How German Address Books at Ancestry.com are Helping Bust Brick Walls
My genealogy research looks a lot like yours. Some family tree lines go back to pre-Revolutionary War. Other lines are richly researched well into the early 19th century.
And then there’s THAT family line. You know the one I mean. The one where the courthouse containing the records we need has burned down, or the records were microfilmed ages ago but are still sitting in the FamilySearch granite vault due to copyright issues. Or worst of all, it appears the needed records just don’t exist.
Don’t let these obstacles allow you to give up hope.

Every day, new records are being discovered and digitized. Records that have been languishing in a copyright stalemate might suddenly be cleared for publication. Or a cousin could contact you out of the blue and has the letters your grandmother sent hers. We never know when the records we’ve been waiting for, searching for, and yearning for, will bubble up to the surface.
Today I’m happy to share my story of a recent breakthrough that I never saw coming. Follow along with me as I take newly unearthed rocks and use tools to turn them into sparkling gems.
This is Almost Embarrassing
My one, agonizing family line that stops short in its tracks ends with my great grandfather Gustave Sporowski.
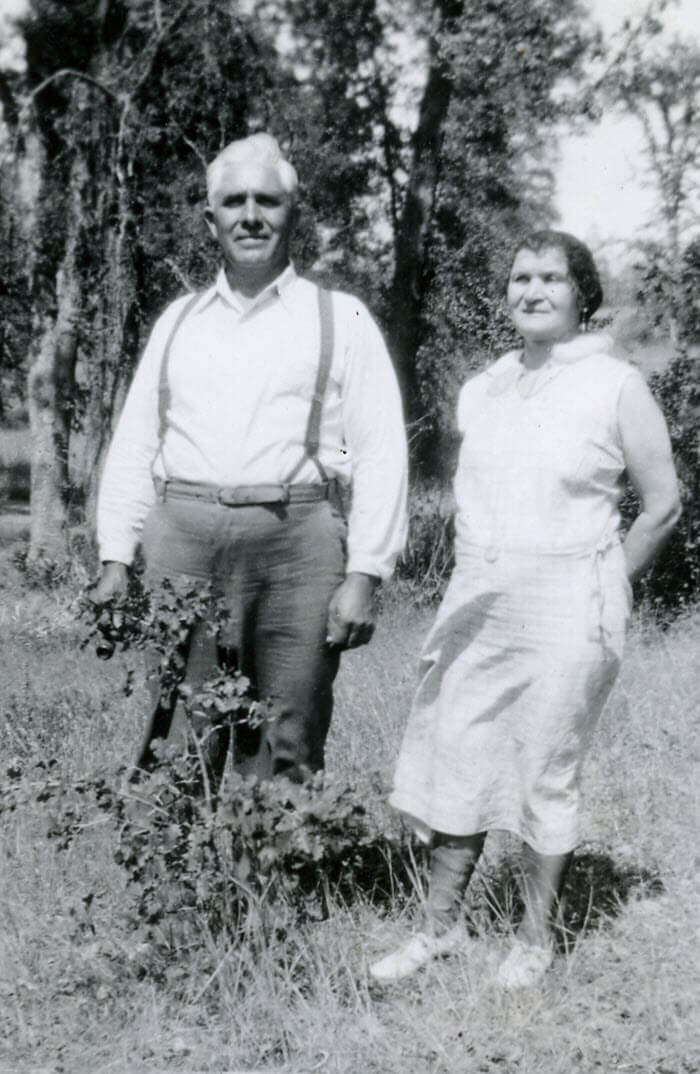

Gustave and Louise Sporowski (personal collection)
It’s almost embarrassing to admit. I’ve been at this nearly my whole life, and genealogy is my career for goodness sake! But there it is, a family tree with lovely far-reaching limbs except for this little stub of a branch sticking out on my maternal grandmother’s side.
I was about eight years old the first time I asked my grandma about her parents and their families. (Yes, this genealogy obsession goes back that far with me!) I still have the original page of cryptic notes she scratched out for me during that conversation.
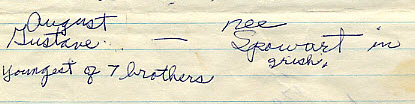
Excerpt from Grandma’s original notes. (Personal collection)
She had several nuggets of information about her mother’s family. However, when it came to her father Gustave, she only recalled that he was the youngest of seven brothers. No names came to mind. I’ve always felt that if I could just identify some of the brothers, one of them may have records that provide more details about their parents.
