by | Feb 26, 2014 | 01 What's New, Ancestry, Beginner, FamilySearch, MyHeritage, Trees
 As you may have already noticed, a lot of websites these days host millions of family trees: MyHeritage.com, Ancestry.com, FamilySearch.org, Geni.com, FindMyPast.com, Archives.com and more. There are virtual forests and forests of family trees out there! How can you find a tree that includes your family? How can you be sure it’s yours? How do you know that what you see is accurate?
As you may have already noticed, a lot of websites these days host millions of family trees: MyHeritage.com, Ancestry.com, FamilySearch.org, Geni.com, FindMyPast.com, Archives.com and more. There are virtual forests and forests of family trees out there! How can you find a tree that includes your family? How can you be sure it’s yours? How do you know that what you see is accurate?
Get started with these 7 Steps: How to Find Your Family Tree Online:
1. Choose a site from the list above and create a free log in.
Which should you choose?
- FamilySearch.org is the only one that offers totally free access to all user-submitted family trees as well as the historical records that can help you with your research. However, the other sites offer a variety of free access options, especially to user-submitted trees.
- MyHeritage is known for its international user base (check out its user map here) and multi-language access.
- Some sites have different portals that specialize in records from different countries. For example, Ancestry.com (with a U.S. focus) owns Ancestry.ca for Canadian genealogy, Ancestry.co.uk for the United Kingdom and Ancestry.com.au for Australian records. Similarly, FindMyPast.co.uk (U.K. focus) also hosts FindMyPast.com (U.S.), FindMyPast.ie (Ireland) and FindMyPast.com.au (Australia). Check out additional sites for specific countries (including non-English-speaking) here. If your family recently immigrated, look for a site about “the old country.’ If you have pretty deep roots in your current country, or you’re not sure, pick a site that specializes in your current home.
2. Enter the name of one of your relatives in the Search bar.
Each site files its family trees a little differently: some with historical records and some separately. Search trees at FamilySearch here. On Ancestry.com, look under the Search option for Public Member Trees. Enter names of your relatives, along with any other details you know (like a birth date and place or a spouse’s name). Try different combinations, sometimes using the person’s first and middle name, trying a maiden name, entering a nickname, etc. Increase your odds of finding people by entering a range of years (like 1880-1890) for a date and a more general place, like a state, rather than the name of a little town. If you get too many results, enter more specific information.
Which relative(s) should you choose?
- One who is deceased, if possible. Records about living people may be restricted for some places (but not all).
- If possible, one with a relatively unusual name. They may be easier to spot.
- One you know several things about: a full name (including maiden for women), dates and places of birth, marriage and death; burial place; where they lived during their lifetime; names of their spouse(s), sibling(s) and/or child(ren).
- One who lived as long ago as possible, to increase the chance that someone has posted a tree. But a grandparent is a great starting point, if that’s as far back as you know. If your grandparent is still alive, ask them their parents’ names, and start with your great-grandparent.
- Need to learn more about your relatives first? Read this article on how to gather information about your family.
3. Click on results labeled as “family trees.” Are they “yours?”
Browse the search results. Do any of these names and details look familiar? Everything doesn’t have to be a perfect match for a tree to include your roots. Sometimes different information is handed down through different branches of a family. Sometimes people get their information from sources that don’t match yours. Sometimes people just guess or patch together parts of different family trees without looking closely to see if they’re right.
Tech tutorial: What exactly are you looking at when you look at a family tree online? Before the days of internet genealogy, researchers organized family history findings on their home computers in one of several specially-designed software programs. These programs could generate .GED files (often referred to as GEDCOMs) that would allow researchers using different software to share their findings. Many people have now uploaded their GED files to genealogy sites like the ones we’re talking about–or they’ve just built a family tree from scratch right on the site.
4. Evaluate the accuracy of what you find.
The best way to judge the accuracy of a family tree without researching it yourself is to see what proof is offered. Do you see any records mentioned (like footnotes) or attached to the tree? Common records include tombstone images; government or church vital records (birth, marriage or death records) and census listings. Do you see photos attached? Photos may indicate the submitter has access to family records or albums (bonus!).
