by Lisa Cooke | Oct 29, 2016 | 01 What's New, Brick Wall, Research Skills |
Another brick wall…busted! We all have trouble spots in our family history research. Sometimes, we just need a little help breaking through. Here’s a tried-and-true method for using the genealogy FAN club principle to overcome brick walls in your family history research from guest author Amie Bowser Tennant.

A FAN club stands for Family, Associates, and Neighbors. Using the FAN club principle is a process in which genealogists identify a list of people (family, associates, and neighbors) that lived and associated with a given ancestor. By researching these other people, you may flesh out some new hints for your own research. Ultimately, identifying our ancestors FAN club is an effective tool for overcoming brick walls in genealogy research.
Renowned genealogist and author Elizabeth Shown Mills, coined the phrase “FAN Club” for genealogical purposes. She points out the significance of not only searching records for an ancestor’s surname, but also paying attention to documents about the ancestor’s “FAN Club” (Friends, Associates, Neighbors). Historical information, she says, is like real estate: the true value of any piece of information is unknown until it is put into community context. Learn more in Elizabeth’s “QuickSheet: The Historical Biographer’s Guide to Cluster Research (the FAN Principle).”
Step 1: “F” Stands for Family
Searching out other family members may prove helpful. Like in the case of Michael Knoop of Miami County, Ohio, I noticed there was another man in the county named Jacob Knoop. What was even more unique is both Michael and Jacob were born in New Brunswick. How unusual, I thought! Two men with the same last name, both born in New Brunswick, living in a small, farming area in Ohio! They had to be related, and they were. Jacob was Michael’s older brother.
Because I was having trouble finding when Michael had come to America, I traced Jacob instead. I located the passenger list with Jacob’s name on it and in doing so, I viewed all the passengers and found Michael, their mother, and lots of siblings!

Image above: Creating a FAN club with Family
In the case of Catherine Fearer Coddington, wife of James Coddington, I was having difficulty finding who her parents were. By searching for other Fearer individuals in the area, I discovered a biographical sketch on a John Fearer, Jr. Historical Encyclopedia of Illinois, Volume 2, reads:
“In 1836[,]John Fearer [Jr.] brought his family to Illinois. From Wheeling, West Va., the journey was made entirely by water. A landing on the Illinois soil was made at Hennepin. James Coddington, from near the Fearer’s old home in Maryland had already settled north of Princeton, in Bureau County, and later married John Fearer’s sister Catherine. The family found a home at Coddington’s until Mr. Fearer rented land near by.”
Catherine had a brother! With this new information, I was able to easily trace John’s father to John Fearer, Sr. of Allegany County, Maryland and finally connect Catherine to her parents through a probate record.
It’s easy to see what a powerful strategy researching the relatives of your ancestors can be!
Step 2: “A” Stands for Associates

