adds up to cousin bait like you’ve never seen. Here’s a little-known technique to utilize both sites together for great results.
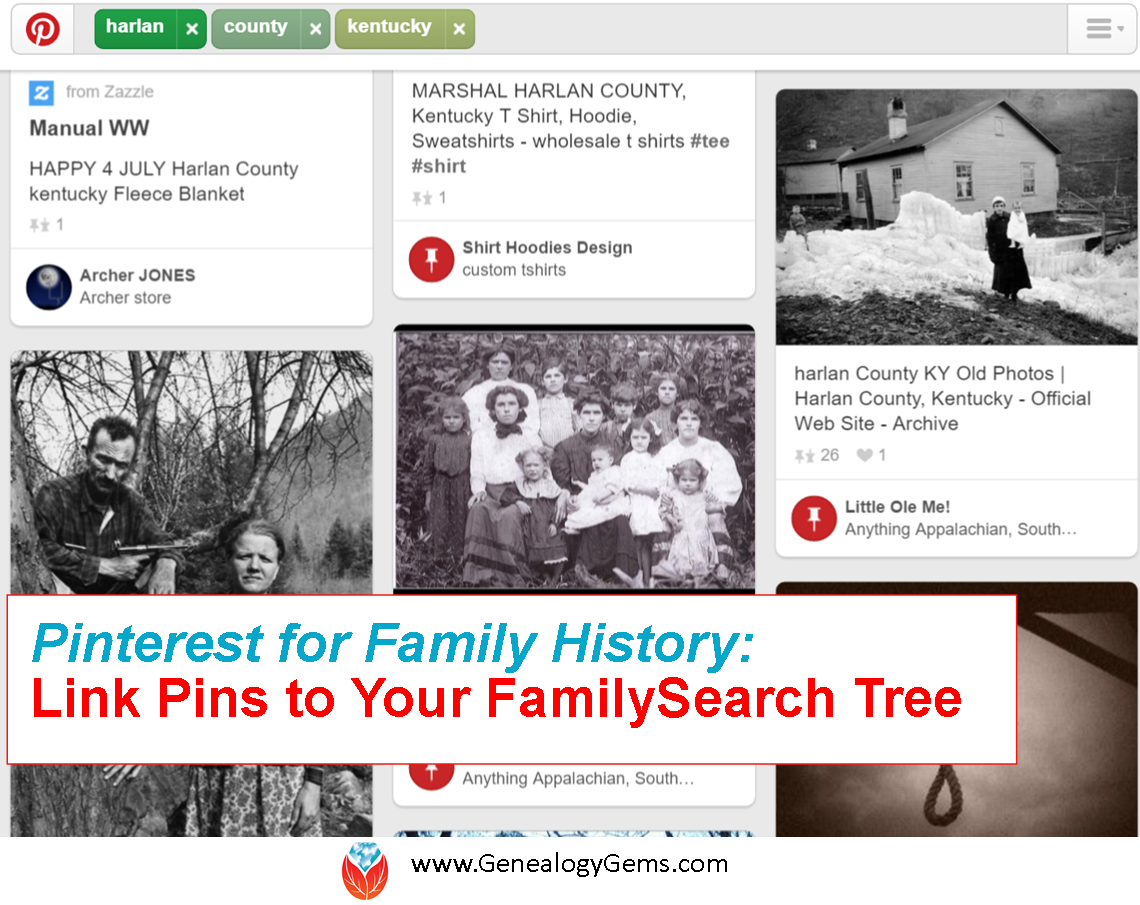
There is a little known secret: Pinterest and FamilySearch Family Tree can work together to reel in new cousin connections.
Pinterest is a free, online bulletin board where you can collect content that you find on the web. It’s a kick-back to the old days when we found pictures of our favorite home decor or recipes and tore out the pages of the magazine. Do you remember doing that? No longer do we need to tear out pages and file pictures and articles of our favorite things in old binders. You can use Pinterest to keep all of your items organized and accessible at the click of the mouse.
Pinterest is not a piece of software or something you download. All you need to do is go to www.pinterest.com and sign-up using your email or Facebook to create a free account.
FamilySearch Family Tree works similarly with their “Memories” section. The Memories section allows users to collect and store family photos, documents, stories, and even audio. But that is just the beginning! Pinterest provides you with a way to put these items to work for you. Photos, documents, and stories you post on a FamilySearch memories page can be pinned to your Pinterest board.