If a tree mentions lots of sources, it’s more likely to be accurate–at least for the pieces of information that are sourced. If a tree doesn’t have sources, it doesn’t mean it’s wrong, it just means you don’t know if it’s right.
Sometimes you’ll find a “branch” on a tree that goes back many generations without a single source mentioned. Beware! Sometimes these branches are just copied from other trees. This may particularly be true if a branch is connected to a royal line. Royal lines are well-documented in history and some people have created family trees with the hope of running into royal relatives. These connections may not have been thoroughly researched–they might just represent “wishful thinking.” Again, look for sources.
5. Optional step: reach out to the submitter of promising-looking family trees.
Some sites allow you to contact them through confidential email routed through the site (you may have to purchase a subscription first). You might contact a submitter to meet a possible cousin, share information you have or ask for more details about what they posted. If you contact them, be polite–don’t open with “you got my grandfather’s birthday wrong” or you may never hear back. You may not hear back anyway, if the submitter is no longer researching, their email changed or they have passed away.
6. Google your surname along with the phrase “family tree” or “genealogy.”
See if any personal websites pop up with your family tree (or other family history information) in them. Evaluate the information by looking for accurate details (as far as you know) and lots of sources mentioned. Look for an “About” or “Contact” page to learn more about the submitter of this information.
7. Verify it yourself.
Wandering through forests of online family trees may give you the urge to create your own tree. An accurate, and sourced tree! If so, good for you. Keep reading the articles suggested below to learn how to get started!
Up next, read:
Get Started: How to Find Your Family History for Free. Perfect for the beginner!
Explore the Genealogy Gems website for more tools, tips and resources that can help you put together your family’s “bigger picture.”
Sign up for our free e-newsletter and receive my FREE ebook on using Google to find your family history.
Check out my step-by-step Family History podcast for beginning genealogists.
Post an Online Family Tree. Listen to a podcast episode (or just read the show notes) on how to post your own family tree online.
by Diahan Southard | Sep 16, 2014 | 01 What's New, Ancestry, Trees
If you’re an Ancestry.com user, you’ve seen those “shaky leaves.” They are automated hints generated when Ancestry.com thinks a historical record or tree matches an individual on yours.
Are you getting the most out of your Ancestry.com shaky leaf hints? Check out this video on YouTube–then keep reading!
In a nutshell: look at all the hints. Then keep searching.
According to the Ancestry Insider blogger, hints are only provided for the top 10% of Ancestry records.
I asked our Genealogy Gems source at Ancestry.com about this. He did clarify that this means the most popular 10% of collections, which accounts for “a majority of the records.” But he also comments, “Hints are not meant to be an exhaustive method to flesh out all of the records for your ancestors. People should always search as well as use hints.”
After checking all the hints, I routinely find a LOT more by then searching records from an individual’s profile.
Search from the profile rather than the main search screen so some of the other data you’ve already found (like dates and relationships and locations) will be included automatically in the search parameters. I think searching from the individual profile also makes it faster to attach records to your person once you’ve found them.
Click here to hear how one woman used Ancestry.com hints to discover a tree for the biological mother who abandoned her when she was five. You’ll also learn her inspiring message about how moving past her mother on her family tree has helped her move on with her life.
by Lisa Cooke | Aug 16, 2017 | 01 What's New, Ancestry, Trees |
Are you worried about access to your online tree if you let your Ancestry.com subscription lapse? The tree should still be there. But take these steps to be sure your Ancestry family tree remains accessible and secure–along with the records you’ve attached to it.
What Happens if Your Ancestry Subscription Expires
Many people start researching their genealogy with an Ancestry subscription. They build their family tree on the web site, adding details about their relatives.
Then they sift through Ancestry’s billions of historical records and add hundreds or even thousands of new names, dates, relationships and other facts to their family trees. Along the way, they attach records to each ancestor as evidence of what they’ve learned.
All of this adds up to a unique family tree that is precious to your family.
However, it is very common for the busyness of life to call them away from their genealogy research for a while. This is what happened to Genealogy Gems reader Beverly. She wrote to me, concerned about what will happen to all her hard work on that Ancestry tree:
“I have been a member of Ancestry.com for a long time and have worked on several trees. I love to work on my genealogy but lately have not had time. Can I drop my membership and still retain my trees? I plan to get my membership back at a later day. Right now I am wasting $20 a month.”