Creating a FAN club with Associates
An associate could be a business partner, a witness on a document, a pastor, a lawyer, or the man that bailed Grandpa out of jail! Associates are often related. To create a list of associates, you might start gathering all witnesses to vital events, such as baptismal or christening records, marriage records, probate, land, and affidavits.
Were the courthouse records in your targeted area destroyed? Check the local newspapers for clues for possible associates. As an example, Jacob Trostel was a signee and vouched for Harvey D. Wattles’ tavern license. The license and names of the vouchers were listed in the newspaper, too. Eleven other men of the community appear on that petition. Later, Jacob himself petitions for a tavern license. That petition is signed by twelve men: George Filler, Conrad Slaybaugh, Lebright E. Hartzell, William G. Eicholtz, Isaac Yount, Joseph Dull, Isaac Myers, George W. Rex, Daniel Filler, William Harlan, and John Bream.
In both of these examples, relatives of Jacob Trostel had been vouchers. By tracing them, we were able to find out more about Jacob and his family.
Step 3: “N” Stands for Neighbors
Where can we find a list of our ancestors neighbors? A census, of course! When looking at a census page, we look for other people on the page with the same surname as our targeted ancestor. There’s a good chance those folks could also be related. But, your ancestor’s neighbors may also hold rich clues that can help you in your research. Many neighbors intermarried, sold land to each other, and even migrated to new locations together.
Besides looking at individuals listed on the same census page as your ancestor, remember to turn the page! Sometimes, a neighbor is not on the same page as your ancestor, but rather the pages before or after. Just because a person appears directly after your ancestor on the census rolls doesn’t necessarily mean they were neighbors. This only indicates the order in which the census taker visited the homes. You might also be able to identify close neighbors by looking at land ownership maps for the area. In this way, you can easily identify who lived near-by.
If you are having difficulty determining where your ancestors came from, researching the neighbors may give the answer. Many neighbors migrated together. Always check at least one page before your ancestor and one page after your ancestor in any given census.
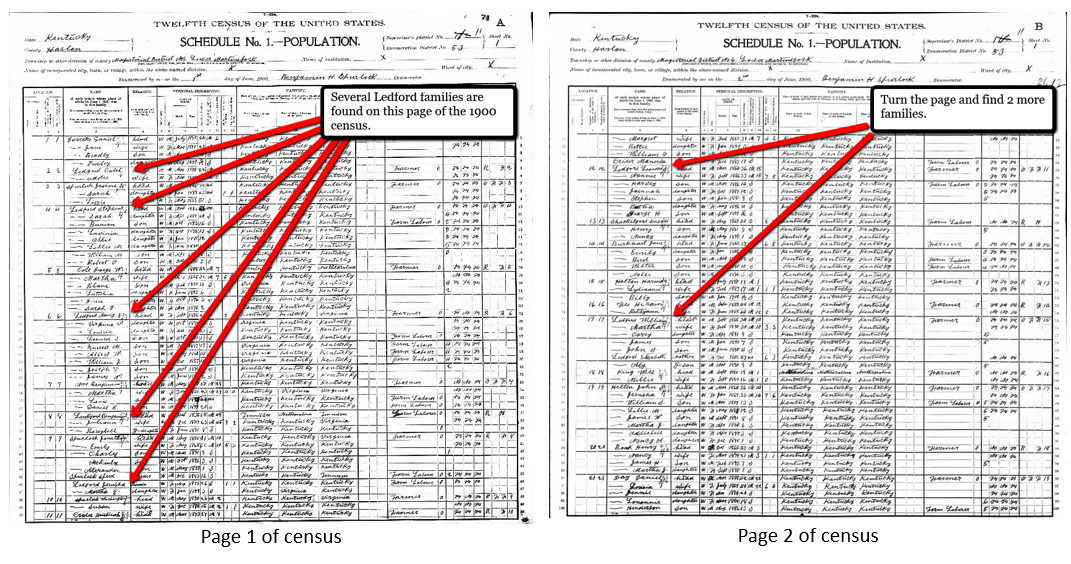
Image above: A FAN Club with Neighbors
Genealogy Fan Club: Comments and More Resources
There are likely dozens of successful ways for creating a FAN club for your ancestor. We would love to hear your examples in the comments below. For even more ways to break through those genealogy brick walls, enjoy these links below.
Read our article Solve Your Genealogy Brick Walls: 3 Tips for Breaking Through!
 Even better: Genealogy Gems Premium Members can watch Lisa’s one hour video class Brick Walls: Cold Case Investigative Techniques. In this video you’ll not only learn how to apply criminal cold case strategies to your brick walls, but you’ll also get loads of fresh and innovative ideas you can try right away. If you are not a Premium Member yet, learn more about becoming a Genealogy Gems Premium Member here.
Even better: Genealogy Gems Premium Members can watch Lisa’s one hour video class Brick Walls: Cold Case Investigative Techniques. In this video you’ll not only learn how to apply criminal cold case strategies to your brick walls, but you’ll also get loads of fresh and innovative ideas you can try right away. If you are not a Premium Member yet, learn more about becoming a Genealogy Gems Premium Member here.
by Lisa Cooke | Mar 24, 2017 | 01 What's New, German, Records & databases
Are you researching German genealogy in the States? If so, you will love what we’ve dug up. German death lists are just the start. Also in this week’s new and updated genealogical record collections, Irish Quaker records, UK pensioners records, and a new product support announcement for Family Tree Maker software.