According to his Petition for Naturalization, Gustave Sporowksi and Louise Nikolowski were married in LutgenDortmund, Germany. This indicated that both moved west from East Prussia before emigrating. While I knew Louise’s immediate family were in the LutgenDortmund area as well, I had no idea whether Gustave moved there on his own or with his family.

Gustave Sporowski’s Petition for Naturalization.
Gus (as he was later known) emigrated from Germany in 1910, landing at Ellis Island. He toiled in the coal mines of Gillespie, Illinois, and eventually earned enough money to move his wife and children west to California in 1918.
After filing his papers and years of waiting, he proudly became a U.S. citizen in 1940.
On that paperwork, he clearly states his birthplace as Kotten, Germany. You won’t find this location on a map today. In 1881, the year he was born, the area was East Prussia. I remember the hours I spent with gazeteers many years ago trying to locate that little village nestled just within the border of Kreis Johannisburg. Being so close to the border meant that he could have attended church there or in a neighboring district.
The records in the area are scarce, and today the entire area is in Poland.
Surprisingly, the records situation is quite the opposite with his wife Louise, also from East Prussia. She lived not far away in Kreis Ortelsburg, and the records for the church her family attended in Gruenwald are plentiful. I’ve managed to go many more generations back with her family.
And so, poor Gus alone sits in my family tree.
I periodically search to see if there’s anything new that has surfaced, but to no avail. I even hired a professional genealogical firm to review my work and suggest new avenues. I guess it is good news to hear you’ve pursued all known available leads, but it’s not very rewarding.