Why is this so groundbreaking, you ask? When potential cousins Google your common ancestor, the list of results will include your Pinterest board, like the search example below that finds my own Pinterest pins:

Then, when they click that great photo of grandma or the WWII story of great-grandpa on Pinterest, they are automatically directed back to your FamilySearch Family Tree where they can see your pedigree chart…for FREE!
(You don’t need an account to see, use, or search within the FamilySearch Family Tree. If you were to try this technique using images you have uploaded to a subscription site such as Ancestry, those clicking from Pinterest would simply land on the log-in page to Ancestry. Without a paid subscription, they go nowhere. How frustrating!)
How to Connect Your FamilySearch Family Tree with Pinterest Pins
1. If you haven’t already set up a Pinterest account, you will need to do that first.
2. Create a board specifically for the purpose of family history. I chose to create a board for each of the surnames that I’m actively researching. I would love to make some connections with other genealogists on these! “Bowser Family of Clark County, Ohio” and “Cole Family of Lee County, Virginia” are two examples. (Notice, I added a county name and state. I wanted to be sure I attracted people who searched by surname and/or place name.) Do not add any pictures to your boards yet.
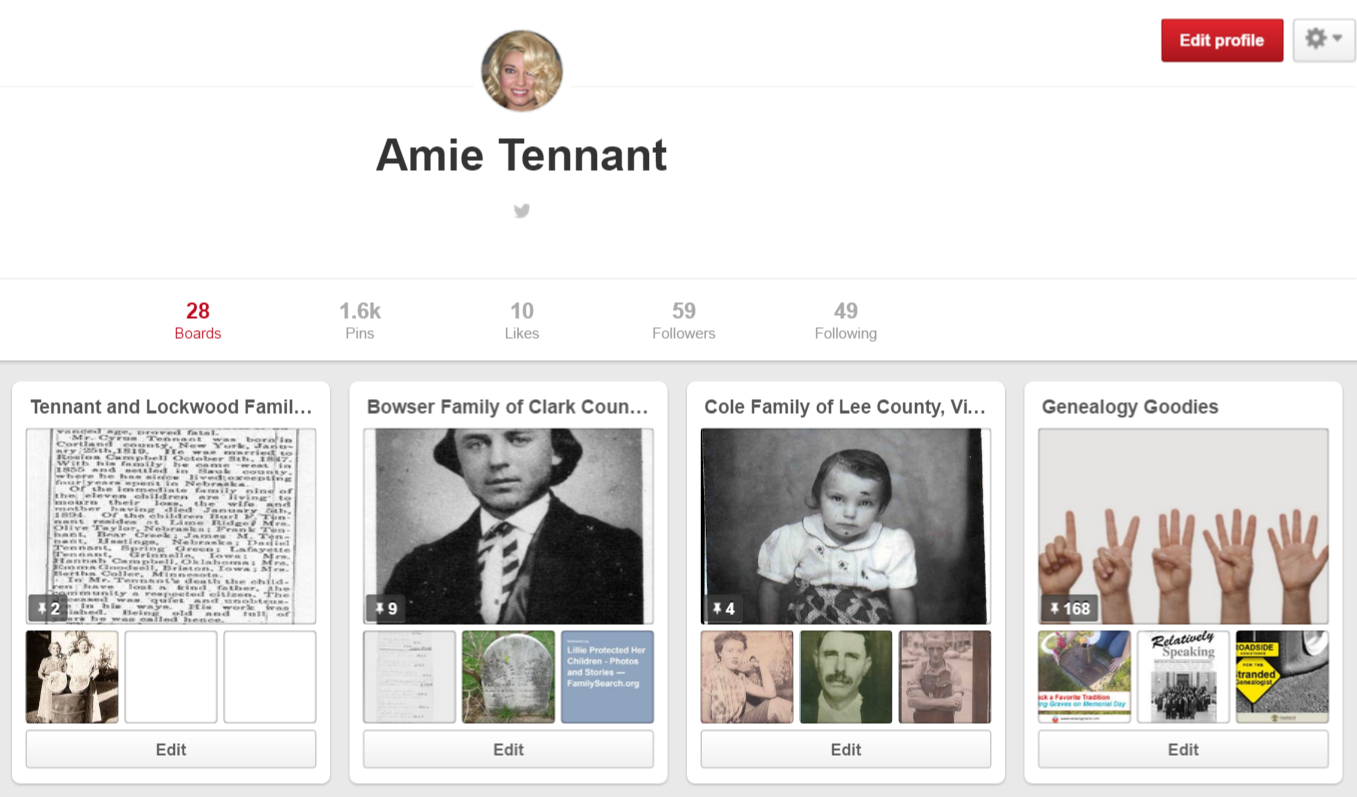
3. Create or log in to your free FamilySearch Family Tree with names and dates of your ancestors.
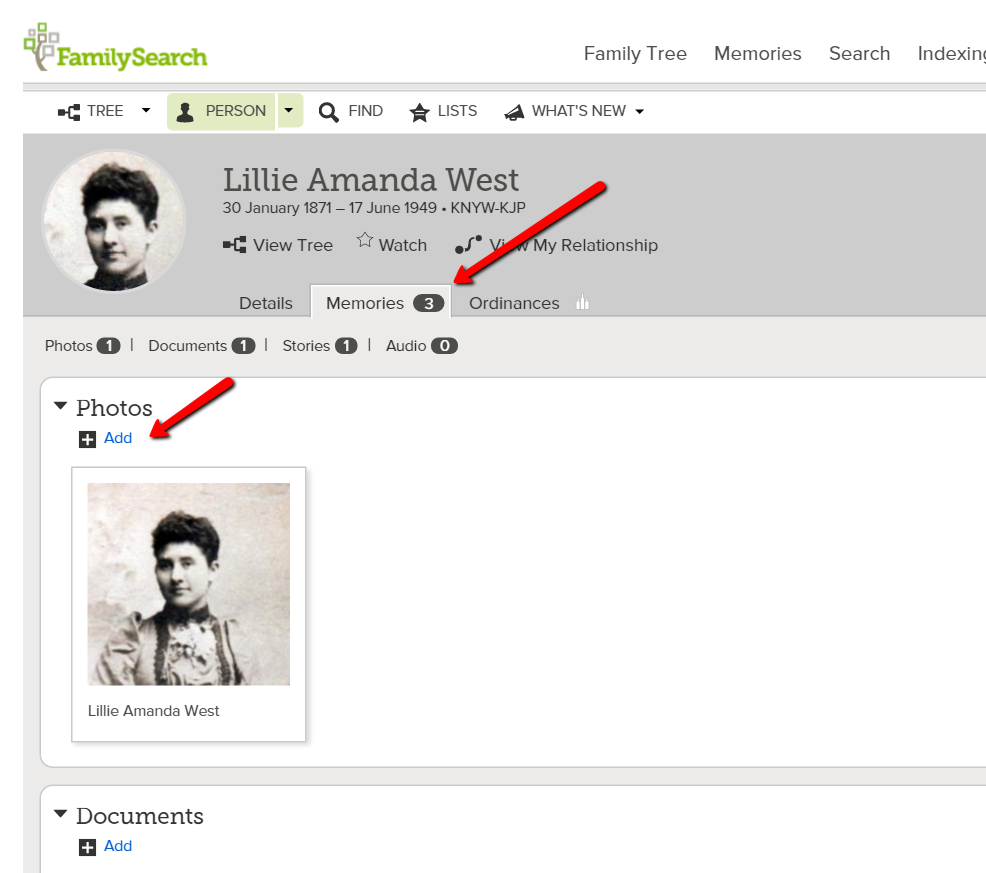
4. Click on an ancestor for whom you want to add a memory. At the “Person” page, click on “Memories” near the top. This will take you to the memory page where you will upload the photos, documents, and so forth for your specific ancestor.
5. Add a title and an accurate, thorough caption. An example of a title might be a full name or a story title like: “When Her Baby Died.” A caption needs to include more details: “Lillie Amanda West, Clark County, Ohio. Wife of George Henry Bowser and daughter of Edmund West and Lavina Wilson. Picture taken ca. 1897.”
