Making Family History Accessible for the Visually or Hearing Impaired
Making your family history accessible to your visually or hearing impaired relatives may require a little extra work. But the effort can mean making your genealogy discoveries more available and vivid for EVERYONE–now and in the future. Let these ideas help you!...Getting Help with a Genealogy Brick Wall

My Genealogy Brick Wall in Eastern Europe
Reviewing My Work
Legacy Tree Genealogists assigned me to a Project Manager, Camille Andrus, who reached out to discuss what I already knew and what I wanted to learn.

Camille Andrus, Project Manager, Legacy Tree Genealogists.
I requested their Discovery Research Plan, for which they just provide guidance about what record collections to consult and what methods or strategies to try. That way I can do the research myself (which I like doing!). I also asked Camille if she would write about her research process so I could share it with you. Here’s what she sent me:
We looked over Lisa’s work, and upon initial inspection everything looked great.
She had looked in the gazetteer (now available digitally at www.meyersgaz.org with maps of the area) and Lutheran church records. (Editor’s note: Learn more about using Meyers Gazetteer in the Genealogy Gems article 5 Expert Tips for Using Meyers Gazetteer for Your German Genealogy.)
She had searched the records for her ancestor’s supposed home parish. When that failed to yield results, she had done a partial radial search, searching records in several adjacent parishes. Check. Check. Check. She was following all of the integral steps, but still not having success.
What had she missed? What had she done wrong? The short answer — nothing. Her research was impeccable, and she was looking in the right places.
Getting Around the Genealogy Brick Wall
Camille had three specific suggestions for where to look next for great-grandpa Gus. At the end, she also offered some helpful reassurance. Here’s what she said:
1. Civil registration in East Prussia
After closer inspection of what Lisa had already tried, we saw several opportunities we could still pursue.
We looked up civil registration records available through a Polish archive, since what was East Prussia is now part of modern Poland.
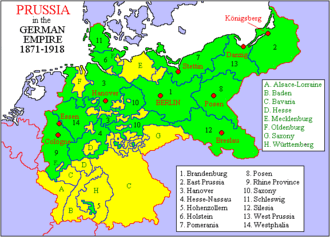
German civil registration in East Prussia began in October of 1874 and is an important resource for researching individuals from this area.
The Meyers Gazetteer confirmed that Kotten (where her ancestor was from) belonged to Kreis Johannisburg in the German Empire province of East Prussia. This village belonged to the Monethen (Kreis Johannisburg) civil registration district.[1]
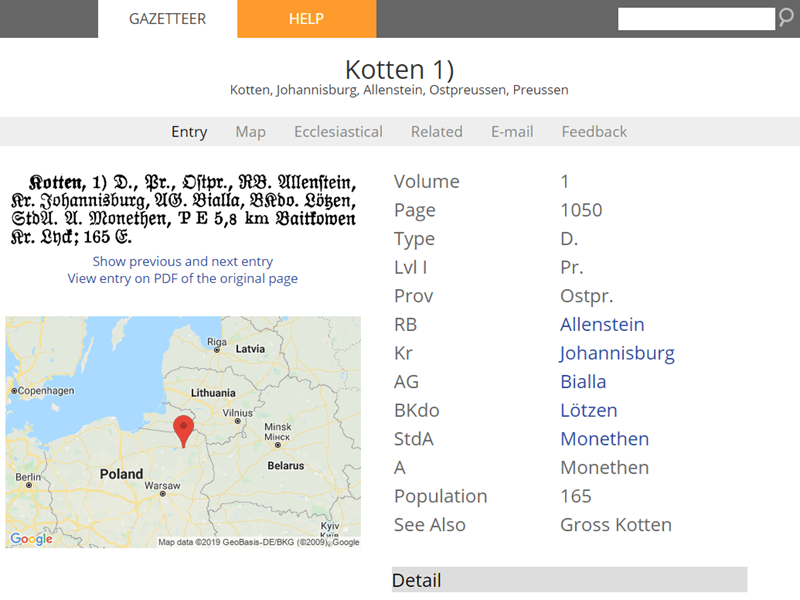
Using Meyers Gazetteer to find German places
The Olsztyn State Archive inventory lists several birth, marriage, death, and family books for the Monethen Civil Registration Office, but the books only cover the late 1930s and early 1940s. The whereabouts of the registers covering 1874 through the early 1930s are unknown.
It appears as though the records covering this time period have been lost or destroyed. This situation is not unusual for East Prussia, in general due to the numerous conflicts that have occurred in the area over time.
2. Church records in East Prussia
Another major resource for German genealogy research is church records.
The Meyers Gazetteer database noted that Protestant residents of Kotten attended church in the nearby town of Baitkowen (Kreis Lyck).[2]
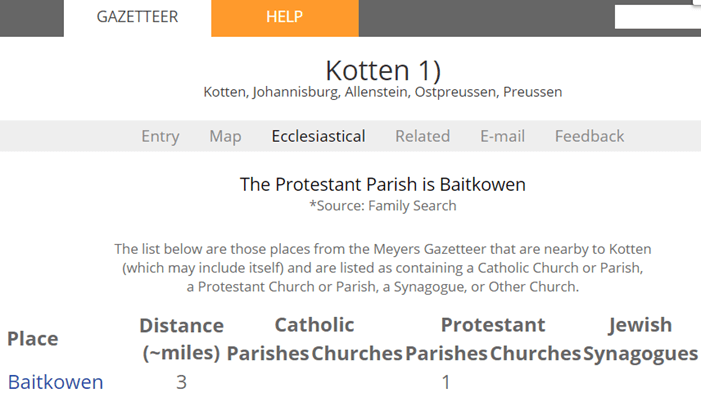
The church book inventory for Baitkowen revealed that the Protestant parish was established in 1891, a decade after the ancestor Gustav Sporowski was reportedly born. No sacramental registers for this parish are known to be extant. It should be noted that the Baitkowen parish was created from parts of the Lyck, Ostrokollen, and Drygallen parishes.[3]
The Protestant parish of Drygallen (Kreis Johannisburg) has extant baptismal records which are available on microfilm at the Family History Library for the years 1730-1821 and 1844-1875.[4] Lisa indicated that she had reviewed these files but did not find any Sporowskis.
The Lyck Landgemeinde (the congregation for parishioners living outside city limits) was founded in 1704, but there are no known extant baptismal records for this parish after 1808.[5]
3. Following up on clues
A key clue came from Lisa’s notes. She mentioned that Gustav and his wife were married in Lütgendortmund, a town hundreds of miles west of Gustav’s birthplace, before ultimately immigrating to the United States.
Louise at the time of her marriage
Luckily, their marriage occurred in a time when civil registration had been instituted. A search for marriage records showed there are civil registration records available for the town of their marriage, which are available at an archive in Detmold.
We were able to advise Lisa that further research should pursue this record, as it may list information about his parents.