Over time, we tend to revisit tough cases like this less frequently. They become quiet. Digital dust begins to settle on the computer files.
And then it all changes.
German Address Books at Ancestry.com
I regularly make the rounds of the various genealogy websites, making note of new additions to their online collections. I typically publish the updates on a weekly basis here on the Genealogy Gems blog. It makes my day when readers like you comment or email, bursting with excitement about how one of the collections I mentioned busted their brick wall. I love my job.
This week I’m the one who is bursting!
It started simply enough. My third stop on my regular records round-up tour was Ancestry.com. The list of new records was particularly robust this week. The word “Germany” always catches my eye, and the second item on the list jumped out at me:
Germany and Surrounding Areas, Address Books, 1815-1974
“Recently Added and Updated Collections on Ancestry,” Ancestry.com (http://www.ancestry.com : accessed 05 Sept 2019)
I should have had a healthy dose of skepticism that I would be fortunate enough to find anything. But to be perfectly honest, I felt instinctively that I would! Have you ever just had that feeling that your ancestors are sitting right there ready to be found? If you’ve been researching your family history for a while, then I’m guessing you have. Such a nice feeling, isn’t it?
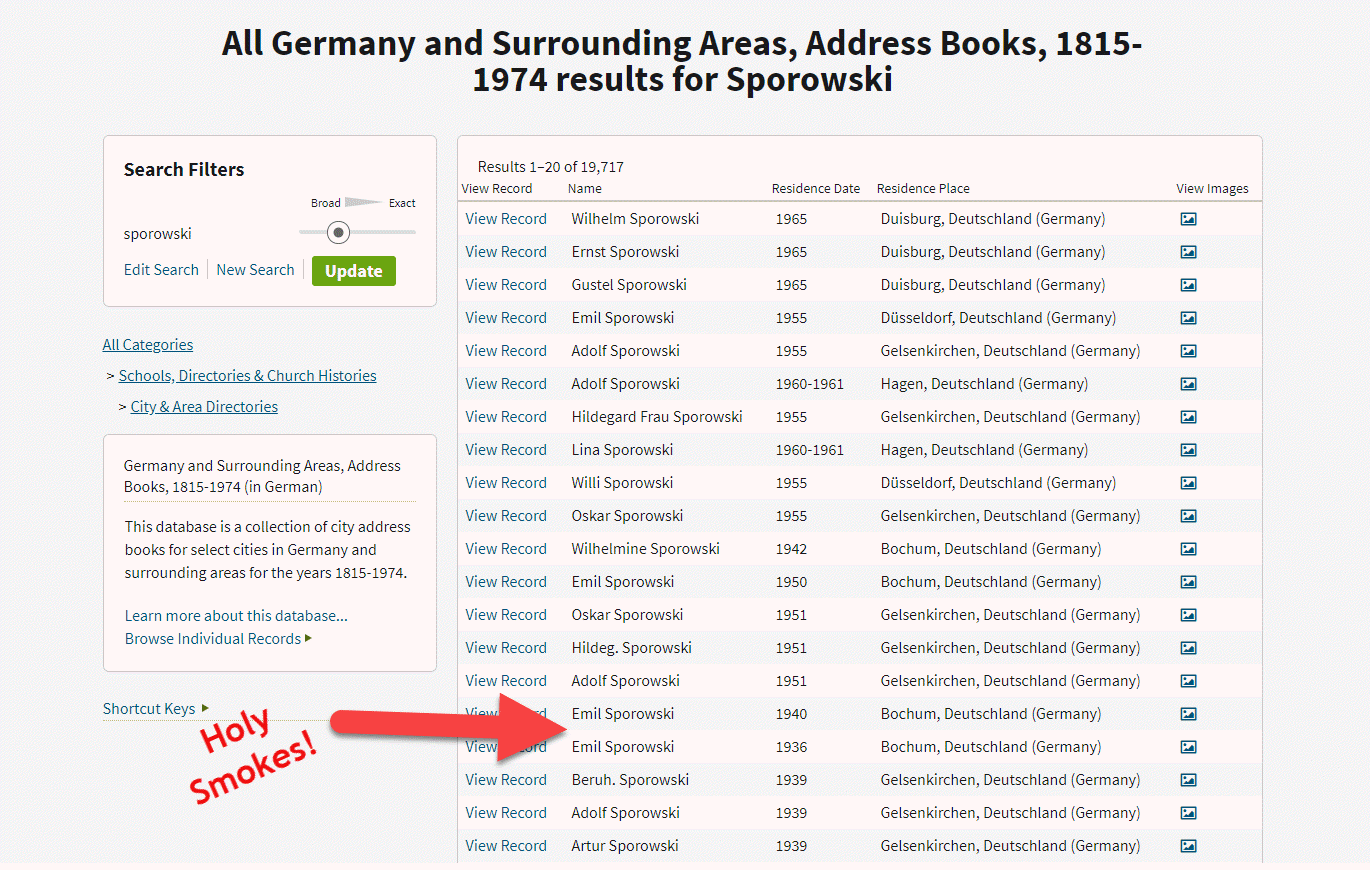
So, I clicked, and I simply entered Sporowski in the last name field and clicked Search.
Experience has taught me that there haven’t been a lot of folks through history with this surname, so I’m interested in taking a look at anyone who pops up in the results. And yippie aye oh, did they ever pop up!
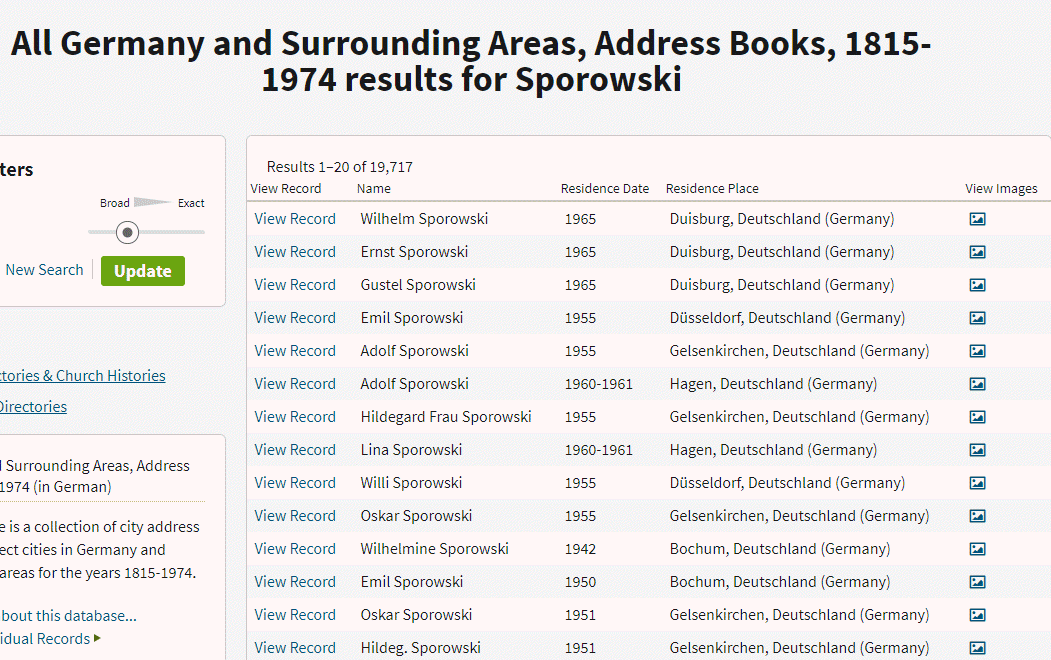
“All Germany and Surrounding Areas, Address Books, 1915-1974,” Ancestry.com (http://www.ancestry.com : accessed 05 Sept 2019)
The results list include 31 people with the surname of Sporowski!
