by Lisa Cooke | Dec 5, 2016 | 01 What's New, Research Skills, Travel
We love the ease with which we can search online, but a genealogy research trip can offer exceptional and unique rewards. If you have been apprehensive about visiting a courthouse or archive, follow our 4 step plan for a successful genealogy research trip that could lead to your own amazing discovery!

By J. D. Cress [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons
In my genealogy world, if an answer can’t be found on one of my favorite genealogy website repositories (like FamilySearch, Ancestry, or Findmypast) then a quick Google search usually does the trick.
However, we new genealogists of the Internet era may be banking on the fact that “everything” we need is online. This is obviously not true. In fact, many local libraries and archives are under-staffed and under-funded making digitizing of their holdings difficult. This is why making a genealogy research trip is a really good idea.
The Unprepared Genealogy Research Trip
Several years ago, I made my first research trip. I was woefully unprepared. On a whim, I drove three hours on a weekday to “go to the courthouse.” I arrived at lunch time…and it was closed for an hour. Sigh. However, a nice receptionist sugg ested I go to the local public library just down the street.
ested I go to the local public library just down the street.
When I arrived at the tiny corner building, I asked at the circulation desk for the history department. She seemed a little taken back, but said, “We have a little room in the basement with some local history and genealogy things.” Note to self: not all libraries are large enough for a “history department.”
In the basement room, no one was on duty, but a nicely printed instruction sheet of what was available and how to use their files laid on the table. “I guess I just dig in,” I thought, and off I went.
Though this was my first genealogy research trip, it proved to be very fruitful. In a scrapbook simply titled “Walls Family,” I found a Xerox
copy of an article from an 1874 newspaper. In this article, my fourth great-grandmother (Susannah Harmarson Walls) had been interviewed because she was the oldest living woman in the township. Her interview began, “I was born in Delaware. The exact year, I do not know, but I suppose I will be 86 years of age on the 16th of July next. My father’s name was Levin Harmarson. He died when I was only three years of age. My mother’s name was Mary Woodard.”
The interview included the story of her mother re-marrying, the family leaving Delaware for Wheeling, Virginia, and she marrying her step-brother there. Then, they traveled on into Scioto County, Ohio. She named each of her eleven children and their spouses.
The information in this one interview was particularly helpful. Before this, we had no idea when or where Susannah and Levi married, and finding the spouses of their children had proved difficult!
Though this was an amazing find, I wonder what other records, items, or photographs I might have dug up had I prepared ahead of time. Perhaps, I would have had time to dig more into their microfilm holdings, archived pictures, atlases, or even had time to go to the local cemetery.
The Prepared Genealogy Research Trip
Fast forward several years and I am making much more prepared genealogy research trips. Get the most from your next genealogy research trip by following these 4 important steps:
1. Run a Narrative Report. Start creating your genealogy research trip plan by printing out a narrative report of your targeted family line. This can be done with the reports feature found in genealogy database programs like RootsMagic.
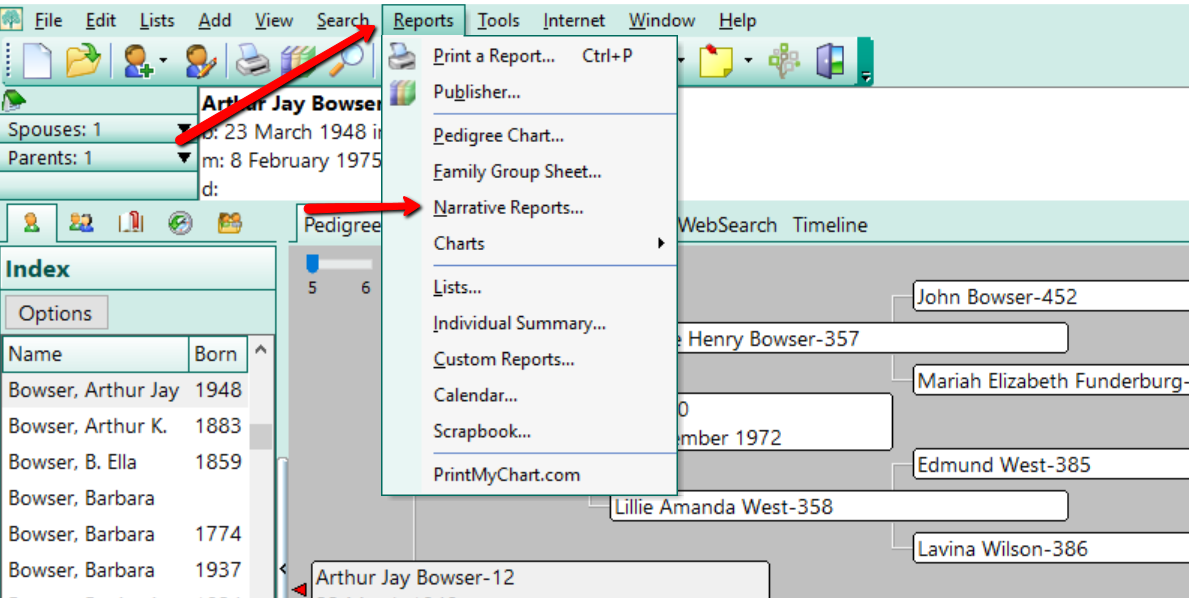
2. Look for holes in your research. Carefully read through the report looking for holes in your research or where you may be missing a source. In this case, a “hole in your research,” may be the missing marriage date of a couple, or the missing birth date of a child. Circle these “holes” and make a list of what the needed piece of information is to correct it and where you can find it.
