by Lisa Cooke | May 23, 2015 | 01 What's New, African-American, images, Listeners & Readers, Military, Records & databases, United States, Volunteer
Dahlgren gun on a Civil War ship (Photo Public Domain)
Recently Tom wrote in with a question about a Civil War veterans database:
“I’ve been a listener of your podcast for quite a long time. Great job.
“We have a grass-roots group trying to locate and document Civil War Veterans buried in Washington state. Is there a good website where I can enter a name and unit identification and get results of the person’s [Civil War] service? I’m having a really hard time finding US Navy sailors.”
It sounds like Tom is conducting a very worthwhile project! (We added the link above to the website for the project, in case you’re interested.) An excellent resource–still in progress for sailors with only about 20% of them–is The Civil War Soldiers and Sailors System (CWSS).
The site describes its resources as a “database containing information about the men who served in the Union and Confederate armies during the Civil War. Other information on the site includes histories of Union and Confederate regiments, links to descriptions of significant battles, and selected lists of prisoner-of-war records and cemetery records, which will be amended over time.”
This is an excellent resource for soldiers. As far as sailors go: “The Civil War Soldiers and Sailors System currently contains the records of approximately 18,000 African American sailors, though additional records will be added in the future. The information in the Sailors Database is derived from enlistment records and the quarterly muster rolls of Navy vessels. Approximately half of the sailors entered the service at the Navy’s established points of enlistment. For these men and women, enlistment records serve as the primary sources of information. The Howard University research team used muster rolls to fill in missing data or to correct apparent misinformation recorded at the time of enlistment. Information about the remainder of the enlistees was derived directly from these muster rolls. When research uncovered inconsistencies in the data (such as conflicting reports of an individual’s age at the time of enlistment) the most frequently recorded response was used.”
“Descendants of Civil War sailors will find biographical details regarding age, place of birth, and occupation that may help supplement or clarify details from such other sources of genealogical information as birth, death, and census records. Moreover, information about any individual sailor’s enlistment and service is necessary for determining the presence or absence of their pension records at the National Archives.” Click here to read an article from the National Archives about African-American servicemen in the Navy in the Civil War. I covered the Civil War Soldiers and Sailors database in the free Genealogy Gems Podcast Episode 149. Be sure to check out the show notes page (click the link I’ve provided.) There you’ll find the information written out for you and the links I discuss in the episode.

Manchester Men available free at Google Books
If a Navy ancestor isn’t among those already listed, my first instinct is always to turn to Google searches first. I ran a search in Google Books for free (fully digitized) books meeting the criteria “civil war” “sailors” and there are some resources there as well. Here’s a link to the search results. One example is the book shown here to the left: Manchester Men, which appears to be a published list of those who served from Manchester, N.H. (click on the book cover to read it in Google Books). Learn more about Google searching for “niche” topics like this in the fully-revised and updated edition of my book, The Genealogist’s Google Toolbox.
by Lisa Cooke | Jan 29, 2015
National Genealogical Society Family History Conference May 8-11, 2019 St. Charles, MO Genealogy Gems Booth #700 Schedule of Booth Activities Check this page again before you go for more specific information and schedule. Sign up to receive our free ebook Prize...
by Lisa Cooke | Sep 21, 2016 | 01 What's New, Cloud Backup |
Using your mobile device for genealogy is a great idea, but with that convenience takes some additional know-how. Back-up your mobile device images in a few simple steps and you’ll never say, “I lost my photos on my phone!”

“I lost my photos on my phone!!”
This is NOT what you want to hear from a dear friend who is also a genealogist. So my heart sank when Genealogy Gems Contributor Amie Tennant’s email dropped into my inbox.
Amie wrote:
“I spent 6 hours researching at a cemetery and archives in a far away location. You won’t believe this, but when I got home I realized my smartphone wasn’t working. I had taken all the tombstone images with it, all the document copies were made with it, all my notes were on it. And I hadn’t even had time to back it up.”
That’s the problem, unless you back up as you go, you can’t be sure that just an hour later it won’t all be gone. These days you’re more likely to snap photos of records with your phone than a camera. But with that convenience comes the need for a new game plan to keep those precious images safe.
Back-up Your Mobile Device Images: The Plan
I put together an immediate email to Amie with a restoration and preservation game plan. If, like Amie, you are using your smartphone and mobile devices more and more, you’ll want to put this plan into place too.
First, I advised Amie to visit her phone store (for example, The Apple Store if you have an iPhone) and see if they could retrieve the lost photos and data. You never know unless you ask!
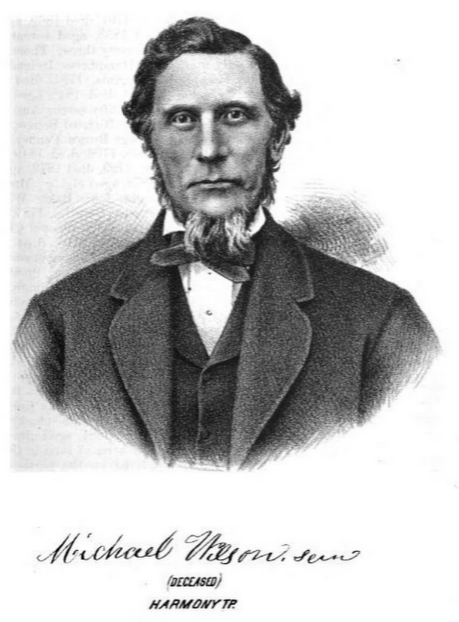