These names came from the pages of address books much like the city directories so common in the U.S. Since this collection was new to me, I took a moment to read up on the history.
______________________________
GENEALOGY RESEARCH TIP: Learning the History of the Genealogy Record Collection
To truly understand what you are looking at when reviewing search results, we need to acquaint ourselves with the history of the collection.
- Why was it created?
- What does it include?
- What does it not include?
Look to the left of the search results and click Learn more about this database.
It’s definitely worth clicking this link because the next page may also include a listing of Related Data Collections, some of which you might not be aware. These could prove very useful, picking up the pace to finding more records.
In the case of foreign language records, look for a link to the Resource Center for that country. There you may find translation help and tips for interpreting handwriting and difficult-to-read script.
Ancestry Help Features
______________________________
On the Learn more about this database page, I learned some important things about these search results.
First, not every citizen was listed. Only heads of households were included. This means that wives and children would not appear. I did find some widows, though, because they were the head of their household.
Second, Optical Character Recognition (OCR) was used on this collection. Ancestry suggests looking for errors and providing corrections. But this information about OCR also implies something even more important to the genealogist. We must keep in mind that OCR is not perfect. In this case, I planned on browsing the collection after reviewing the search results to ensure I didn’t miss anyone. This would include targeting people listed in the “S” section of directories for towns I might expect the family to be.
I was particularly thrilled to see the name “Emil Sporowski” on the list.
Several months ago I found a World War I Casualty list from a newspaper published in 1918.

On it was listed Emil Sporowski and he was from the village of Kotten. This was the first mention of Gustave’s birthplace in the record of another Sporowski that I had ever found. So, you can imagine my delight as I stared at his name in the address book search results.
“All Germany and Surrounding Areas, Address Books, 1915-1974,” Ancestry.com (http://www.ancestry.com : accessed 05 Sept 2019)
The icing on that cake was that he was listed in the address book of Bochum. That town name was very familiar to me because I had seen it on a few old family photos in Louise Sporowski’s photo album. Although the photos did not have names written on them, I could easily identify the folks who had the facial characteristics of Louise Nikolowski’s clan, and those sporting the large eyes with heavy lids like Gus.
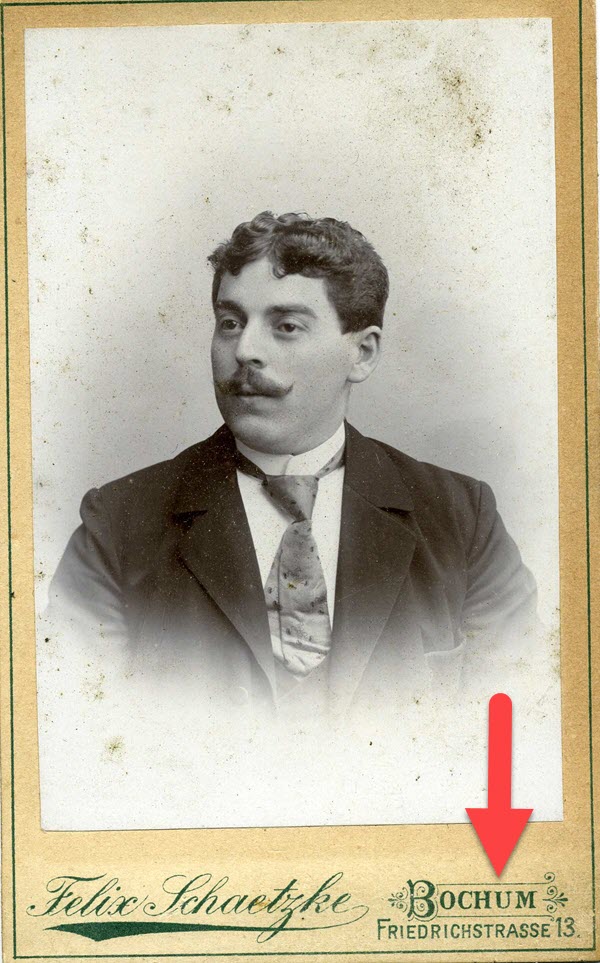

Photo from Louise Nikolowski’s photo album.
