by Lisa Cooke | Dec 9, 2016 | 01 What's New |
New and updated genealogical collections for the Royal Irish Constabulary are just the tip of the iceberg this week. Scroll down for more cool finds for New South Wales, Scotland, U.S. marriages, and an update to the Freedmen’s Bureau collections at FamilySearch.

Ireland – Royal Irish Constabulary Records
You can now search the Ireland, Royal Irish Constabulary Service Records 1816-1922 at Findmypast for over 486,000 records that uncover the details of your ancestor’s career with the R.I.C.
Each search result includes an image of the original document and a transcript. The nature of the information recorded will vary significantly depending on the subject and type of the original document. The following is a list of what types of records can be found in this collection:

Auxiliary division general registers: These are nominal rolls that recorded member’s service number, rank, dispersed date, and company name. The registers also include division journals that recorded dates of appointment, promotions, and medical details.
Clerical staff: record of service and salaries: These lists of clerical staff include birth date, age at appointment, rank, department and salary.
Constabulary Force Funds: These correspondence registers are of members who paid into the fund with notes on whether they had been pensioned, died or received any rewards from the fund.
Constabulary lists: These are lists of chief constables created during the first year of the Royal Irish Constabulary.
Disbandment registers: These registers are of serving members who were with the force in 1922 when it disbanded after the creation of the Free Irish State. They also noted the number of years the constable served and their recommended pension.
General registers: Records of constables’ service history are contained in these general registers. The entries include the individual’s birth date, native county, religion, previous occupation, date of appointment, and promotions, as well as any rewards or punishments received and the date of pension or discharge.
Nominal returns, arranged by counties: Nominal returns are lists of all serving members of the Royal Irish Constabulary organised by county that recorded the individual’s number, rank, name, religion, date of appointment, marital status, and station location.
Officers’ registers: These registers are lists of Officers that include transfers and dates, favorable and unfavorable records, dates of promotions and details of previous military service.
Pensions and gratuities: Pension records reveal the constable’s rate of pay and the amount of pension calculated.
Recruits index: Lists of new recruits, their dates of appointment and arrival, and their company can be found in the recruits index.
Also at Findmypast, Ireland, Royal Irish Constabulary History & Directories has had a significant addition of over 43,000 records. You will be able to explore a variety of publications between the years of 1840 and 1921. These records will provide insight into the administration and daily operations of the police force.
Each record includes a PDF image of the original publication. The collection includes training manuals, codes of conduct, salary scales, circulars and staff lists that cover promotions, deployments, and rules & regulations.
Ireland – Valuation Books
At FamilySearch, the Ireland, Valuation Office Books, 1831-1856 are now available to search. These records are the original notebooks that were used when the property valuations were conducted between the years of 1831-1856. They are arranged by county, then alphabetically by parish or townland.
Land valuation records may contain the following information:
- Land occupier’s name
- Location, description, and monetary valuation of each land plot surveyed
New South Wales – Passenger Lists
The New South Wales Passenger Lists is a collection at Findmypast that contains over 8.5 million records. The collection includes records of both assisted and unassisted passengers. The assisted passenger lists cover 1828 to 1896 and the unassisted passenger lists span the years 1826 to 1900. Assisted passengers refers to those who received monetary assistance from another party or agency/government for their passage.
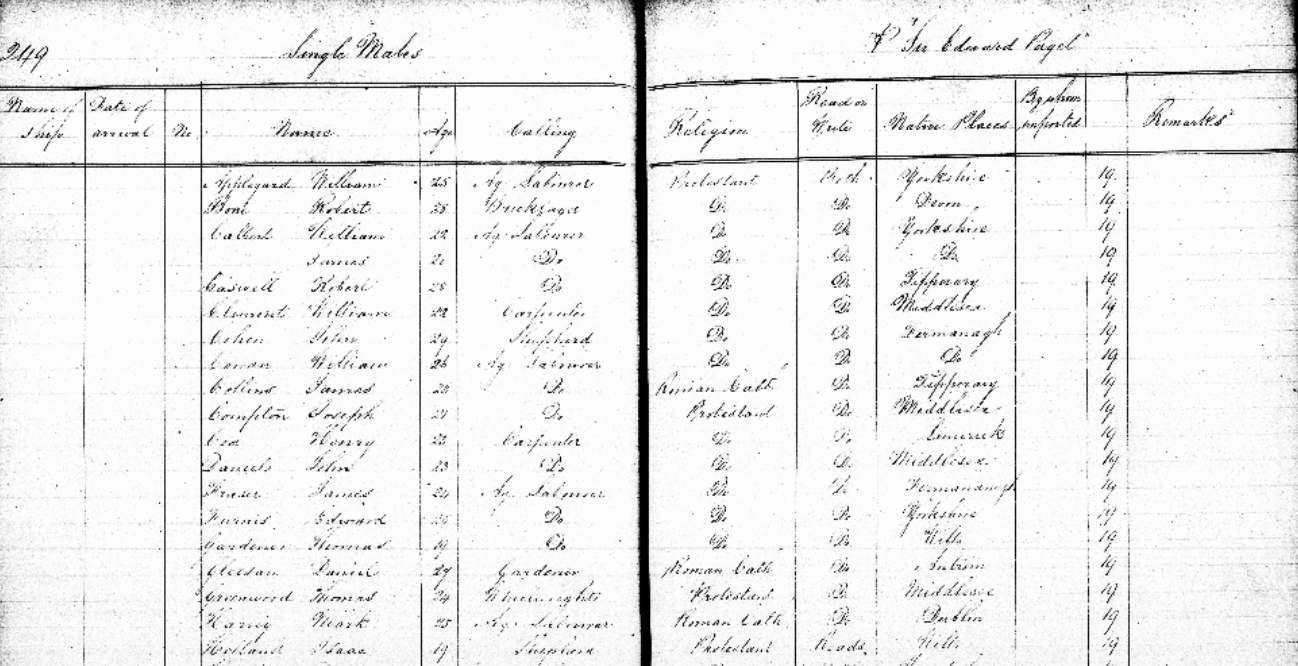
Each result will provide a transcript and image of the original record. The information included on the transcript will vary depending on whether your ancestor was an assisted or unassisted passenger, although most will include your ancestors name, passage type, birth year, nationality, departure port, arrival port and the dates of their travels.