Beverly, I hear your pain!
We all go through busy seasons. It’s easy to cringe at the thought of paying for genealogy website subscriptions we aren’t currently using.
But the idea of losing all our progress on those web sites if we let our subscription lapse is worse. Your Ancestry subscription has not only included your online family tree, but also all of the records that you found and attached to that tree.
I did a little research along with Sunny Morton, Genealogy Gems Editor and our resident expert on the “Genealogy Giants” websites” (Ancestry, FamilySearch, Findmypast and MyHeritage). Here’s what we can tell Beverly and everyone else who is wondering what will happen to their family tree and all that research if their Ancestry account expires:
According to Ancestry, the answer is yes, you can still access your trees with your login credentials after your subscription lapses. The most important thing is that you don’t delete the tree or the account altogether.
Ancestry continues to host people’s trees because they want our tree data to share with others, and to give people a reason to come back!
But be aware that if you do not renew your Ancestry subscription, your account will revert to a free guest account. (Your user name and password will remain the same.) This means that you will not be able to access most of Ancestry’s historical records, including the ones you’ve already attached to your trees. And I say “trees” because many people have multiple family trees on Ancestry to be concerned about.
To see the historical genealogy records that you have attached to an ancestor in your online tree, click on a person in your family tree, and then click Profile:
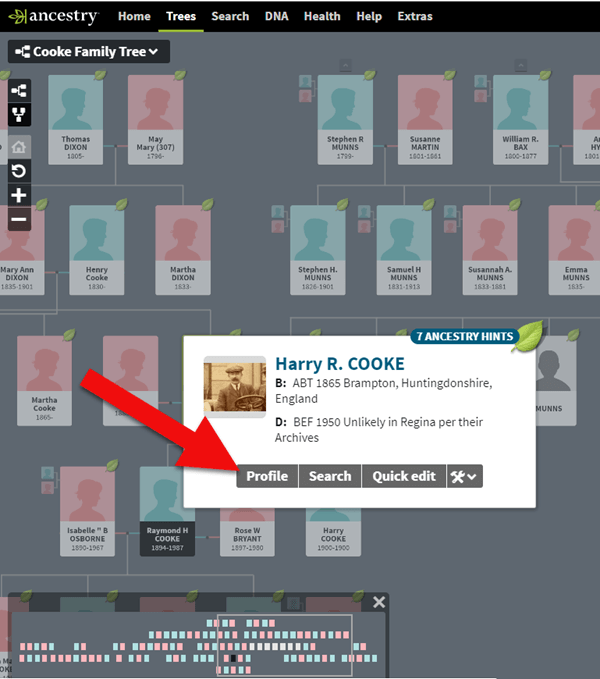
How to find genealogy records attached to a person in your Ancestry tree.
You will be taken to their profile page where you will see the genealogical sources you have attached.
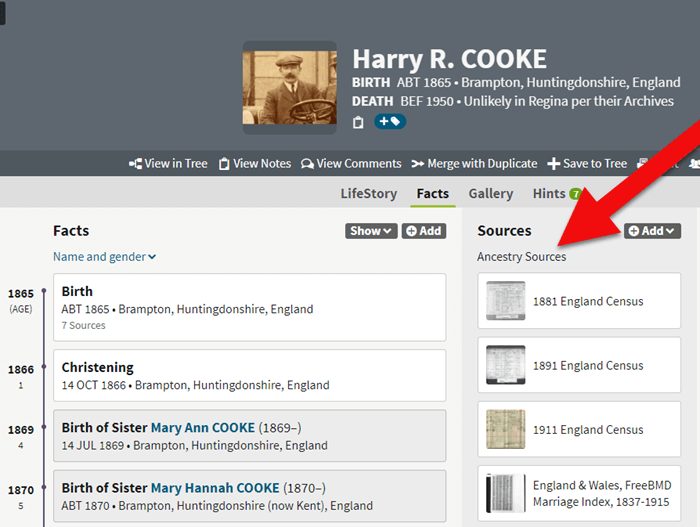
If your Ancestry account expires you can’t access records attached to your tree.
