by Lisa Cooke | Aug 13, 2015 | 01 What's New, Beginner, Blogs, images, Writing Family History
 More and more people are blogging about their family history. Here’s why!
More and more people are blogging about their family history. Here’s why!
When it comes right down to it, many of us want to write up our family stories, but we don’t really want to write or publish a 300-page book. Blogging your family history in short snippets is a perfect alternative! Why?
1. Its shorter, flexible format is much less intimidating for many people. You don’t have to lay out a book or fill hundreds of pages. You can write a little bit at a time, as your time and mood permit.
2. A blog is like your own family history message board. Every word you write is searchable by Google–which means others researching the same family lines can find and connect with you.
3. A family history blog can help bust your toughest brick wall. I’ve heard and shared countless stories here at Genealogy Gems from readers and listeners of how just “putting it out there” on a blog led to someone contacting them with a treasure trove of new information about their family tree.
4. Writing a narrative about your research will help you identify gaps in your research. Sometimes errors or bad assumptions you made will jump out at you.
5. Your kids and grandkids are (or will be) online. They will more likely want to read quick and easy stories on the go on their smart phones and tablets. Putting your research out there on a blog provides them with an easy way to digest the family heritage and subscribe to it, since blogs can be delivered to their email inbox or to a blog reader.
6. Because there are no excuses. You can start a blog for free. There are no rules, so you can decide how often and how much you write at once.
7. If you leave the blog online, it will still be there even when you’re not actively blogging. You will continue to share–and you may continue to attract relatives to it.
Resource:
Start a family history blog with this free series from our Family History Made Easy podcast (an online radio show)
Part 1: What to Consider when Starting a Genealogy Blog. The “Footnote Maven,” author of two popular blogs, talks about the process of starting a genealogy blog. She gives great tips for thinking up your own approach, finding a unique niche, commenting on other people’s blogs and more.
Part 2: Insights from Popular Genealogy Bloggers. We hear from two additional popular genealogy bloggers, Denise Levenick (author of The Family Curator and alter ego of “Miss Penny Dreadful” on the Shades of the Departed blog) and Schelly Tallalay Dardashti (author of the Tracing the Tribe blog).
Part 3: Step by Step on Blogger.com. How to create your own free family history blog on Blogger.com. Learn tricks for designing a simple, useful blog and how NOT to overdo it!
Final tips: Wrap-up and inspiration. In this concluding episode, learn how to add a few more gadgets and details to your blog; pre-plan your blog posts, publish your first article, and how to help your readers subscribe. You’ll also get great tips on how to create genealogy content that others looking for the same ancestors can find easily online.
 SHARE! Invite someone you know to start a family history blog by sending them this post. They’ll thank you for it later!
SHARE! Invite someone you know to start a family history blog by sending them this post. They’ll thank you for it later!
by Lisa Cooke | Mar 6, 2020 | 01 What's New, MyHeritage, Records & databases |
Here’s news we love to hear: the publication of a huge collection of historical U.S. city directories that has been two years in the making!

City Directories at MyHeritage
MyHeritage Announces US City Directories Collection
TEL AVIV, Israel & LEHI, Utah —
MyHeritage, the leading global service for discovering your past and empowering your future, announced today the publication of a huge collection of historical U.S. city directories that has been two years in the making.
The collection was produced by MyHeritage from 25,000 public U.S. city directories published between 1860 and 1960. It comprises 545 million aggregated records that have been automatically consolidated from 1.3 billion records. This addition grows the total size of MyHeritage’s historical record database to 11.9 billion records.
MyHeritage teams applied innovative technologies to produce this collection and make it as useful and easy-to-use as possible.
Machine-Learning and OCR Technology
The city directories in this collection were published by cities and towns all over the U.S., and each directory is formatted differently. To overcome the formatting differences and unify the structures, MyHeritage corrected errors in the Optical Character Recognition of the scanned directory pages, and then employed several advanced technologies, including Record Extraction, Name Entity Recognition, and Conditional Random Fields to parse the data. By training a machine learning model how to parse raw free-text records into names, occupations, and addresses, the company produced a searchable, structured index of valuable historical information.
As an important resource for family history research, city directories can provide fascinating new discoveries for anyone exploring their family history in mid-19th to mid-20th century America. The records contain valuable insights on everyday American life spanning the time period from the Civil War to the Civil Rights Movement.
Cities in the United States have been producing and distributing directories since the 1700s, providing an up-to-date resource to help residents find and contact local individuals and businesses.
What You Can Find in City Directories
The city directories provide a wealth of information regarding family life during those years, listing names, residences, occupations, and relationships between individuals.