Scotland – Parish Records
The Scotland Non-Old Parish Registers Vital Records 1647-1875 found at Findmypast is a collection of registers created by churches outside of the established church. It contains over 12,000 transcripts of births, marriages, and deaths.
Non-old parish registers are different from the Church of Scotland’s old parish records.
Though these are only transcripts and do not include a digital image of the original, you may find the following information on the records included in this collection:
With each result you will be provided with a transcript of the details found in the original source material. The detail in each transcript can vary depending on the event type and the amount of information that was recorded at the time of the event. Here are some of the facts you may find in the records:
- Name
- Birth year, date, and place
- Event year
- Event type – birth, marriage, or death
- Register name
- Parish and county
United States – Freedmen’s Bureau Records
FamilySearch has updated their magnificent collection of United States Freedmen’s Bureau, Records of Freedmen, 1865-1872. Records found in this collection include census returns, registers, and lists of freedmen. They also include letters and endorsements, account books, applications for rations, and much more. Many of the records will hold valuable genealogical data.
For a complete list and coverage table of the full collection, click here.
United States – Marriages – Oregon and Utah
Ancestry.com has recently updated two marriage collections. The Oregon, County Marriages, 1851-1975 and the Weber and Piute Counties, Utah, County Marriages, 1887-1940 have some new records. Marriage records will often provide many helpful genealogical details. Depending on the year, you may find:
- Name of the groom and bride
- Date and place of the event
- Birth dates and places of bride and groom
- Names of parents of both bride and groom
- How many previous marriages and marital status
- Place of residence of bride and groom
United States – Washington – Newspapers
Washington State historic newspapers added to their digital collection of newspapers this week. With nearly 50,000 digitized pages from historical newspapers based in Centralia, Eatonville, Tacoma, and Spokane newest titles include the Centralia Daily Hub (1914-16), The Eatonville Dispatch (1916-61) and Den Danske Kronike (1916-17), a Danish-English publication based in Spokane.
The Centralia and Eatonville papers were added this month and Den Danske Kronike was added last summer, along with the Tacoma Evening Telegraph (1886-87).
You will be able to search this newspaper collection for free from the Washington State Library website.
by Lisa Cooke | Aug 19, 2016 | 01 What's New, British, Records & databases |
England emigrants to its U.S. colonies appear in new genealogy records online this week. Also: the 1891 New South Wales census; Czech church, land and school records; English parish records; and U.S. collections from the Freedmen’s Bureau, Marine Corps, Coast Guard and New England towns and cities.

Australia – New South Wales census
Findmypast.com has published over 200,000 records from the 1891 New South Wales census. The census collectors’ books are the source, as these are the only surviving documents. “While they provide less detail than a full census would, they can still be a useful aid to historians and genealogists alike in placing people at a specific moment in time,” states the collection description. “Each result will provide you with a transcript and image of the original collector’s books from the 1891 census. Original images may provide you with additional details, such as the number of individuals living in the same household or the number of residents who were Aboriginal or Chinese.”
Czechoslovakia – Church, Land and School
FamilySearch.org has added to its collection of Czech Republic Church Records spanning more than 400 years (1552-1963). You’ll find “images and some indexes of baptisms/births, marriages, and deaths that occurred in the Roman Catholic, Evangelical Lutheran, and Reformed Church parishes, as well as entries in those registers for Jews.” These are taken from parish registers and synagogue records now in regional archives. Though not fully indexed, the browse-only records number over 4 million! (Click here to learn how to use browse-only collections on FamilySearch.org; remember you can use the FamilySearch wiki for help in translating records in another language.)