Spreading the German Addresses Out with Spreadsheets
With one and a half pages delivering a total of 31 Sporowski names, I knew I had some work ahead of me to tease them apart. This got me thinking of Genealogy Gems Podcast episode that I’m currently working on, which features a conversation with professional genealogist Cari Taplin. When I asked Cari how she organizes her data, she told me that she uses spreadsheets. I’m not typically a spreadsheet kind of gal, but in this case, I could see the benefits. Spreadsheets offer a way to get everybody on one page. And with the power of Filters and Sorting you slice and dice the data with ease. My first sort was by town.
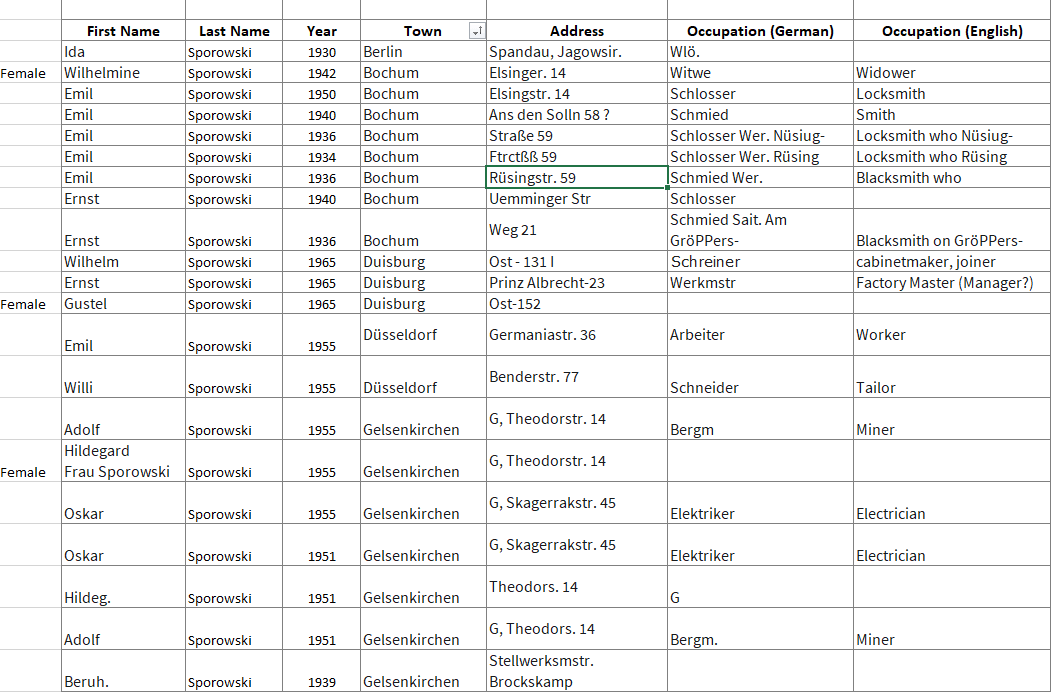
My Excel spreadsheet tracking German Address Books search results at Ancestry.com
______________________________
GENEALOGY RESEARCH TIP: Free Genealogy Gems Download
Click here to download the simple yet effective spreadsheet I used for this research project. If you find your German ancestors in this collection, it’s ready to use. Otherwise, feel free to modify to suit your needs in a similar situation.
______________________________
As you can see in the spreadsheet, these address books include occupations. For example, Emil was listed both as a Schmied and a Schlosser. A simple way to add the English translation to my spreadsheet was to go to Google.com and search Google Translate. Words and phrases can be translated right from the results page.