These are records that you will not be able to access when your subscription expires.
If Your Ancestry Subscription Expires: Tree Preservation Strategy
If you plan to let your Ancestry.com subscription lapse for a while, but you want to continue to work with your online trees, consider taking these steps:
1. Download a copy of every record.
The first thing to do is download a copy of every record that you’ve attached to your ancestors’ individual files on Ancestry.com.
You can do this by opening the image of the record, clicking on the Save/Saved button at the upper right, and clicking Save to your computer. I suggest doing this even if you don’t foresee letting your subscription go in the near future.
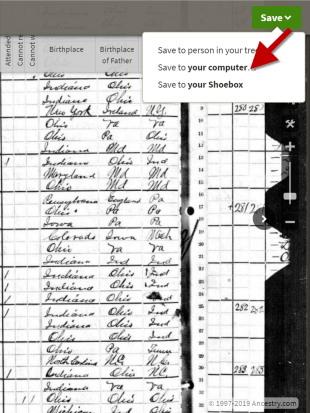
Saving a document to your computer from Ancestry before your subscription expires
2. Save each record in an organized way on your computer.
I recommend using a consistent system to organize these, which I explain in the free Family History: Genealogy Made Easy podcast, in episodes 32-33. (Genealogy Gems Premium website members have access to a 2-part video tutorial on organizing their hard drives.)
If you don’t have a consistent way to organize these document images, you’ll soon become overwhelmed with files that all sort of look the same and you won’t be sure what year they are or which ancestors they pertain to without opening each one!
You may be wondering “What about cloud storage options, such as Google Drive or Dropbox?” These type of cloud storage solutions are ok too. However, I recommend using these platforms more as temporary or backup storage or to share with relatives, rather than as your primary storage.
A better alternative would be to invest in cloud-based backup for your home computer. I use Backblaze personally and for my business.

3. Download copies of your Ancestry.com trees.
Click here for instructions; it’s really easy.
Yes, Ancestry does continue to maintain your trees, but what guarantees do you have?
Data loss does happen even on big websites, and sites change their practices and policies sometimes. If that happens, you could lose all the information you’ve carefully added to your tree.
4. Start using computer software for your “master family tree.”
Don’t just keep your family tree online where you don’t have complete control.
A “master family tree” is your most complete, up-to-date version of your tree (or trees, if you build separate ones for separate family lines).

Keeping your master tree on your own computer keeps all your tree data at your fingertips without any subscription required. Having one master file matters even more once you start sharing your tree on other websites or with relatives.
I use RootsMagic, and that is why I happily agreed to them sponsoring my Genealogy Gems Podcast. It works for Mac and the PC.

I like its affordability: there’s a free version you can try for as long as you like, and the full software will cost you the same as about 90 days of access to Ancestry.com.
RootsMagic also has solid relationships with the major genealogy sites: it now syncs with your trees on Ancestry.com and FamilySearch.org, and you can research records on MyHeritage.com and Findmypast.com.
RootsMagic has tons of advanced features to help you create family history charts, books, and reports, and a great user support community online.
Learn More about Ancestry and the Other Genealogy Giants
Keep up with news and changes on the “genealogy giants” websites with our ongoing coverage of Ancestry.com, FamilySearch.org, Findmypast.com, and MyHeritage.com here.
Disclosure: this post recommends carefully-chosen products and services for which we receive compensation. Click here to read my full disclosure statement, and thank you for supporting the free content we provide at Genealogy Gems.
 As you may have already noticed, a lot of websites these days host millions of family trees: MyHeritage.com, Ancestry.com, FamilySearch.org, Geni.com, FindMyPast.com, Archives.com and more. There are virtual forests and forests of family trees out there! How can you find a tree that includes your family? How can you be sure it’s yours? How do you know that what you see is accurate?
As you may have already noticed, a lot of websites these days host millions of family trees: MyHeritage.com, Ancestry.com, FamilySearch.org, Geni.com, FindMyPast.com, Archives.com and more. There are virtual forests and forests of family trees out there! How can you find a tree that includes your family? How can you be sure it’s yours? How do you know that what you see is accurate?







