FamilySearch Indexing in Another Language: A Call to Arms
According to an article on the FamilySearch blog, 90% of all indexed records on FamilySearch are those for English-speaking countries. While this is super exciting for me and my family tree, many of my friends are unable to trace their family histories past their great-grandparents. Why? Because the records in their native country have been digitized, but not indexed.
FamilySearch Indexing in These Easy Steps
I have been indexing at FamilySearch for years and you can join me! Just follow these simple steps:
- Go to www.familysearch.org.
- Sign-in and click on Indexing and choose Overview from
 the pull-down menu.
the pull-down menu. - Click on Get Started, which will direct you to the Get Started page. You will need to download the indexing program directly to your device.
- From your desktop, open the FamilySearch Indexing program by clicking on the icon.
- Sign-in again and click Download Batch at the top left corner.
- Choose a project to work on.
If you feel you need some further instruction, watch these helpful videos below:
FamilySearch Indexing: How to Start
FamilySearch Indexing Training: Video 1
FamilySearch Indexing in Another Language
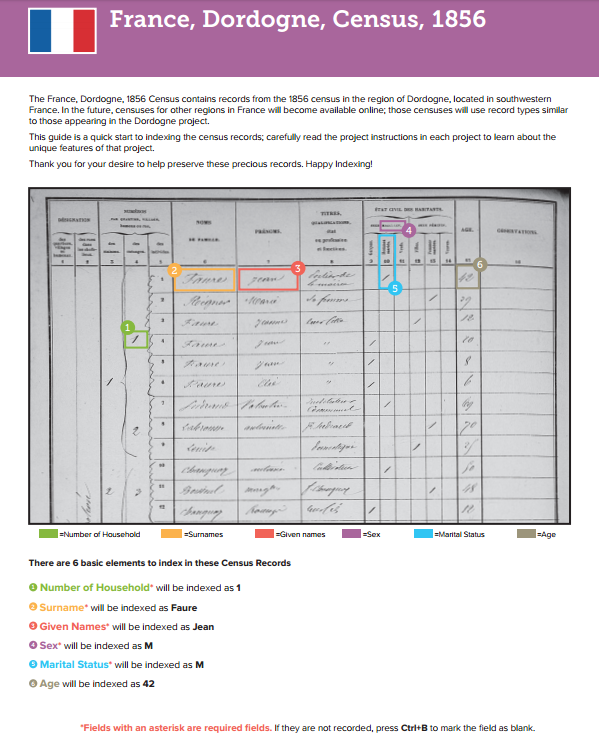
Training for French Language
FamilySearch is looking for three kinds of people:
- Fluent, native speakers of non-English languages living in their native county or in an English-speaking country.
- People who have extensive training in a non-English language.
- English speakers who are willing to learn how to index specific types of non-English records.
I know what you are thinking…you hardly passed French 101 in high school! But, you can do it.
There was recently a very successful Italian indexing training initiative in the U.S. It more than doubled the worldwide number of individuals working on Italian records. You can be a part of the growing need for French, Spanish, Italian, and Portuguese record sets.
Training guides and videos have been created for the French, Spanish, Portuguese, and Italian languages. As we accomplish the work for these places, FamilySearch will add more languages. The videos and guides will help volunteers to learn how to index specific types of records. Click here to learn about this language learning initiative and to get started.
What Else Can You Do for FamilySearch Indexing?
If you have friends or family who are fluent in another language, ask them to join you. Share this post with your friends on Twitter and Facebook to get the word out. Does your teen need some service hours for graduation, Girl/Boy Scouts, or other organization? This is a unique service project that even teens can do and that will be meaningful to many.
We would love to hear your stories of successes in indexing. Leave a comment below or post to our Genealogy Gems Facebook page.
More Gems on Indexing
Volunteer Gem: He Indexed Milwaukee Journal Obituaries Himself!