Example: Clark County, Ohio. Need a death date for Edmund West. County didn’t keep death records that early. Likely died between 1830-1840. Check probate record books, estate files, tax records, cemetery records, and tombstones at Wilson Cemetery.
Maybe you have a birth date, but no source. A source is the proof of a particular fact. For example, a good source for a birth date is a birth register or even a marriage record. If you are lacking sources for your genealogy facts or are not sure how to begin sourcing your genealogy, learn more about that here.
3. Decide what repositories you will need to visit. After creating your list, determine where these items are held by asking yourself important questions, such as: Will I need to visit the courthouse, a library, an archive, cemetery, or all the above? Which location will produce the most results? Should I visit the archives first, or the courthouse?
4. Contact each repository ahead of time. Finding out the days and times when each of these places is open before you go is a must! Try to pick a day when all, or most, of the places are open so that you can get a lot done. If this isn’t possible, consider making an extended stay overnight to accomplish your goals.
Keep in mind that not all websites are up-to-date. Just because the library says it is open from 10 to 5 every day but Sunday on the webpage doesn’t necessarily mean that is still the case. Always call each establishment to verify days and hours of operation.

Remember, there are newspapers, maps, documents, and pictures just waiting to be uncovered. By thinking about what you want to achieve while on your trip and what information you need to find and where, your genealogy research trip can be a successful one. Happy hunting!
More on Genealogy Research Trips
Still feeling unmotivated to get on the road, read or listen to these features for inspiring tips to make a courthouse records research trip in your near future!
Courthouse Records Research Trip
Premium Podcast Episode 126 – Road Trips for Genealogy
Premium Video – Using Evernote to Create a Genealogy Research Plan
by Lisa Cooke | Apr 21, 2016 | 01 What's New, Conferences
NGS 2016 live streaming options have expanded this year–and include FREE Genealogy Gems classes you can watch on your mobile device wherever you  are.
are.
Can’t make it to NGS 2016? You’re not the only one! You can still join the fun, though–and for free. Lisa Louise Cooke will be live-streaming several lectures from the Genealogy Gems booth “theater” in the Exhibit Hall at NGS from May 4-7, 2016.
Streaming classes are scheduled as follows (so far–more may be added). The time zone for the conference is Eastern standard.
Wednesday, May 4:
9:45 am: Diahan Southard, 3 Reasons to Test Your DNA
10:15 am: Diahan Southard, AncestryDNA Help
1:15 pm: Lisa Louise Cooke, Beginner Evernote
1:45 pm: Lisa Louise Cooke, Advanced Evernote
Thursday, May 5:
12:45 pm: Lisa Louise Cooke, 3 Cool Tools for Newspapers
1:45 pm: Diahan Southard, FTDNA’s Family Finder Help
Friday, May 6:
1:15 pm: Lisa Louise Cooke, Create Google Earth Map Overlays
Saturday, May 7:
12:15 pm: Diahan Southard, Genetic buy medicine online philippines Genealogy & Health
1:45 pm: Lisa Louise Cooke: Genealogy Protection with Cloud Backup
How to watch the free NGS 2016 live streaming sessions from Genealogy Gems
Lisa will stream again through the free Periscope app, which she used for RootsTech 2016. Get the Periscope app in Apple’s App Store or Google Play,  sign up for a free account, and follow Lisa Louise Cooke to tune in. Sign up for notifications in Periscope, and your phone will “ping” when she starts streaming.
sign up for a free account, and follow Lisa Louise Cooke to tune in. Sign up for notifications in Periscope, and your phone will “ping” when she starts streaming.