Thanks to their exceptional level of detail, city directories can also provide a viable alternative to U.S. census records during non-census years, and can fill in the gaps in situations where census records were lost or destroyed. In 1921, a fire at the U.S. Department of Commerce destroyed most of the records from the 1890 census. Despite the loss of the records in the fire, much of the data can be reconstructed using the 1890 city directories on MyHeritage, which consist of directory books from 344 cities across the country, including 88 of the 100 most populated cities during that year.

Example: Thome Edison in US City Directories at MyHeritage
“We are harnessing new technologies to make family history research more accessible than ever before,” said Tal Erlichman, Director of Product Management at MyHeritage. “The use of machine learning to process the city directory records highlights the major strides MyHeritage is making in digitizing global historical records.”
MyHeritage automatically consolidated multiple entries for the same individual into one robust record that includes data from all the years an individual lived at the same address. This makes it easy to track changing life circumstances over the years. Users may be able to see more easily when their ancestors changed professions or got married, divorced, or were widowed — and MyHeritage automatically inferred approximate dates for such life events. Inferred dates contribute to improved matching between family trees and historical records on MyHeritage.
MyHeritage is currently indexing thousands of additional U.S. city directories that will be added to the collection in the coming months. This addition will include directories dating back to the late 18th century, as well as a large and unique set of directories from the late 20th century.
The online collection of U.S. city directories is now available on SuperSearch™, MyHeritage’s search engine for historical records. Searching the collection is free. A subscription is required to view the full records and to access Record Matches.
How to Search the Collection
Click here to go to MyHeritage. Under Research in the menu click Collection Catalog and then click Directories in the side menu.

City Directories at MyHeritage
Searching the U.S. City Directories is free, but a subscription is required to view the records.
Users with a Data or Complete subscription can view the full records including the high-resolution scans of the original directories, confirm Record Matches, extract information from the record straight to their family trees, and view Related Records for the person appearing in a historical record they are currently viewing.
Click here to go to MyHeritage.
by Lisa Cooke | Feb 27, 2017 | 01 What's New, DNA, Health History |
Exploring our family health history is just another reason to look forward to the future of DNA testing. As science advances and we find out more regarding the specific genetic code responsible for various nefarious outcomes in our health, we learn there is more in play than just our genetics.
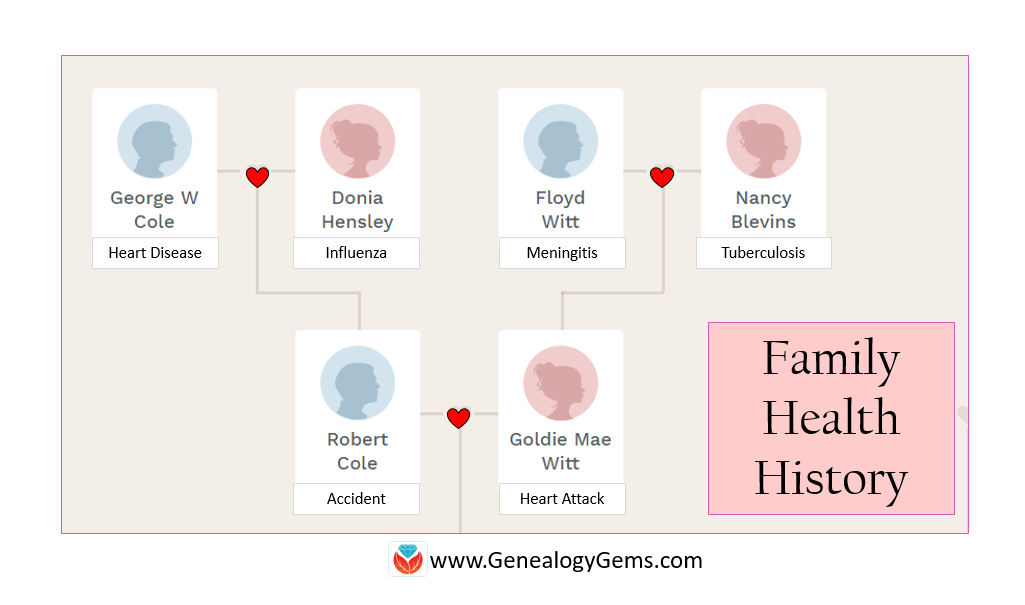
I recently read an article in the Wall Street Journal about a family who has been plagued with sudden deaths, ten in recent generations. Without warning, their hearts were stopping and no one knew why. That is until Daniel Wiggins died suddenly at the age of 29 and his family sought out a molecular autopsy. Becoming more accessible to researchers as the cost of running these tests drop, molecular autopsies allow a scientific team to analyze the DNA of the deceased, looking for genetic clues to the cause of death. In this case, the genetic sleuthing was able to turn up the perpetrator: a mutation that alters the electrical signals in the heart, causing it to stop. [Read more about this here.]