FamilySearch has also added more than 850,000 browsable images to its existing collection of Czech Republic Land Records 1450-1889 and more than a million browsable images to the existing collection Czech Republic School Registers 1799-1953.
England Emigrants
Remember recently when we blogged about emigrant records, or those created about people leaving a country? Ancestry.com recently posted a new database called Emigrants in Bondage, which it says is “the most important list of ships’ passengers to be published in years.” Indexed are names of “more than 50,000 English men, women, and children… sentenced to be deported to the American colonies for crimes ranging from the theft of a handkerchief to bigamy or highway robbery.” The collection dates cover 1614 to 1775, after which time the British empire was not permitted to ship its “undesirables” to U.S. shores.
England – Parish records – Staffordshire and Sussex
Findmypast has added to its collections of church vital records for Staffordshire, England. Its browsable parish registers, 1538-1900 now includes 300,000 full-color page-by-page images. Separate databases of baptisms, wedding banns, marriages and burials have also been updated.
Also, more than 1.2 million indexed records have been added to FamilySearch’s collection of England, Sussex, Parish Records, dating 1538-1910. Sussex parish registers contain baptisms, marriages/banns, and burials. Date ranges of available records vary by locality; you will want to use the coverage table at the FamilySearch wiki to see what’s available.
U.S. – Freedmen’s Bureau Records
Now that the Freedmen’s Bureau collections have been fully indexed, FamilySearch is dumping them onto its website in batches. This week, they added these new databases:
U.S. – Military
FamilySearch.org has added just over 4 million indexed records to its database of United States Muster Rolls of the Marine Corps (1798-1937). The collection is described as an “index and images of muster rolls of the United States Marine Corps located at the National Archives. The records are arranged chronologically by month, then by post, station or ship.”
This week, the Fold3.com blog reminds us of its Coast Guard collections, in honor of the Coast Guard’s 226th birthday. Hundreds of thousands of search results on the site relate to Coast Guard history, from disapproved Navy survivors pension files to photos dating to the Civil War; accounts of shipwrecks or accidents, WWII war diaries for several units, images of insignia and Navy cruise books.
U.S. – New England
FamilySearch has posted a new index of New Hampshire Vital and Town Records Index for the years 1656-1938. It contains shy of half a million records of births, marriages and deaths. Entries were sourced from multiple archives in New Hampshire; the citation for each record is included in the index entry at the bottom of the record screen.
The New England Historic Genealogical Society has announced improvements to its databases for three New England cities, which now include more searchable fields and images. “Hartford, CT: General Index of Land Records of the Town of Hartford, 1639-1839, is now searchable by grantee and grantor name, and results provide the record type and volume and page of the record (available on microfilm at the Connecticut State Library). Boston, MA: Births, 1800-1849, and Dover, NH: Vital Records, 1649-1892, are now searchable by first name, last name, record type, family member names, date, and location.”
by Lisa Cooke | Feb 15, 2017 | 01 What's New, African-American |

Not all people of color were enslaved prior to the emancipation. In fact, many were freed long before that. Researching free people of color can be quite complex. Tracing my own family line (who were free people of color) continues to be a real learning process for me. However, don’t let the challenges deter you from exploring this rich part of your heritage. In this “Getting Started” post, we discuss the manumission process, “negro registers,” and more for tracing your free people of color.
Who are Free People of Color?
[Note: Throughout our post, we will be using terminology that was used at the time the records were created.] A ‘free negro’ or ‘free black’ was a fairly recent status in the U.S. which differentiated between an African-American person who was free and those who were enslaved prior to emancipation. If a person was referred to as a ‘free negro’ or ‘free black’, that meant the person was not living in slavery. It is a fascinating and little know fact that, as Ancestry Wiki states, “one in ten African-Americans was already free when the first shots were fired on Fort Sumter.”
Step 1 for Tracing Free People of Color: Censuses
Sometimes, the story of your ancestors being free people of color was passed on through oral traditions. In my own family, our “line of color” was not talked about. Instead, my first clue was when I found my ancestor in the 1840 population census listed as free. I also found that one woman (presumably his wife) was marked in the column for “free white persons,” but John and the children were marked as “free colored persons” in this census. This was the first step to identifying my ancestor as a free person of color.
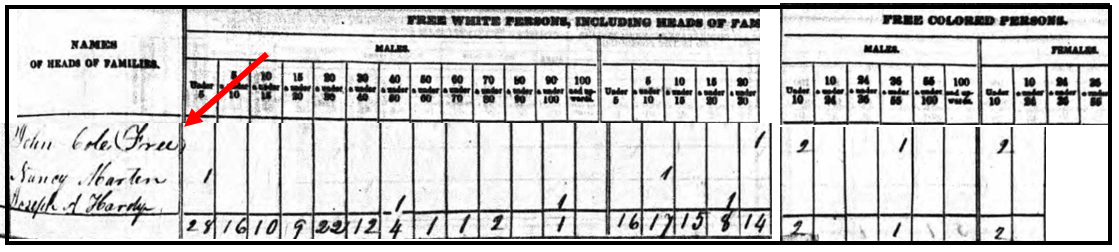
Let’s see another example. The 1850 and 1860 U.S. Federal Censuses included two population schedules. One enumerated free inhabitants, and the additional schedule, referred to as a Slave Schedule, was for making an enumeration of those persons who were enslaved. [We will discuss this further, below.]
