Getting Started with Australian Genealogy: Tips from Legacy Tree Genealogist
Ready to start your Australian genealogy research? A Legacy Tree Genealogist walks you through essential Australian history, geography, genealogical record types and online resources to trace your family tree “down under.”
 Thank you to Legacy Tree Genealogists for providing this guest post.
Thank you to Legacy Tree Genealogists for providing this guest post.
Australian genealogy can be straightforward, but you do need to know a time period and a place, as well as the family name you are researching. Australia has only been a single country since 1901; before that there were colonies and territories beginning with the first European settlement in 1788. Even today the individual states and territories have their own governments and record systems with no single combined place to research. Therefore, knowing the time period and place where your ancestors lived is essential.
Australian history and geography
European settlement began with the arrival of the First Fleet in 1788, which included both male and female convicts and military and naval personnel. The colony became known as New South Wales, and occupied the eastern half of the continent of Australia including Tasmania (previously known as Van Diemen’s Land). The western half of the continent was never part of New South Wales and was originally known as the Swan River Colony, and later Western Australia.
With the exception of Western Australia, the other states and colonies were originally part of New South Wales. Victoria was known as the Port Phillip settlement before it became self-governing in 1851, and Queensland was the Moreton Bay settlement until 1859. Early records for both of those colonies will be in New South Wales, so it is important to know when the individual colonies and territories were established.
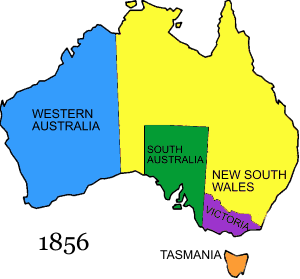
Australia in 1856 – image courtesy Wikipedia (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Territorial_evolution_of_Australia)
Similarly, a knowledge of geography is essential, as Australia is a huge continent with most of the population along the coastline. Another complicating factor is that there may be places with the same name in one or more colonies/states. For instance, if researching ancestors from Maryborough, it would be necessary to identify whether you should be researching Maryborough in Queensland or Maryborough in Victoria.
To make matters even more confusing, some places changed their name! For instance, until 1911 Innisfail in Queensland was called Geraldton, not to be confused with Geraldton in Western Australia on the other side of the continent. Bendigo was originally known as Sandhurst, and many of the goldfield towns in central Victoria were known under the broader name of the Mount Alexander goldfield. Knowing the history and geography will help you immensely as you embark on your Australian genealogy research.
Getting started with Australian genealogy research
If you have Australian genealogy there are many wonderful free online Australian resources that will give you a head start in researching your ancestors and learning more about their heritage. Wikipedia – Australia is a good starting place for an overview if you are unfamiliar with Australian history and geography. Depending on where your ancestors were, read the appropriate sections of history and geography. For example, convicts were sent to New South Wales and Tasmania until 1842 when the colony was opened up for free settlement, but Western Australia only received convicts from 1850 to 1868. The gold rushes in Victoria in the 1850s attracted thousands of people, as did later rushes in Queensland in the 1860s and Western Australia in the 1890s.
Many immigrants were looking for their own land and a better life for their families. Each of the colonies had their own immigration schemes in a bid to attract as many people as they could. Most colonial passenger lists are now indexed and can be searched online at the various state archives. Some states have even digitized the passenger lists, which may be viewed freely online. State archives are a wonderful free online resource, and include offices such as the Queensland State Archives, Public Record Office Victoria, or the Tasmanian Archive and Heritage Office.
A free useful portal site is CoraWeb – helping you trace your family history in Australia and elsewhere. It is divided up into categories such as archives, cemeteries, convicts, maps, probate and will records, shipping, migration, and other genealogy-related topics.
Australian birth, marriage, and death records
Like everything else, you need to know an approximate date and place before you begin to research birth, marriage, and death records. Prior to civil registration there are some church records which consist of mostly baptisms and marriages, with a few burials. Civil registration started at various times, and different colonies collected different information at different times, with South Australia having the least information on the certificates.