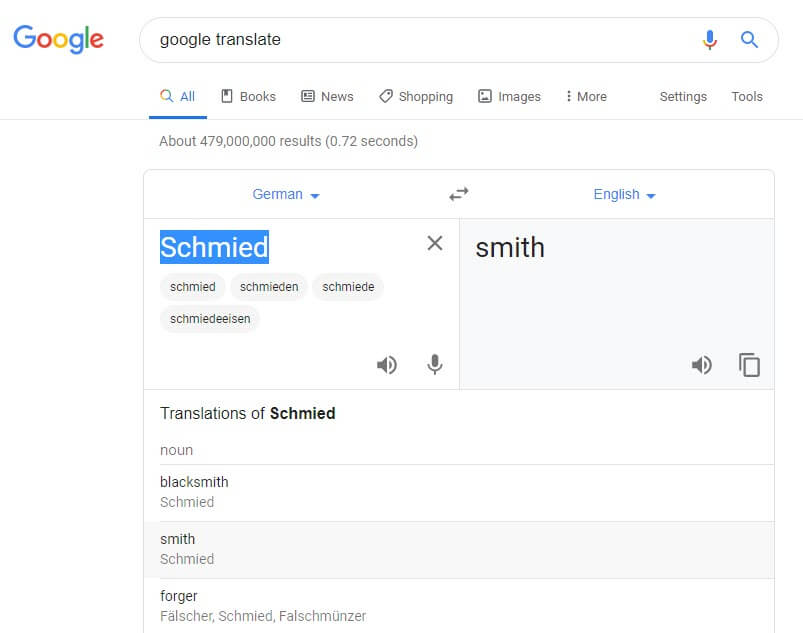
Translating the Occupation found in the German Address Books using Google Translate (Available at https://translate.google.com. Accessed 05 Sept 2019)
You can also find several websites listing German occupations by Googling old german occupations.
I quickly ran into abbreviations that were representing German words. For example, Lina Sporowski is listed with as Wwe .
A Google search of german occupations abbreviations didn’t bring a website to the top of the list that actually included abbreviations. However, by adding one of the abbreviations to the search such as “Wwe.” it easily retrieved web pages actually featuring abbreviations.
One of the top results was by friend of the podcast Katherine Schober and her SK Translations blog post called 19 Most Common Abbreviations in German Genealogy.
______________________________
GENEALOGY RESEARCH TIP: Use Search Operators when Googling
Notice that I placed the abbreviation in quotation marks when adding it to my Google search query. Quotation marks serve as search operators, and they tell Google some very important information about the word or phrase they surround.
- The quotation marks tell Google that this word or phrase must appear in every search result. (If you’ve ever googled several words only to find that some results include some of the words, and other results include others, this will solve your problem.)
- They also tell Google that the word(s) MUST be spelled exactly the way it appears on each search result. This is particularly helpful when searching an abbreviation like Wwe. which isn’t actually a word. Without the quotation marks, you will likely get a response from Google at the top of the search results page asking you if you meant something else.
Click here to receive my free ebook including all the most common Google search operators when you sign up for my free newsletter (which is always chock full of goodies).
______________________________
Katherine was my guest on Genealogy Gems Premium Podcast Episode #151 available exclusively to our Premium eLearning Members. She’s also written a couple of articles for Genealogy Gems on German translation:
When to Use Google Translate for Genealogy–And Best Translation Websites for When You Don’t
Translating German Genealogy Records: 9 Top German Translation Websites
Deciphering Place Names Just Got Easier
I’ve written an article you may find helpful not only for translation but also to help you with pronunciation called How to Pronounce Names: Google Translate and Name Pronunciation Tools.
As it turns out, Wwe. stands for Widow. This tells me that Lina’s husband was deceased by 1961.
Finding the German Addresses in Google Earth
The most glorious things found in these old address books are the addresses themselves!
Google Earth is the perfect tool to not only find the locations but clarify the addresses. Many were abbreviated, but Google Earth made quick work of the task.
Unlike other free Google Tools, Google Earth is available in a variety of forms:
- Free downloadable software
- Google Earth in the Chrome Web browser
- A mobile app
Each has powerful geographic features, but I always recommend using the software. The web version and app don’t have all the tools available in the software. All versions require an internet connection. You can download the software here.
In the Google Earth search box I typed in the address. Don’t worry if you don’t have the full address or if you think it may be spelled incorrectly. Google Earth will deliver a results list of all the best options that most closely match.
In my case, reliable Google Earth not only gave me complete addresses, but also the correct German letters.