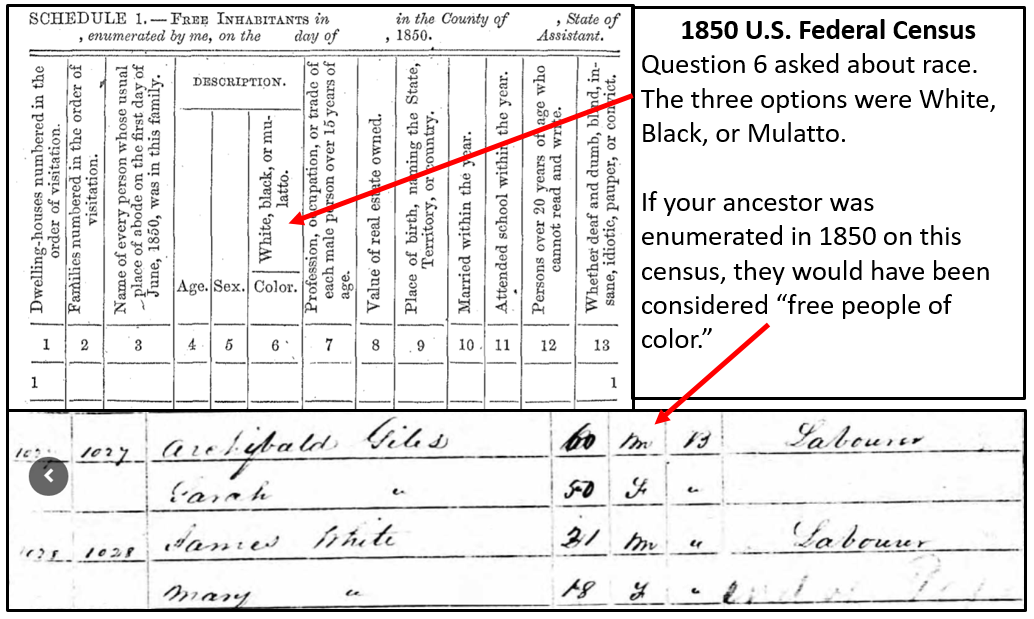
If your ancestor appears on the 1850 U.S. Federal Census for free inhabitants, they are considered free, even if their race was listed as “Black.” An example of a Black man enumerated on the 1850 census is shown in the image below. Archibald Giles is recorded as “Black,” but appears on this census for “free inhabitants.” Therefore, he would be considered a free person of color.
If your targeted ancestor does not appear on either the 1850 or 1860 population schedule for free inhabitants, they might have been enumerated on the slave schedules of 1850 or 1860.
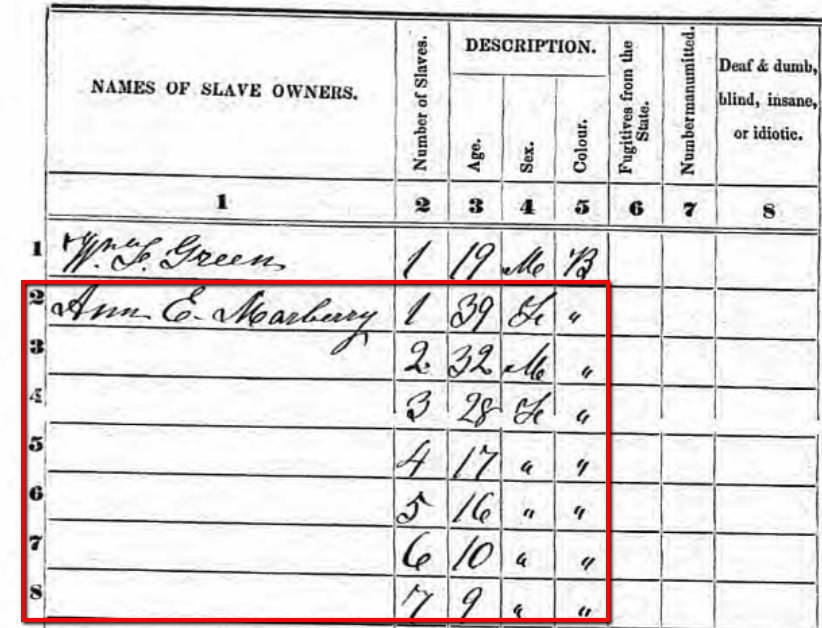
1850 Slave Schedule for Henry County, Tennessee. Snapshot via Ancestry.com.
You can check the 1850 Slave Schedule and the 1860 Slave Schedules at Ancestry.com. The 1850 census is also available at Findmypast, MyHeritage, and FamilySearch.