Image of Amie’s 4th great-grandfather she was able to retrieve.
Next, it’s important to consider automatic back-up options. Automatic back-ups are great, which is why I love BackBlaze. But BackBlaze is back up for your computer. The BackBlaze app on your phone only gives you access to those computer files, and doesn’t back up your phone.
One option is to back-up manually as you go. In other words, as soon as you snap that image of a record, save it to a Cloud storage service such as Google Drive or Dropbox. You could even activate Cloud back-up so that it happens automatically, though with the size of image files, you would likely need a paid subscription service to allow for adequate storage space. However, if you are going to continue to use your phone as a genealogy tool, it may be well worth the investment. Let’s look more closely at these two options:
Free Manual Option: If cost is an issue, you can save your photos to a free Dropbox account at the time you take the photo, and then move to more permanent storage on your computer at a later time.
1. Take the photograph
2. Tap the photo in my iPhone’s Photos app
3. Tap Edit and do a quick edit to clean it up (improve contrast, rotate so that it is right side up, crop to get as close-up as possible)
4. Tap Done to close the editor
5. Tap the Share icon and tap Save to Dropbox
6. Select the folder in Dropbox where I want to save the image and tap Save
However, it would definitely be faster and simpler to have your phone automatically backing up to the Cloud.
Low Cost Automatic Option: If your phone is going to be one of your genealogy tools, then automatic cloud back-up may be worth the low cost of around a dollar a month.
Personally, I am not a fan of iCloud even though I have an iPhone. I just don’t find it very user friendly to work with. Setting up your photos and videos to automatically back up to your Google Photos library via Google Drive is another option. Again, since photos and videos do take up a lot of space you’ll likely need to invest in a low cost monthly storage plan. Click here to learn more, or Google search Google Drive Plan Cost (or substitue the name of the service you are considering) for current plans.
Bottom line: There are several Cloud services available for our smartphones and mobile devices, so there’s sure to be one that’s right for you. Where ever your images find their final resting place, make sure it has Cloud back-up.
Amie’s Response to the Plan
I quickly sent the plan to Amie. She responded by saying:
“Thank you, Lisa! It was devastating. You were right, a nice man at the phone store was able to restore them! But, I don’t ever want to have this happen again. When I set up my new phone, a Samsung Android, I noticed a setting that said something like “automatic save to Google drive” and it would sync your images. So I clicked it “on” but now I can’t find where I did that! Any ideas?”
Troubleshooting Backing-up Your Mobile Device
When people shoot me a question, my usual response is “Just Google it!” I Googled Automatic backup of android phone and got several great hits on the results list.
One article on Android Fact.com was particularly helpful. (Read the full article here.) Remember, it can get pretty expensive to be instantly uploading images with your cell phone carrier. I suggest clicking Wi-Fi Only to ensure that uploading only takes place when you are connected to Wi-Fi.
I regularly emphasize backing up important documents that live on your computer. But let’s face it: If you have a smartphone, it would be oh, so sad to have to say “I lost my photos on my phone!” So don’t wait—back up your smartphone or mobile device today.
Another Tip for Using Smartphones for Genealogy
 Here’s a another mobile computing tip my book Mobile Genealogy: How to Use Your Tablet and Smartphone for Family History Research.
Here’s a another mobile computing tip my book Mobile Genealogy: How to Use Your Tablet and Smartphone for Family History Research.
Smartphones and other mobile devices offer a plethora of editing tools. It is well worth the investment of a few extra seconds to clean up and maximize images as you go. This is particularly true of records that need to be clear for future reference or printing.
Try applying a filter to your images for maximum readability. I like the Noir filter in my iPhone’s Photos app editor.
More Gems on Using Mobile Devices for Genealogy
How to Use Your Mobile Device for Genealogy: Free Video!
3 Tips for Getting the Most Out of Your Mobile Device