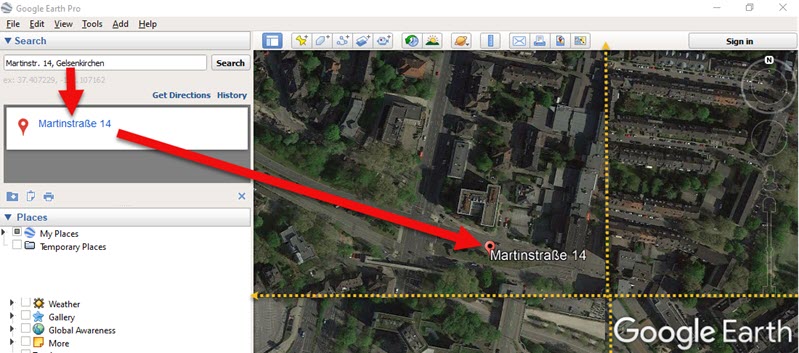
Finding the full name of the German address. (Map data ©2019 Google Earth software: accessed 6 Sep 2019)
Soon I found myself virtually standing outside their homes thanks to Google Earth’s Street View feature!

Home of my German ancestor found in Google Earth in Street View. (Map data ©2019 Google Earth software: accessed 6 Sep 2019)
Here’s how to use Street View in Google Earth:
- Zoom in close to the location
- Click on the Street View icon in the upper right corner (near the zoom tool)
- Drag the icon over the map and blue lines will appear where Street View is available
- Drop the icon directly on the line right next to the house
- Use the arrow keys on your keyboard to navigate in Street View or simply use your mouse to drag the screen
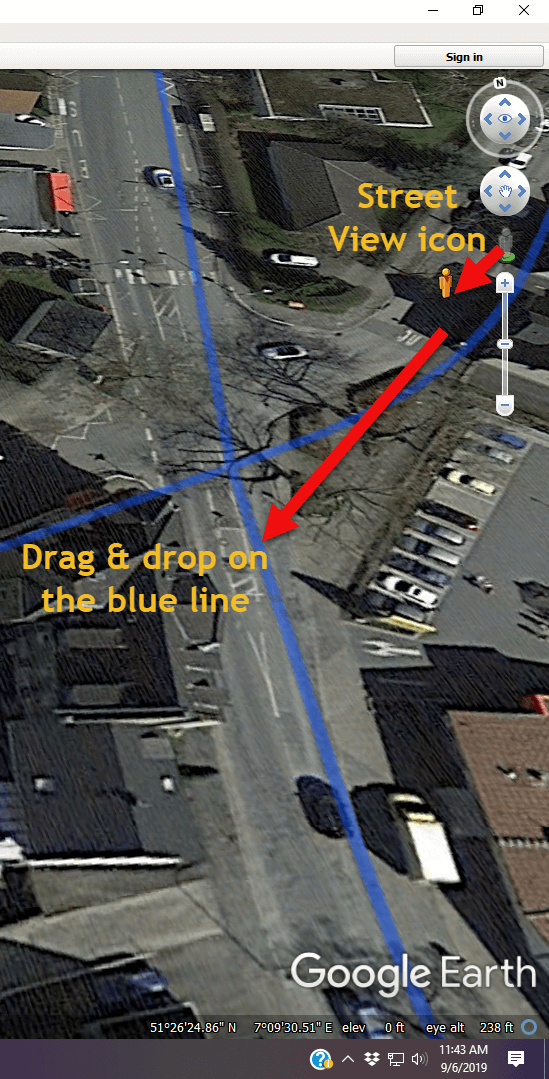
Using Google Earth Street View. (Map data ©2019 Google Earth software: accessed 6 Sep 2019)
I went through the entire list. As I found each location in Google Earth, I checked it off on the spreadsheet.
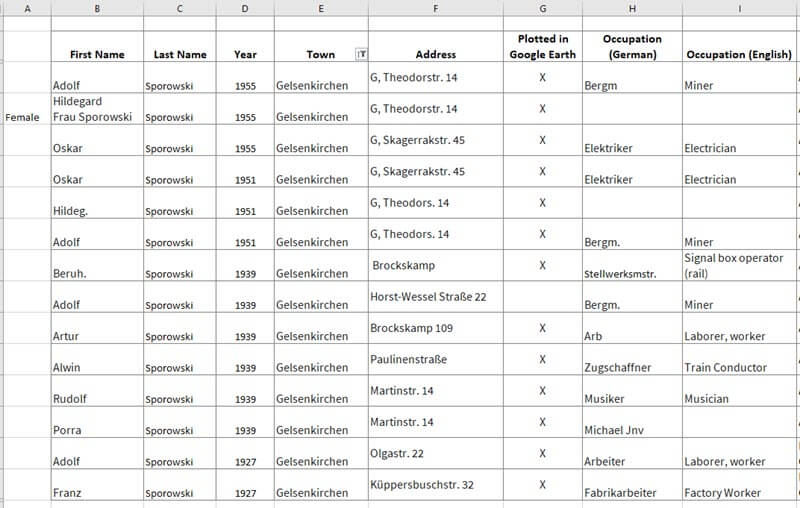
Addresses found in German Address Books at Ancestry.com marked in the spreadsheet
GENEALOGY RESEARCH TIP: Create a Folder in Google Earth
When you have several locations like this to plot, I recommend creating a folder in the Places panel in Google Earth. It’s super easy to do and will help you stay organized. Here’s how:
- Right-click (PC) on the MyPlaces icon at the top of the Places panel (left side of the Google Earth screen)
- Select Add > Folder in the pop-up menu
- A New Folder dialog box will appear
- Type the name of your folder
- Click OK to close the folder
- You can drag and drop the folder wherever you want it in the Places panel
- Click to select the folder before placing your Placemarks. That way each placemark will go in that folder. But don’t worry, if you get a placemark in the wrong spot, just drag and drop it into the folder.