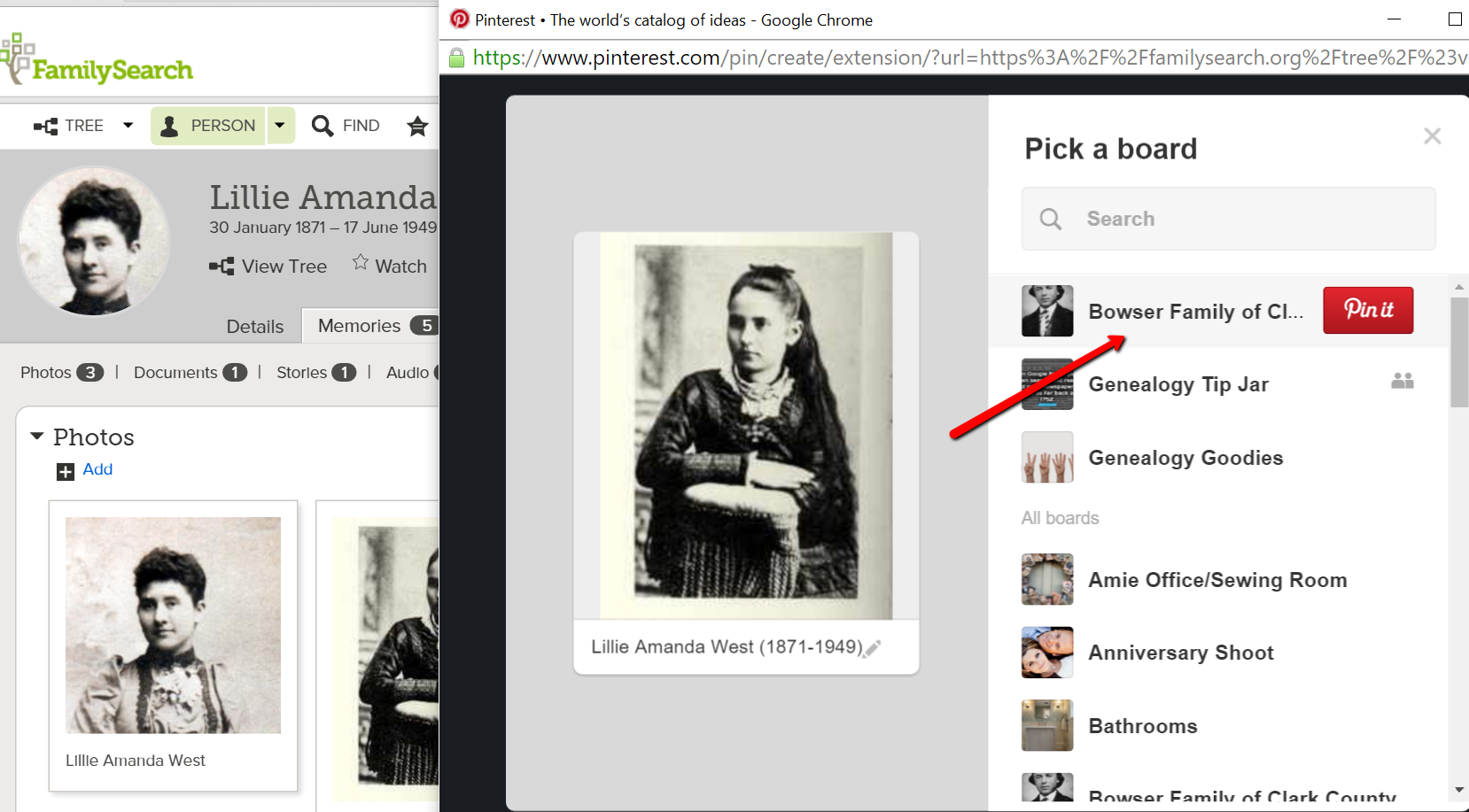
6. Once you have uploaded everything you wish with your titles and captions, go back to the FamilySearch Memories gallery page by simply clicking on “Memories” again. If you hover your cursor over a picture, document, or story you uploaded, a little “Pin It” box will pop up. (Important Note: FamilySearch reviews all items uploaded to the Memories section for inappropriate content. Because of this, you may have to wait a few minutes before your items are able to be pinned.) Now, click “Pin It” and follow the prompts to pin the item to the Pinterest board of your choice. You will need to copy and paste or create a new caption for your pin. Click the little pen below the picture to edit the caption. (Remember, this caption will be what you want to be Google-searchable, so pack it with names and words that you think your long-lost cousins might type into the Google search box when searching for those ancestors. (Need help with Google search terms? Lisa Louise Cooke’s book The Genealogist’s Google Toolbox, 2nd Edition is your go-to resource.)
Cousin connections often bring to light new and exciting pieces of your family’s story. Try using Pinterest and FamilySearch Family Tree today as cousin bait to find long-lost family members anywhere in the world.