Click here for the full list of NGS 2016 free Genealogy Gems booth classes, being taught on-site by Lisa Louise Cooke and Diahan Southard from Genealogy Gems and their partners from Family Tree Magazine. More streaming sessions may be added. Be sure to like and follow the Genealogy Gems Facebook page for last-minute additions!
FREE: Watch Classes that Streamed Live from RootsTech 2016
How to Use Your Mobile Device for Genealogy
Powerful Google for Genealogy Search Strategies
by Lisa Cooke | Nov 17, 2015 | 01 What's New, Ancestry, DNA
It’s no surprise to find another DNA post in the #8 spot on our Top 10 genealogy blog post countdown. The topic: understanding your AncestryDNA matches.
In this post, Genealogy Gems resident DNA expert Diahan Southard takes on a confused question sent in by a listener, who didn’t understand why certain people were showing up in her AncestryDNA results.
This post explains SO beautifully a couple of key concepts:
- the difference between your AncestryDNA genetic matches and the DNA Circles/New Ancestry Discoveries that pull from both your genetic results and your family tree; AND
- three reasons someone may show up in your AncestryDNA matches as a New Ancestry Discovery–and which one of those scenarios actually helps your research.
Since running my own autosomal test through AncestryDNA a few months ago, I find myself coming back repeatedly to Diahan’s series of posts to help me  better understand and use those results. I know I’m not alone, since three of Diahan’s DNA posts made our Top 10 this year! (We covered #10 yesterday.)
better understand and use those results. I know I’m not alone, since three of Diahan’s DNA posts made our Top 10 this year! (We covered #10 yesterday.)
Click here to read the above post, and click here to find a list of all DNA-related posts on our genealogy blog.
 If you’ve done your homework and decided that an AncestryDNA test is what should be next for your family history research, thank you for purchasing one by clicking here. Your purchase supports the free Genealogy Gem blog and podcast. (Thank you! YOU are a gem!)
If you’ve done your homework and decided that an AncestryDNA test is what should be next for your family history research, thank you for purchasing one by clicking here. Your purchase supports the free Genealogy Gem blog and podcast. (Thank you! YOU are a gem!)
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links and Genealogy Gems will be compensated if you make a purchase after clicking on these links (at no additional cost to you). Thank you for supporting Genealogy Gems!
by Lisa Cooke | Jul 21, 2018 | 01 What's New, Trees |
Is the tail wagging the dog in your genealogy research? Resist the temptation to jump at each hint and online family tree. Instead, take the lead in your own research and follow the scent of each clue with genealogical best practices. Here’s how…
Almost as soon as you start adding information to your family tree on any of the major genealogy records sites (Ancestry, MyHeritage, Findmypast) you will start getting suggestions. These suggestions are known by a variety of names on the various sites, such as hints, Shaky Leaves, Smart Matches, record matches, etc. No matter what they’re called, they can be a great way to quickly make even more progress in growing your family tree.
There’s an old saying: you get what you pay for. In the case of hints, you have technically paid for them by subscribing to the genealogy website’s service. However, you didn’t pay for them through careful research following solid genealogical methodology. You haven’t yet verified their accuracy, or in the case of suggested online family tree, verified their sources.

Online family trees are one of the most common types of hints you’ll receive. And it’s no wonder: there are billions of names entered in online family trees*, so your tree is very likely to match some of them.
However, with all those matching trees there are bound to be problems. If you’ve been wondering about the reliability and usability of other people’s online family trees being recommended as hints, you’re not alone. Keep reading to learn more about using information gleaned from other’s online family trees.
The question of trusting online family trees
Brenda is a Premium eLearning member, and she wrote me recently with a question about using online family trees:
“I’m just getting back into my genealogy research after 10 years of not having time. It seems that research has completely changed to online work! I’m getting [hints that link to other] family lines, but can I trust them?”