In this example to the left, you will see a portion of the Henry County, Tennessee Slave Schedule for 1850. Notice, only the heads of household or the “owners” were listed by name. Slaves were not named, but rather listed by age and sex under the names of their “owners.”
Step 2: The Manumission Process
Once you have identified that you have free people of color in your family tree, the next step is to determine how they became free. Many free people of color came from families that had been free for generations. This could have been due to a manumission of an ancestor or a relationship between an indentured white woman and a black slave. I make mention of this relationship between races because it is helpful to remember that the status (whether free or enslaved) of the child was based on the status of their mother. If the mother was free, then the child was free. If she was a slave, then the child was enslaved. [1]
Manumission was a formal way in which slaves were set free. There are many reasons why a slave owner may have released or freed his slaves. In some cases, slave owners would free their mistresses and children born to her. In one case, I found the following comment made by the slave owner, “I give my slaves their freedom, to which my conscience tells me they are justly entitled. It has a long time been a matter of the deepest regret to me…” And thirdly, it was possible for a slave to obtain their manumission through the act of “self-purchase.”
If the mother was free, then the child was free. If she was a slave, then the child was enslaved. [1]
Private manumission through probate. A private manumission decree could be made in a last will and testament. You can find these manumissions in wills, estate papers, or in probate packets. Many of these county level probate records have been microfilmed or digitized and are easily accessible online.
Sometimes, a manumission in a will would be contested. When this happened, a long paper trail of court documents may have been created. A thorough search of all of these proceedings may offer a wealth of genealogical data and clues.
Usually, manumission papers included the name of the slave owner, the name of the slave, and the reason for manumission. In the case of the slaves of John Randolph of Roanoke [Virginia,] his slaves were not named individually in his will written on 4 May 1819. Instead he stated, “I give my slaves their freedom, to which my conscience tells me they are justly entitled. It has a long time been a matter of the deepest regret to me, that the circumstances under which I inherited them, and the obstacles thrown in the way by the laws of the land, have prevented my manumitting them in my lifetime, which is my full intention to do, in case I can accomplish it.”[2]
John freed over five hundred slaves, and though each of them was not listed by name in his will, a codicil at the end of the will did name two of his slaves when he asked that Essex and his wife Hetty “be made quite comfortable.”[3]

Record of Arthur Lee purchasing his freedom.
Manumission through self purchase. Self-purchase may seem impossible; however, many slaves were not required to work on Sundays for their masters.[4] On this day, men and women could hire themselves out to do work for others. With frugality, they could save their earnings to buy their freedom or the freedom of their loved ones, though this was very, very difficult.
As you can see in this example of Arthur Lee, he was able to pay for his freedom and the freedom of his wife, though it took many years. This type of record could be found in a published book, a record listed in notarial books of the county, civil minutes books, or other courthouse holdings. It is important to speak with a knowledgeable person in your targeted area about where you should look. A knowledgeable person may be those working with the local historical or genealogical society, or a head of the local history department of the public library.
Step 3: “Negro Registers”
If you do not find the manumission in a last will and testament, perhaps due to a courthouse fire or other loss, you may have luck searching the county records where your free people of color later settled. Free people of color were often required to register, using their freedom papers, when they relocated to a new area. These types of records are called ‘negro registers’ or ‘records of free negros.’
Newly freed people carried with them their freedom papers which were given to them when they were manumitted. Once they relocated, they would register with the county clerk. They would need to show the county clerk these freedom papers and a record was made in the register. The record may include the name of members of the family, ages, and most recent place of residence.
The book titled Registers of Blacks in the Miami Valley: A Name Abstract, 1804-1857 by Stephen Haller and Robert Smith, Jr. provides the following information about registers of freed people:
“From 1804 to 1857, black people in Ohio had to register their freedom papers with the clerk of courts of common pleas in the county where they desired residency or employment. State law required this registration, and clerks of court were to keep register books containing a transcript of each freedom certificate or other written proof of freedom (see Laws of Ohio 1804, page 63-66; 1833, page 22; 1857, page 186). Few of these registers have survived to the 20th century.”[2]
Though this author says that only a few of the registers have survived, I found some microfilmed registers listing the names of free people of color who had settled in Miami County, Ohio at the local historical society archives. Again, it is important to ask those people who would be most knowledgeable, and in this case, it was the historical society.
In conclusion, we understand that tracing both our enslaved and manumitted ancestors is often a difficult task. We also know there is much more to learn and share for the best techniques to researching these lines. We encourage you to review some of the additional sources below. Please let us know what other resources have been most helpful to you in researching your free people of color in the comments section below. We want to hear from you!