The Protestant Bartholomew Church in Lütgendortmund, Dortmund, Germany. Von Smial – Eigenes Werk, FAL. Click to view.
The Bottom Line
The bottom line is if you feel stuck, it’s not necessarily because you are doing anything wrong.
Review the “checkboxes” of your research plan to ensure you aren’t missing any integral clues.
If after final review of methodology concludes that you’ve pursued every avenue, the lack of success may be attributed to gaps in the records or perhaps they have been lost completely. Other times all you need is one clue to put you back on the right track.
This is exactly the kind of advice I was hoping for: expert and specific!
Hire a Professional Genealogist for a Quick Consult or Project
If you have hit a genealogy brick wall in Eastern Europe (or anywhere else) and would like a professional to review your work, I recommend contacting Legacy Tree Genealogists. They have helped many clients like me to solve their family history mysteries, and would love to help you as well!
You can hire a genealogist like Camille through their Genealogist-on-Demand™ service. Receive research strategies and advice from a professional genealogist during your 45-minute consultation that will help you continue your own research. Your virtual genealogy consultation will allow you to have your questions answered in real-time by an expert–all from the comfort of your own home!
Need even more help? Here’s an exclusive offer for Genealogy Gems readers: Receive $100 off a 20-hour research project using code GGP100. To learn more about Legacy Tree services and its research team, visit https://www.legacytree.com.
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links and Genealogy Gems will be compensated if you make a purchase after clicking on these links (at no additional costto you). Thank you for supporting Genealogy Gems!
[1] Search the Meyers Gazetteer, Kotten, Johannisburg, Allenstein, Ostpreussen, Preussen, http://meyersgaz.org/place/11050078, accessed August 2017.
[2] Search the Meyers Gazetteer, Kotten, Johannisburg, Allenstein, Ostpreussen, Preussen, http://meyersgaz.org/place/11050078, accessed August 2017.
[3] Ostpreussen, Genealogische Quellen, Kirchbuchbestände Kreis Lyck, ev. Baitkowen (Baitenberg), http://wiki-de.genealogy.net, accesesed August 2017.
[4] Ostpreussen, Genealogische Quellen, Kirchbuchbestände Kreis Johannisburg, ev. Drigelsdorf (Drygallen), http://wiki-de.genealogy.net, accesesed August 2017.
[5] Ostpreussen, Genealogische Quellen, Kirchbuchbestände Kreis Lyck, ev. Lyck Stadtgemeinde, http://wiki-de.genealogy.net, accesesed August 2017.