While this case was clear-cut and the gene was acting seemingly alone without an accomplice, researchers of this disorder say it only happens in 20% of cases. Which means, this devious genetic criminal has other methods we still haven’t tracked.
But for Daniel’s family, they can pursue genetic testing to determine if this specific culprit is lurking in their own genes. If found, they can take precautionary measures, like having a defibrillator installed.
Doing Our Part
Similarly, a family from Pennsylvania used their family reunion as a format for gathering family history and genetic information in order to arm its members with an action plan against a plague of cancer that is sweeping through their family. [See an article on this family here.]
Several members of the Shaffer-Peterson family have discovered a genetic test can alert them to possible pancreatic or skin cancer. Again, a gene affecting a very small number of melanoma patients was identified as the perpetrator of the Shaffer-Peterson family and has been given a 67% crime rate. This means that the chance of developing cancer if you have this particular gene is elevated by 67%.
Thankfully, melanoma is a particularly curable kind of cancer when caught early. This family has done their part in informing the family as a whole. And, they now have a sort of insurance plan that may protect the lives of their loved ones.
For both the Shaffer-Petersons and the family of Daniel Wiggins, genetic tests produce actionable results to those testing positive. There is something they can do to positively impact their health once they are aware of the presence or absence of these genes in themselves.
Environment or DNA?
Not all diseases or conditions can be attributed to our DNA. This past fall, after talking with my mother about kids and schedules, she added almost in passing, “Oh, by the way, they found another spot on my back, I am going to have it removed next week.” This is the third melanoma spot she has had removed in the past 5 years.
While my mom’s melanoma is less likely to be the result of a genetic abnormality and more likely linked to spending hours lifeguarding at the local pool, the fact she had melanoma was the sole reason I went to the dermatologist. My spot wasn’t cancer. I was just getting older. But, I am glad I went and I feel like knowing my health history has made me more aware of the measures I can take to improve it.
Tracking Your Family Health History

Diahan offers Genealogy Gems fans a discount on access to her series of videos on understanding DNA testing for genealogy. Click here to learn more.
For most people, molecular autopsies and DNA health tests are not easily available. Not yet. For those that are, there are hundreds of questions surrounding the kinds of genetic tests and the implications for both health and legal issues.
One thing is certain. In these cases, the common thread is family history. We need to know not only the dates and places of our ancestors lives and deaths, but also the stories behind them. Whenever possible, we need to track our health history, so we can identify any trends that our DNA might be trying to tell us.
If you want to start tracking your own health history there are plenty of free and subscription online tools to get you started. In particular, TapGenes was the winner of the 2016 Innovator Showdown at RootsTech. This online and app tool is designed specifically for your family health management.
You can also create your own alternate family tree. In this unique way, you can visually look at age-at-death, diseases, or other factors pertaining to your health. Read our article titled, “How and Why to Create an Alternate Family Tree.”
Learn More About Genetics and Genealogy
 This special bundle features the 3 new advanced DNA guides by Diahan Southard!
This special bundle features the 3 new advanced DNA guides by Diahan Southard!
Digital download also available.
Gedmatch: A Next Step for Your Autosomal DNA Test
Gedmatch is a third‐party tool for use by genetic genealogists seeking to advance their knowledge of their autosomal DNA test. This guide will navigate through the myriad of options and point out only the best tools for your genetic genealogy research.
Organzing Your DNA Matches
With over 2.5 million people in the possession of a DNA test, and most with match lists in the thousands, many are wondering how to keep track of all this data and apply it to their family history. This guide provides the foundation for managing DNA matches and correspondence, and for working with forms, spreadsheets, and 3rd party tools.
Next Steps: Working With Your Autosomal DNA Matches
This guide outlines what to do next to maximize the power of DNA testing in genealogy. With this guide in hand, genealogists will be prepared to take their DNA testing experience to the next level and make new discoveries about their ancestors and heritage.
by Lisa Cooke | Aug 20, 2016 | 01 What's New, DNA, Societies |

The Daughters of the American Revolution (DAR) accepts limited DNA evidence to prove descent from a Revolutionary War veteran. In my opinion, the DAR DNA policy is a little too limited. Here’s why–and what you can do.