Source Citations
[1] Kenyatta D. Berry, “Researching Free People of Color,” article online, PBS, Genealogy Roadshow, accessed 1 Dec 2016.
[2] Lemuel Sawyer, A Biography of John Randolph with a Selection From His Speeches, New York: 1844, page 108, online book, Google Books, accessed 20 Dec 2015.
[3] Ibid.
[4] History Detectives Season 8, Episode 10, PBS, online video, originally aired 29 Aug 2010, accessed 1 Dec 2016.
Additional Reading
by Lisa Cooke | Apr 1, 2016 | 01 What's New, Records & databases
Here’s our weekly roundup of new genealogy records online. This week: Australia, Belgium, Czech Republic, England, Germany, Japan, Mexico, Wales and U.S. passport  and homestead records.
and homestead records.
AUSTRALIA – QUEENSLAND. Ancestry.com has added several indexes for Queensland, Australia: Prison and Reformatory Indexes (1824-1936), Property Indexes (1842-1895), Index to Aliens (1913) and Occupational Indexes (1857-1922). These indexes all come from the Queensland State Archives. You can search them for free at Ancestry.com or from the QSA website.
BELGIUM CIVIL REGISTRATIONS. FamilySearch has updated its civil registration collections for several parts of Belgium (dating back to the 1500s for some areas): Antwerp, Brabant, East Flanders, Hainaut, Liège and West Flanders. According to FamilySearch, these collections include “civil registration(s) of births, marriages and deaths from the Belgium National Archives. The collection also includes marriage proclamations, marriage supplements, and some original indexes.”
CZECH REPUBLIC SCHOOL REGISTERS. Over a million browsable digital images from the Opava State Regional Archive have been added to a free collection of Czech Republic School Registers (1799-1953) at FamilySearch.org. “School registers contain the full name for a child, birth date, place of birth, country, religion and father’s full name, and place of residence.”
ENGLAND AND WALES SCHOOL RECORDS. Findmypast.com has just added about 687,000 new school admission records for 41 counties in England and Wales (1870-1914). Original records may include names, residence, birth data, school name and location, parents’ names, admission information, father’s occupation, any exemption from religious instruction, previous school attendance, illnesses/absence and even exam results.
ENGLAND – CORNWALL. Several new collections on Cornwall are searchable at Ancestry.com: Congregational and Baptist Church Registers (1763-1923), Workhouse Admission and Discharge Records (1839-1872), Militia and Sea Fencibles Index (1780 – 1831), Bodmin Gaol Records (1821-1899), Penzance Dispensary Admissions (1828-1841), Truro Police Charge Books (1846-1896) and Inmates at St. Lawrence’s Asylum, Bodmin (1840-1900).
GERMANY VITAL RECORDS. Ancestry.com has recently added a new collection of death records for Mannheim. It has also updated collections of birth records for Hamburg; birth, marriage and death records for Regen County (dating to 1876) and birth, marriage and death records for Oldenberg.
JAPAN GENEALOGIES AND VILLAGE RECORDS. FamilySearch.org has added nearly a quarter million browsable images to its collection of Japanese village records (dating back to 709 AD) and nearly 60,000 browsable records to its collection of Japanese genealogies (dating to 850 AD).
MEXICO CIVIL REGISTRATIONS. Ancestry.com has updated its collections of indexed images to Chihuahua, Mexico birth, marriage and death records from civil registrations. The collections are in Spanish, so use Spanish names and locations.
U.S. HOMESTEAD RECORDS. Ancestry.com’s collection of U.S. Homestead Records (1861-1936) has recently been updated. According to the collection description, “Homestead files consist of unbound documents that include final certificates, applications with land descriptions, affidavits showing proof of citizenship, register and receiver receipts, notices and final proofs, and testimonies of witnesses. These documents are part of the Records of the Bureau of Land Management (formerly known as the General Land Office), Record Group (RG) 49. The collection currently includes records from Arizona, Indiana, Nebraska, Nevada, Ohio, and part of Iowa. Additional records will be added in future updates.”
U.S. PASSPORTS. Nearly 40,000 indexed names have been added to FamilySearch.org’s free collection of United States Passport Applications (1795-1925). These are a fantastic resource for finding immigrant ancestors and those who traveled a lot. Click here to learn more about U.S. passport records.

Thanks for sharing this post with others who have ancestors from these parts of the world. You’re a gem!
by Lisa Cooke | Sep 30, 2017 | 01 What's New, Military, Records & databases, United States |
Do you have ALL your ancestors’ U.S. draft registration records–from the Civil War until after World War II? These documents may be filled with genealogy clues, whether your ancestor served in a war or not. Military expert Michael Strauss presents this roll call of U.S. draft registration records you’ll want to check!

Thanks to Michael L. Strauss of Genealogy Research Network for providing this guest post.
Military records can lead genealogists to many new sources of information. One of the first records that you may come across (for our United States ancestors) that could provide unknown information are found in draft registrations. The records are civilian in scope, but can provide clues of prior military service or proof of current war conditions.