By Photos by Donna Hyatt (United States Army) [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons.
German Genealogy in the States – Kentucky
You may not realize there was a large German population in Louisville, Kentucky, here in the United States. Our Book Club Guru, Sunny Morton, brought a new found website to our attention called German Genealogy Group. Among many other things, the German Genealogy Group has recently added newspaper death listings from the Louisville Anzeiger, a German newspaper from the Louisville, Kentucky area, to their website. The years covered are 1849-1865. Though only an index, the information provided will help you locate the newspaper itself.
Ireland – Quaker Birth Records
With over 302,000 new birth records from all over Ireland, you may finally find your Irish Quaker ancestors birth information. Ireland, Society of Friends (Quaker) births collection may help you uncover generations of your family tree. The amount of information listed on a birth record in this collection will vary, but most will include the child’s name, birth date, birth place, parish, and address. Most will also contain the parents’ names, addresses, and occupations.
Ireland – Quaker Marriage Records
Also at Findmypast, a collection titled Ireland, Society of Friends (Quaker) marriages has been updated. In fact, there have been over 20,000 new additions. These records will likely include data such as an occupation, parents’ names, and who attended the ceremony. As well as the names, address and marriage details of the newlyweds, parents’ names, an attendee list including names and dates of birth, and even details of the meeting may be found.
Ireland – Quaker Death & Congregational Records

By Holmes after Honthorst in 1654 [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons. George Fox, Quaker founder.
Findmypast collection, Ireland, Society of Friends (Quaker) congregational records offers a wealth of knowledge about the role your ancestor might have played within the Quaker community. An additional 250,000 Irish congregational records have been added. Details of meetings and activities are just a sampling of what you will find. These records include a transcript as well as an image of the original handwritten record.
Ireland – Quaker School Records
Over 9,000 new records have been added to the Findmypast collection titled Ireland, Society of Friends (Quaker) school records. This collection covers six different schools and dates back as far as the 1700s. The records are compiled from various Quaker school registers and lists. Each entry includes both a transcript and an image of the original document. Details contained in each record will vary, but most will list the pupils name, age at last birthday, school and department, admission year, leaving year, parents’ names, and their occupations.
British Newspaper Archive Announcement
The British Newspaper Archive has recently announced a major new milestone in their project to digitize up to 40 million newspaper pages from the British Library’s vast collection of historic British & Irish newspapers. Following the addition of a newspaper for the country’s smallest county, Rutland, the Archive now covers at least one title from each of the country’s 48 counties and is now available to search and explore.
As part of this push to improve the British Newspaper Archive experience, a new “In Pictures” feature has also been added.
The British Newspaper Archive now contains over 18.7 million pages from 747 titles from England, Wales, Scotland, and Ireland and spans nearly 300 (1709-2003) years.
United Kingdom – Chelsea – Pensioner Service Records
Fold3.com has a collection titled UK, Royal Hospital Chelsea Pensioner Soldier Service Records. This collection includes those who would have been eligible to receive a pension from the British Army between 1760-1920.

The collection contains records for British soldiers (not officers) who received a pension from the British Army. They typically do not include records for soldiers who died in service or who were discharged early and did not receive a pension.
Some records contain more information than others, and pension documents after 1883 typically have more details regarding the soldier such as, information about next of kin, details of marriage, and children. Common details may include age, birthplace, service details (including any decorations,) physical description, previous occupation on enlistment, and the reason for discharge to pension. Documents that are most common include:
On Fold3, the records in this collection are organized as such:
- For the period 1760-1872, the documents are arranged alphabetically by name within regiment, including militia to 1854.
- From 1873-1882, the documents are arranged alphabetically under cavalry, artillery, infantry and corps.
- From 1883-1913, two alphabetical sequences for the entire army for discharge papers are arranged by range of surname and date 1883-1900 and 1900-1913.
United Kingdom – Leeds – Cemetery Burial Registers
Not everything is on the Genealogy Giants (meaning Ancestry, Findmypast, FamilySearch, or MyHeritage.) The Leeds General Cemetery Burial Registers Index is free and available to search online. This database of transcriptions covers all entries in the burial registers of the Leeds General Cemetery and covers the years of 1835-1992. There are 97,146 entries in the index. Digital images of the registers are available to view alongside the transcribed data.