Van Diemen’s Land (later Tasmania) was the first to introduce civil registration in 1838, with Western Australia following in 1842, South Australia in 1842, Victoria in 1851, and New South Wales (including Queensland at that time) in 1856. Most states have online indexes available for searching, but only Queensland and Victoria provide digital copies of certificates for download after purchase. Western Australia still requires researchers to mail their applications with no online ordering.
Tasmania is perhaps the most helpful – with their early church records and births, marriage, and death certificates indexed, and digital copies online for free through the Tasmanian Archive and Heritage Office. The Tasmanian Name Index includes free indexed and digitized copies of various genealogical resources.
Federation in 1901 and the National Archives
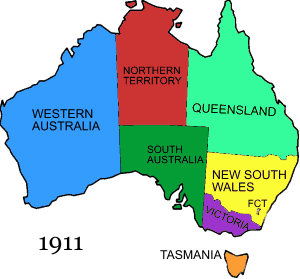 The individual colonies voted to form the Commonwealth of Australia in 1901, and since then there has also been a Commonwealth (later Federal) government. This took over some government functions such as the military, immigration, citizenship, and naturalization, although some states continued to have their own immigration schemes. This means that post-1901, researchers need to use the National Archives of Australia, as well as the various state archives.
The individual colonies voted to form the Commonwealth of Australia in 1901, and since then there has also been a Commonwealth (later Federal) government. This took over some government functions such as the military, immigration, citizenship, and naturalization, although some states continued to have their own immigration schemes. This means that post-1901, researchers need to use the National Archives of Australia, as well as the various state archives.
In 1911 the final changes to the map of Australia took place, with the separation of the Northern Territory from South Australia, and the establishment of the Australian Capital Territory within southern New South Wales.
With the centenary of World War One, the National Archives of Australia has digitized all army dossiers and made them freely available online. RecordSearch is the main database, and it can be searched in a number of ways including a “Name Search” and “Passenger Arrivals.” While not every record series is indexed by name, it can be useful to search for an individual’s name, especially if they arrived post-1901 or served in the military during either World War.
Australian Newspapers and Photographs
In Australia, digitized newspapers are freely available online through Trove, which is maintained by the National Library of Australia. Along with newspapers, Trove also includes government gazettes, books, articles, maps, manuscripts, photographs, archived websites, and other resources. If you are interested in what a place looked like at the time your ancestors lived there, then try an image search in Trove. Remember that it is continually being added to, so it is essential that you revisit your searches from time to time. (Click here to read another Genealogy Gems article about Trove.)

Christoe Street, Copperfield Queensland in 1876 when my ancestors lived there. Image courtesy State Library of Queensland via Trove.
Individual state libraries also have genealogy sections with online guides to various family history topics. These can be a good place to start, and most participate in the ‘Ask a Librarian’ where you can get advice and information. However, they cannot do individual research – just answer questions.
 About Legacy Tree Genealogists
About Legacy Tree Genealogists
 EXCLUSIVE OFFER for Genealogy Gems readers! Receive $100 off a 20-hour+ research project from Legacy Tree Genealogists with code GGP100.
EXCLUSIVE OFFER for Genealogy Gems readers! Receive $100 off a 20-hour+ research project from Legacy Tree Genealogists with code GGP100.
Legacy Tree Genealogists is the world’s highest client-rated genealogy research firm. Founded in 2004, the company provides full-service genealogical research for clients worldwide, helping them discover their roots and personal history through records, narratives, and DNA. To learn more about Legacy Tree services and its research team, visit the Legacy Tree website.
Disclosure: This article contains offers with affiliate links, which may expire without notice. Genealogy Gems will be compensated if you make a purchase after clicking on these links (at no additional cost to you). Thank you for supporting Genealogy Gems!