The National Archives holds custody overall for the bulk of the draft registrations from the Civil War to post-war World War II. The Archives organizes their records by grouping numbers. The Civil War draft registrations are found in two record groups, RG59 and RG110. Later draft registrations are found in RG147. In all cases, finding aids are available to locate and obtain copies.
Civil War Draft Registration Records

Recruiting poster, New York printed by Baker & Godwin, June 23, 1863. Public domain image hosted at Wikipedia.org (click to view).
Civil War draft records date back to the first national draft which was signed by Abraham Lincoln on March 3, 1863. This draft only applied to men residing in states under Union control. The draft includes several lists detailing information about men eligible to be drafted to fight for the Federal Army. This included consolidated lists for men between the ages of 20-45, which are grouped and divided into two classes of records. This list contains the name, residence, age, race, marital status, place of birth, any former military service, occupation, and remarks for each registrant. (Remarks might include ineligibility based on religious reasons or former service in the Confederate Army.)
Other registrations included medical exams, statements of substitutes, and case files of persons who were draft aliens. (Aliens were ineligible for military service and therefore contain files that document their nativity.) All of these are at the National Archives.
The last group of records includes the descriptive rolls that contain the name, age, physical descriptions, where born, occupation, when and where drafted, and remarks. The descriptive books are located at the regional branches of the National Archives and can be accessed by researchers, as these have not been filmed or scanned. Records are divided into two separate record groups: RG59 (Department of State) covered those men who were aliens and RG110 (Provost Marshal) has all the other lists of men being drafted.
The only Civil War draft registration records available online are the consolidated lists; click here to search them at Ancestry.com (subscription required). On the Confederate side, there are a limited number of draft records available, some at the National Archive and some in the custody of individual state archives.
World War I Draft Registration Records
For a number of years, there was no draft or draft registration. However, when the United States entered the war in Europe on April 6, 1917, the country was totally unprepared for overseas campaigning. This conflict forced our government to consider other means to recruit the tens of thousands of men it would take to wage this war. The Selective Service Act of 1917 authorized the President of the United States to increase the military establishment being passed by Congress on May 18, 1917. The Act directed the Provost Marshal General Office (P.M.G.O.) to select men eligible for military service.
All men were required to register, native-born or aliens. The draft is separated into three registrations:
- The 1st draft registration was dated June 5, 1917 for men aged 21 to 31 and consisted of 12 questions.
- The 2nd draft registration was dated June 5, 1918 for men who had turned 21 since the previous registration and included a supplemental registration on August 24, 1918 for men turning 21 after June 5, 1918. Each consisted of 10 questions.
- The 3rd draft registration was dated September 12, 1918 and was intended for all men aged 18 to 45 years. It consisted of 20 questions.
Each registrant was required to provide their name, age, birth date, and birthplace (in 2 of the 3 registrations), occupation or employer, nearest family, and a summarized physical description.


WWI draft registration of Henry Fox. Image from Ancestry.com.
By the end of World War I, nearly 24 million men had registered for the draft (this number excluded registered enemy aliens and those already in the military). The original draft cards are at the National Archives branch in Morrow, Georgia. World War I draft registrations are available online at Ancestry.com, FamilySearch.org, Findmypast.com and fold3. FamilySearch is the only one with free access (a personal subscription or library access is required for the others).
World War II Draft Registration Records
The eve of World War II saw the passage of another conscription act. This act was the Selective Training and Service Act of 1940, and was the first peace time conscription in United States History. This act officially established the Selective Service System. The draft during World War II consisted of seven registrations. The “Old Man’s Draft,” or 4th registration, was for men born between 1877 and 1897, with the other six registrations intended for the younger adult men born after 1897:
- 1st: October 16, 1940, included all men 21-31.
- 2nd: July 1, 1941, for those men who reached age 21 since the first registration.
- 3rd: February 16, 1942, for men ages 20-21 and ages 35-44.
- 4th: April 27, 1942, for all men between the ages of 45 and 64. The registrants were not eligible for military service (this is the “Old Man’s Draft”).
- 5th: June 30, 1942, for all men between the ages of 18 and 20.
- 6th: December 10 – 31, 1942, for all men who had reached the age of 18 since the previous registration.
- 7th: November 16 – December 31, 1943, for American men living abroad between the ages of 18 and 44.
Registrants were required to provide their name, address, birth date, birthplace, and employer’s information, along with a contact individual who would always know the registrant’s information or address. The form also asked for the telephone number of the registrant in addition to a more complete physical description.