Membership to the Daughters of the American Revolution (DAR) has been a holy grail for U.S. genealogists for 125 years. With its requirement of proof of a “lineal bloodline descendant from an ancestor who aided in achieving American independence” in three categories: birth, marriage, and death, as well as proof of Revolutionary War Service, membership is exclusive to those with an iron-clad paper trail.
That is, until 2014, when the DAR added DNA evidence to its list of acceptable documents proving a relationship to a Revolutionary War ancestor.
What does the DAR DNA Policy Accept?
The DAR only accepts one of the three forms of DNA testing which is the Y chromosome test, or YDNA. The YDNA traces only a direct paternal line, making it a great choice when trying to link living males with their Revolutionary counterparts. This YDNA is basically passed unchanged from generation to generation, making the modern day holder of the YDNA the proud owner of possibly exactly the same YDNA that fought the Redcoats. That’s pretty cool, don’t you think?
The DAR recently announced that to further help those wanting to use their YDNA as part of their application, they have formed a project at Family Tree DNA, the company that provides the YDNA testing. Projects are absolutely the best way to get the most out of your YDNA testing. There are surname projects, location projects, haplogroup (deep ancestral group) projects, and even special interest group projects, such as this one for the DAR.
While the results of the testing are only available to members of the group, the statistics page gives us an idea of the scope of this project. They currently have 1,242 total members and what looks to be about 430 YDNA tests completed (though it is admittedly difficult to tell based on the chart online.) This means if you think your paternal line may be a candidate for the DAR, you can have a representative of your line tested and compared to the group. If you find a match, you will have relative certainty that you do connect to that Patriot, and can then be more confident in your traditional research in pursuit of the necessary paper connections.
In April the DAR opened up project membership to include mtDNA and autosomal DNA. They will not be using these two kinds of DNA in their applications (yet), but hopefully this project will pave the way for the addition of those tests in the future (though, for several reasons, inclusion of these tests in the application process will be more difficult.)
Though, in all honesty, they have made the YDNA process difficult enough. Let’s say that you are actually able to trace down multiple generations to find a direct male descendant of your Revolutionary guy to be tested, an individual who is, the DAR mandates, “sharing your maiden name or your mother’s maiden name,” and you convince that unassuming relative to give up his saliva, you still are only half way there. The DAR guidelines also state that you have to have a second individual who is “a descendant of the same Revolutionary War ancestor through a different unbroken male lineage that has been previously proven on a DAR application…” (I added the emphasis here.)
A Practical Example of the DAR DNA Policy
OK, so let’s say you are a genealogical whiz and, let’s face it, you were lucky, and you find two such candidates and have them tested.
Well, the DAR tells us that those two men must match EXACTLY on the 37 YDNA markers tested. Now there is no telling when that YDNA might experience a mutation. So to me it seems a little unfair to require perfection. So it is possible, that even after all the work of finding the right guys to be tested, the test itself may work against you, as even one difference is enough to keep this YDNA off of your application, at least for now.
So while I applaud the DAR for using YDNA testing at all, and for spearheading a special interest project at Family Tree DNA, the reality is that the limitations of direct paternal line genealogy and the requirements of testing make it unlikely that very many will be able to take advantage of the YDNA in their DAR applications.
However, there are a few things you can take away from this article now:
- First, collect those DNA samples whenever you can, especially for key relatives, like your paternal line and the oldest living generation (whose DNA is less likely to have experienced any mutation.)
- Second, keep your research paper trail strong. Nothing in the near future of the genetic genealogy industry tells us that distant relative connections (like to your Revolutionary War ancestor) will be provable by DNA alone.
- And third, definitely look at crowd-sourced studies for your particular DNA. Those surname, location, haplogroup, and special interest group projects I mentioned from FTDNA are just some of the ones that might help your research—or that you could use to help someone else’s. I’ve talked about these studies before: click here to read about them.
My Complete DNA for Genealogy Research Guide Series
I am Diahan Southard, Your DNA Guide, and the author of a series of genetic genealogy quick guides. My guide called Y Chromosome DNA for the Genealogist is the perfect tool to help guide you through the testing and analysis process. Click here to learn more about this guide and here for all of my guides, or click here to learn more about my series of how-to videos, also available to Gems fans for a special price.
Thanks for sharing this post with your genealogy friends who do DNA research (especially those who may have Revolutionary War ancestors!)
 More and more people are blogging about their family history. Here’s why!
More and more people are blogging about their family history. Here’s why! SHARE! Invite someone you know to start a family history blog by sending them this post. They’ll thank you for it later!
SHARE! Invite someone you know to start a family history blog by sending them this post. They’ll thank you for it later!





 This special bundle
This special bundle