And this related question comes from Douglas:
“Weekly, I get emails with family tree matches, asking me to confirm the match. My problem is not with the matching but with when I dig into their tree, the source for their information is another tree. That info may be a clue but I learned way back that the info needed to be backed up by good primary and sometimes secondary sources, not what somebody thought was right. Info that I entered in my tree years ago and found subsequently to be wrong is still hanging out in a dozen trees. What is your opinion?”
My guess is that at some point you’ve had some of the same questions as Brenda and Douglas. Am I right? Well, even though it’s exciting to find someone who’s already built a family tree that includes your ancestors, it’s important to proceed with caution. Avoid the temptation to “graft” or copy the tree onto your tree.
That’s not to say you should ignore online trees. Instead, let’s discuss how reliable they are and how to use them wisely and responsibly.
How to use online family trees as hints
Douglas has stated the problem accurately. The researchers behind those tantalizing trees may have made mistakes or copied unfounded information without verifying it. Unfortunately, this is a very common occurrence.
Once copied to one tree, incorrect information can easily get picked up by others and copied over and over again. And the problem is made worse because the more it’s copied, the more unskilled researchers may assume it must be accurate because they see everyone using it. It’s a vicious circle indeed!
Mistakes can happen in online family trees
Approach every online hint and tree as a clue – a lead – to be considered and scrutinized. You won’t know the accuracy of it for sure until you review the research and verify the sources. That being said, the next logical questions would be “how in the world will I have enough time to verify all of the information in all of these trees?”
The answer is, you don’t.
Instead, do your own genealogical research first, one person and one generation at a time. Work from the present generation backward and learn everything you can from known and trusted primary and secondary sources. If this idea sounds new to you, I strongly encourage you to start listening to my Family History: Genealogy Made Easy podcast. It’s free, and available here on my website, as well as through all major podcast apps. If you’re new to genealogy or returning after a long spell, this podcast will cover the basics in genealogical research and help you get on track.
 It’s easy to let other people’s online trees give you a false sense that you are quickly and easily building your own family tree, but it’s just not true. A tree worth having is a tree worth researching. Don’t let the tail wag the dog here. Follow the proven genealogical research process, and then tap into online family trees when you need a fresh new lead.
It’s easy to let other people’s online trees give you a false sense that you are quickly and easily building your own family tree, but it’s just not true. A tree worth having is a tree worth researching. Don’t let the tail wag the dog here. Follow the proven genealogical research process, and then tap into online family trees when you need a fresh new lead.
Automated record hints and matches
On genealogy websites, you’ll get two types of automated hints or matches. The first is for other people’s trees, which we’ve already discussed. The second is for historical genealogical records.
In order to deliver the historical record hint, the website has compared the data on your tree with the data available in the transcriptions of their records. Since many people share the same name and other distinguishing characteristics like birth dates, it’s important to look at each record closely and carefully.
Review both the record transcription and the digitized image of the document (when available), keeping in mind that not all the useful genealogical data is always transcribed. And in the process of transcribing, errors may have been made.
You first want to evaluate whether this document pertains to your relative. Next, you will need to determine what else it adds to your knowledge of them. Compare what that document says to what you’ve already learned about your family. Watch for multiple, specific pieces of evidence that support or are consistent with what you already know.

Genealogy Giants guru Sunny Morton says that “record hints on Genealogy Giants FamilySearch and MyHeritage are especially known for a high degree of accuracy; Ancestry.com’s are generally pretty good, too, but the site is clear about reminding you that these are just hints. I don’t have data on how accurate Findmypast hinting is, but I do know that they’ve been adding more records to the pool of records they hint on, and that’s also good.”
 After reviewing all the record hints you’ve received, conduct additional searches yourself for records about each ancestor. Use the same process described above to scrutinize and evaluate each record.
After reviewing all the record hints you’ve received, conduct additional searches yourself for records about each ancestor. Use the same process described above to scrutinize and evaluate each record.
Remember that even a digitized record hosted on one of the major websites can have transcription, spelling, or other errors, and sometimes you’ll have to make judgment calls. There’s no substitute for your brain! And there’s no substitute for carefully verifying and documenting every discovery as you go.
Next steps for using hints and trees wisely
By using hints for online family trees and historical records as leads when needed rather than the main path to follow will help you build an accurate family tree.
We are here to help you take control of your family tree and your research every step of the way. For specific information about reviewing record hints, read Getting started on Ancestry.com.