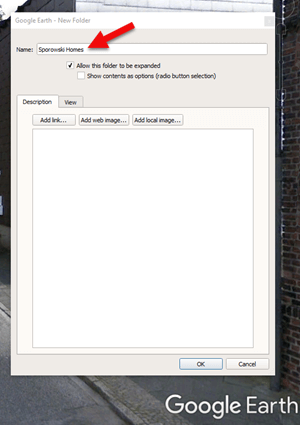
Creating a Folder for the German Addresses found at Ancestry.com (Map data ©2019 Google Earth software: accessed 6 Sep 2019)
It didn’t take long to build quite a nice collection of Sporowski homes in Germany!
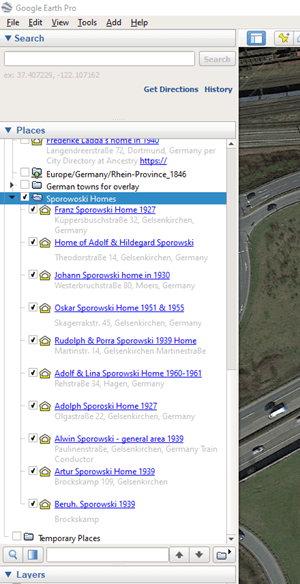
German addresses in the Places panel. (Map data ©2019 Google Earth software: accessed 6 Sep 2019)
The beauty of Google Earth as that you can start to visualize your data in a whole new way. Zooming out reveals these new findings within the context of previous location-based research I had done on related families. As you can see in the image below, all the Sporowskis that I found in the German Address books at Ancestry.com are clustered just five miles from where photos were taken that appear in Louise Sporowski’s photo album.
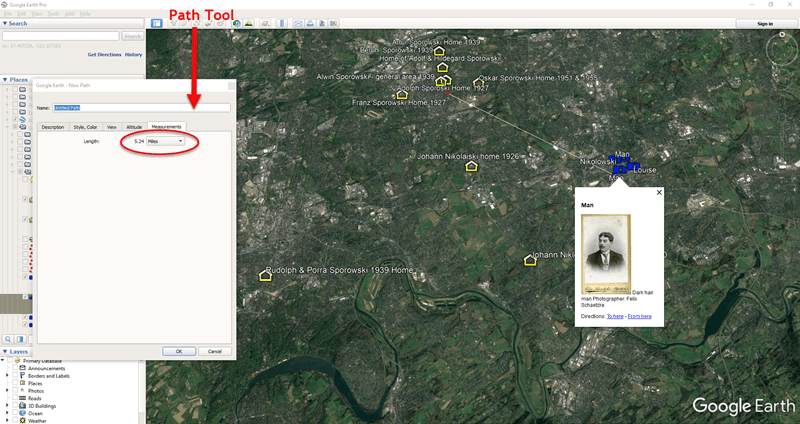
Data Visualization in Google Earth: My German Families found in Address Books. (Map data ©2019 Google Earth software: accessed 6 Sep 2019)
I’ve Only Just Begun to Discover my German Ancestors at Ancestry.com
We’ve covered a lot of ground today, but this is just the beginning. There are additional sources to track down, timelines to create, photos to match up with locations, and so much more. In many ways, I’ve only scratched the surface of possibilities. But I need to stop writing so I can keep searching! 😊
I hope you’ve enjoyed taking this journey with me. Did you pick up some gems along the way that you are excited to use? Please leave a comment below! Let us all know which tips and tools jumped out at you, and any gems that you found.