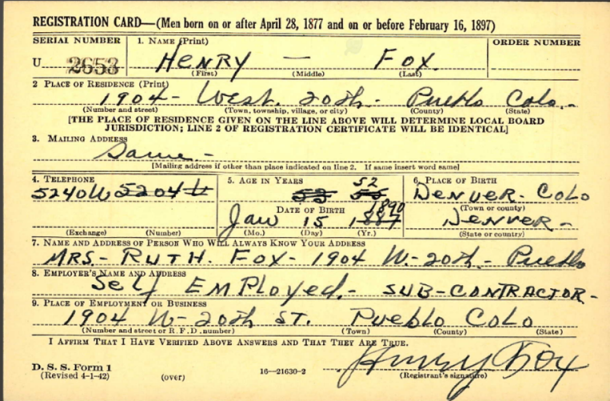
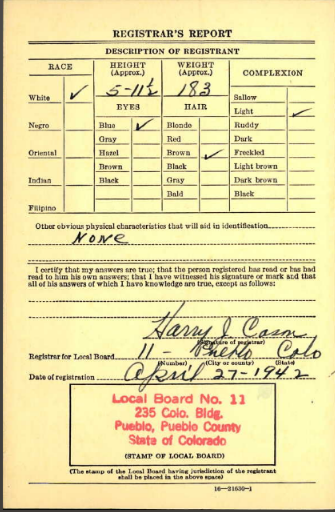
WWII draft registration of Henry Fox. Image from Ancestry.com.
Several of the states that recorded the “Old Man’s Draft” were lost. The National Archives no longer has these records available. These states include: AL, FL, GA, KY, MS, NC, SC, and TN.
Not all of the World War II Draft registrations are available online. Less the states above, view 4th registrations online at Ancestry.com, Familysearch.org (index and browse-only images) and fold3. The fold3 database includes 25 states and territories: AL, AK, AR, AR, CO, CT, DE, FL, GA, HA, ID, LA, MD, NV, NM, NC, OK, PA, UT, VA, WV, WY, and the District of Columbia and the Virgin Islands. (On Ancestry.com, the number of states is limited to AR, GA, LA, and NC.) Other states are in the process of being added. However, the remaining states are only available directly from the National Archives in St. Louis, MO.
Some of the other registrations are also available online for a selected grouping of states.
Expert tip: It is not uncommon to find men registered for both World War I and World War II draft registrations, which would depend on their ages.
Post-World War II Draft Registration Records
The draft and registrations didn’t cease with the conclusion of World War II. It was active from 1948 until 1973, when President Richard M. Nixon officially signed legislation that ended the draft. This was suspended in 1975, and five years later, in 1980, President James E. Carter again brought back into activity the Selective Service System. This came in response to the Soviet invasion of Afghanistan. To date, the Selective Service System still remains active, requiring all men to register within 30 days of their reaching the age of 18 years.
To gain access those records not online from World War II, and for the later registration cards for men for the Korean and Vietnam conflicts and for other years, researchers will need to contact the National Archives in St. Louis, MO. This office handles the original cards for all men born between April 28, 1877 and March 28, 1957. The National Archives fee schedule is in place to request the records by mail. A copy of the Draft Registration Card (SSS Form 1) alone costs $7.00, or order a copy of it along with the Draft Classification History (SSS Form 102) for $27.00. Click here to go to the National Archives’ webpage for ordering Selective Service records.
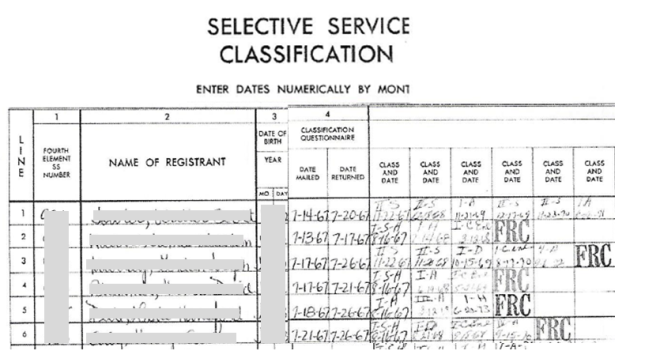
Draft Registration Records for Men Born after 1960
The law never required men to register who were born between March 29, 1957 and December 31, 1959. The National Archives doesn’t hold copies of records for men born after January 1, 1960. To gain access to draft registration for all other years, contact the Selective Service System directly. Click here for all the details.
 Michael L. Strauss contributes the new Military Minutes segment on the Genealogy Gems Podcast. Listen to this segment in the free Genealogy Gems Podcast episode 207.
Michael L. Strauss contributes the new Military Minutes segment on the Genealogy Gems Podcast. Listen to this segment in the free Genealogy Gems Podcast episode 207.
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links and Genealogy Gems will be compensated if you make a purchase after clicking on these links (at no additional cost to you). Thank you for supporting Genealogy Gems!










 and homestead records.
and homestead records.







 Michael L. Strauss contributes the new Military Minutes segment on the Genealogy Gems Podcast. Listen to this segment in the free
Michael L. Strauss contributes the new Military Minutes segment on the Genealogy Gems Podcast. Listen to this segment in the free