When you do find errors in someone else’s tree, here’s some sound advice for How to approach someone about errors on their family tree.
And finally take a moment to read Don’t lose control when you post your family tree online.
If you’re a Genealogy Gems Premium eLearning member like Brenda, I suggest Genealogy Gems Premium Podcast episode 152. It features my audio interview with Sunny Morton on take-home strategies for using hinting tools at the Genealogy Giants.
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links and Genealogy Gems will be compensated if you make a purchase after clicking on these links (at no additional cost to you). Thank you for supporting Genealogy Gems!
by Lisa Cooke | Feb 4, 2015 | 01 What's New, Ancestry, Book Club, DNA, Genealogy Gems Podcast, Genealogy TV, Google, Italian, Who Do You Think You Are?
 Are you ready for a hearty dose of genealogy edu-tainment? It’s all there in the newest episode of the free Genealogy Gems podcast: a genealogy television celebrity, a best-seller for our new Genealogy Gems Book Club title and an industry insider peek at Ancestry’s DNA products.
Are you ready for a hearty dose of genealogy edu-tainment? It’s all there in the newest episode of the free Genealogy Gems podcast: a genealogy television celebrity, a best-seller for our new Genealogy Gems Book Club title and an industry insider peek at Ancestry’s DNA products.
Since it’s the beginning of the year, a lot of television shows are ramping back up (like WDYTYA in March). Genealogy Roadshow on PBS will it be back with new episodes and a new addition to the panel of hosts: professional genealogist Mary Tedesco. She joins Lisa in this episode to talk about her experience on the show and about Italian research, her specialty.
 Did you hear about our new featured book for Genealogy Gems Book Club? It’s the internationally best-selling novel Orphan Train by Christina Baker Kline! Tune in to the episodes or click to the show notes to learn more about the book and why I chose it for our virtual book club. And don’t forget the best part of our book club: the author will join us for an exclusive interview! The interviews are fun even if you haven’t read the book, and fantastic if you have. That interview is coming up in May.
Did you hear about our new featured book for Genealogy Gems Book Club? It’s the internationally best-selling novel Orphan Train by Christina Baker Kline! Tune in to the episodes or click to the show notes to learn more about the book and why I chose it for our virtual book club. And don’t forget the best part of our book club: the author will join us for an exclusive interview! The interviews are fun even if you haven’t read the book, and fantastic if you have. That interview is coming up in May.
DNA Guide Diahan Southard also makes an appearance on the January Genealogy Gems podcast episodes. She offers a frank insider’s opinion of what’s going on with AncestryDNA and Ancestry.com’s DNA Circles feature. Stay up-to-date in this fast-moving and fascinating aspect of genealogy with Your DNA Guide on Genealogy Gems!
Finally, you’ll hear about Lisa’s newest project. Available by popular demand is the revised and updated 2nd edition of The Genealogist’s Google Toolbox!


 ested I go to the local public library just down the street.
ested I go to the local public library just down the street.



 are.
are.

 better understand and use those results. I know I’m not alone, since three of Diahan’s DNA posts made our Top 10 this year! (We covered
better understand and use those results. I know I’m not alone, since three of Diahan’s DNA posts made our Top 10 this year! (We covered 


 It’s easy to let other people’s online trees give you a false sense that you are quickly and easily building your own family tree, but it’s just not true. A tree worth having is a tree worth researching. Don’t let the tail wag the dog here. Follow the proven genealogical research process, and then tap into online family trees when you need a fresh new lead.
It’s easy to let other people’s online trees give you a false sense that you are quickly and easily building your own family tree, but it’s just not true. A tree worth having is a tree worth researching. Don’t let the tail wag the dog here. Follow the proven genealogical research process, and then tap into online family trees when you need a fresh new lead.
 After reviewing all the record hints you’ve received, conduct additional searches yourself for records about each ancestor. Use the same process described above to scrutinize and evaluate each record.
After reviewing all the record hints you’ve received, conduct additional searches yourself for records about each ancestor. Use the same process described above to scrutinize and evaluate each record. Did you hear about our new featured book for Genealogy Gems Book Club? It’s the internationally best-selling novel Orphan Train by Christina Baker Kline! Tune in to the episodes or
Did you hear about our new featured book for Genealogy Gems Book Club? It’s the internationally best-selling novel Orphan Train by Christina Baker Kline! Tune in to the episodes or 