Search by surname of deceased or surname of the parents. Information found on the record will vary, but you are likely to find the name of the deceased, date of death, age at death, parents names, occupation, and cause of death. This is a great resource if you have been having trouble finding a civil death record.
United Kingdom – Sheffield
If you had ancestors who lived in the Sheffield area, you will find this next website a great help to your research. The Sheffield Indexers website provides full, online, searchable indexes to numerous collections, for free. These collections include, but are not limited to:
- 1841 Sheffield Census
- Cemetery records
- Burial records
- School records
- Directories
Be sure to check out their extensive indexes!
Family Tree Maker Announcement
Last year, Ancestry.com announced the purchase of Family Tree Maker desktop software by Software MacKiev. Their goal has always been to maintain the capability to share your family tree data between files on your computer and your personal Ancestry online trees. They’ve been working on a new Ancestry gateway with Software MacKiev to use in their Family Tree Maker 2017, which will be available soon.
What you should know (hat tip: Ancestry.com):
- TreeSync will be replaced by Software MacKiev’s FamilySync™. In the new FamilySync, Ancestry’s search, merge, and Ancestry hints will all work as they do now for users who sync with their Ancestry trees.
- FamilySync will be available only in Software MacKiev’s Family Tree Maker 2017 edition, which will be released on March 31, 2017.
- The upgrade is free for all users who purchased a copy of a MacKiev Family Tree Maker edition since March 1, 2016. Those with previous Ancestry editions, or who got a free copy of Family Tree Maker 2014.1 or Mac 3.1, are eligible for discounted upgrades. The pre-order upgrade is $29.95 for those who sign up for Software MacKiev’s mailing list before March 29 and the upgrade will continue to be a discounted price ($39.95) for a limited time after March 29.
- Between Wednesday, March 29 and Friday, March 31, there will be a short period where syncing functionality may be interrupted as Software MacKiev rolls out their new syncing technology.
- As of March 29, 2017, Ancestry will no longer be supporting TreeSync, given the introduction of Software MacKiev’s FamilySync™. Software MacKiev will continue to handle all related customer questions for Family Tree Maker. Visit Software MacKiev’s Family Tree Maker Support Center at support.familytreemaker.com if you have questions.
More on German Genealogy in the States
 German Newspapers in America is a virtual conference OnDemand video class by Jim Beidler. Stateside ethnic newspapers are a revealing resource for those searching their German ancestors. In this video you’ll learn:
German Newspapers in America is a virtual conference OnDemand video class by Jim Beidler. Stateside ethnic newspapers are a revealing resource for those searching their German ancestors. In this video you’ll learn:
-
- How newspapers are helpful for your genealogy
- The special role of German-language newspapers
- Special concerns such as fonts
- How to access German language newspapers




 Even better: Genealogy Gems Premium Members can watch Lisa’s one hour video class Brick Walls: Cold Case Investigative Techniques. In this video you’ll not only learn how to apply criminal cold case strategies to your brick walls, but you’ll also get loads of fresh and innovative ideas you can try right away. If you are not a Premium Member yet, learn more about becoming a Genealogy Gems Premium Member here.
Even better: Genealogy Gems Premium Members can watch Lisa’s one hour video class Brick Walls: Cold Case Investigative Techniques. In this video you’ll not only learn how to apply criminal cold case strategies to your brick walls, but you’ll also get loads of fresh and innovative ideas you can try right away. If you are not a Premium Member yet, learn more about becoming a Genealogy Gems Premium Member here.




 German Newspapers in America is a virtual conference OnDemand video class by Jim Beidler. Stateside ethnic newspapers are a revealing resource for those searching their German ancestors. In this video you’ll learn:
German Newspapers in America is a virtual conference OnDemand video class by Jim Beidler. Stateside ethnic newspapers are a revealing resource for those searching their German ancestors. In this video you’ll learn: