by Lisa Cooke | May 13, 2014 | 01 What's New, Family History Podcast, Immigration
Family History: Genealogy Made Easy Podcast
with Lisa Louise Cooke
Republished May 13, 2014
Listen to the Family History: Genealogy Made Easy podcast by Lisa Louise Cooke. It’s a great series for learning the research ropes and well as refreshing your skills.
https://lisalouisecooke.com/familyhistorypodcast/audio/fh31.mp3
Download the Show Notes for this Episode
Welcome to this step-by-step series for beginning genealogists—and more experienced ones who want to brush up or learn something new. I first ran this series in 2008-09. So many people have asked about it, I’m bringing it back in weekly segments.
Episode 31: Immigration and Naturalization Records for Family History, Part 3
Did you know that all those annotations and scribbles on passenger lists may hold important clues to your family history? In this episode, we continue our discussion with Stephen Danko about immigration and naturalization records. (If you missed them, they are Episodes 29 and 30.) Specifically,we’ll listen in on a presentation he gave on passenger list annotations and what the immigrant’s experience was like at Ellis Island.
So we’ve talked already about ship passenger arrival lists. Now let’s get out the magnifying glass, so to speak. We’ll look closely at the little notes on this records.
Annotations on passenger lists could have made upon departure, arrival or later when that immigrant applied for citizenship. One of the common misconceptions about passenger lists is that they were not filled out at Ellis Island, as many people believe. Rather they were completed at the port of departure. So notes could have been made at a variety of different times.
Here are three examples of annotations that were made upon a person’s arrival in the United States:
D=detained for inquiry
SI or DSI=Special Inquiry or Detained for Special Inquiry—this was really bad! (listen to the podcast to hear why)
USC=Was born in the U.S. or was a U.S. citizen
For a more thorough list of annotations on passenger records, read Stephen’s handout he graciously shared with us: A New Look at Immigrant Passenger Manifests. His companion blog posts (see Updates and Links below) show you real-life examples.
Here are some more great tips from that conversation:
- Check at the end of the manifest for pages called Record of Detained Alien Passengers, and Records of Release of Aliens Held for Special Inquiry.
- Our ancestors could have traveled back and forth from their homeland several times before they became citizens. Those passenger lists are just as valuable as their original immigration. If they hadn’t completed the naturalization process yet, then you may find an indication of that re-entry number or their citizenship status.
- As Stephen mentioned in a previous podcast, depending on the timeframe, your ancestor may have had to request a certificate of arrival when applying for citizenship. And if you haven’t found their naturalization records yet, and are lucky enough to find a certificate of arrival annotation on the passenger list, then you will have a really good chance for tracking them down.
- Certificates of arrival were required for anyone who applied for citizenship beginning in 1926 who had arrived after 1906. Annotations on the passenger list about the certificate of arrival (C/A) can lead you to where and when they applied for citizenship. A number like 1X-151953 indicates a request for a certificate of arrival was made after 1926 to help with the naturalization process. The first number “1” is the naturalization district, if there is an “X” it means the person didn’t have to pay for the Certificate of Arrival and the numbers after the dash are the certificate of arrival number or the application number. The date of the certificate of arrival may appear after this number sequence.
- Another code, VL, is the verification of landing, often seen for arrivals before 1906, before certificates of arrival were issued.
- Numbers like 432731 / 435765 = the passenger was a permanent resident of the U.S. and was returning home with a re-entry permit.
- If someone’s name was crossed out on the passenger list but the rest of the line was not, it probably means their name was amended. It was likely misspelled.
- Look through every page of the ship’s manifest for your ancestor’s voyage. You may find record of stops the ship made along the way, recording of friends or relatives, or even a second entry for your ancestor as Stephen mentioned in the case of changing class of ticket.
- The more recent the passenger list, the more information we’ll find and possibly the more annotations we may find. In my case my great-grandparents made the journey from Antwerp Belgium in 1910. In looking back over their passenger lists (they each have their own because they traveled three months apart) I found numbers and markings on their record that I hadn’t really paid much attention to. So when I heard Stephen’s talk I was very excited to figure out their meaning!
Listen to the podcast itself for more details on:
- Head taxes charged;
- Names entered at port of departure for people who may not have sailed;
- Why a person might appear twice on a passenger list;
- Notations that they were hospitalized upon arrival—or that they died there;
- The number of meals eaten at Ellis Island; and
- Grounds for exclusion for entry to the U.S.
Updates and Links
A New Look at Immigrant Passenger Manifests. This pdf by Stephen Danko provides a timeline history of the information requested on passenger lists. You’ll also find annotations made before and after arrival.
Stephen’s Blog: A New Look at Immigrant Passenger Manifests
Stephen’s Blog: More Annotations on Immigrant Passenger Manifests
One-Step Webpages by Stephen P. Morse (Ellis Island Search Tool)
by Lisa Cooke | Jun 27, 2015 | 01 What's New, Craft & Displays, Gifts, images, Listeners & Readers, Photographs
 Recently, Genealogy Gems Premium member Mary Ann shared some beautiful family history crafts with us. One is this exquisite family history photo display she made for a cousins’ gift exchange. It’s a collage concept that incorporates pictures with mementos and meaningful embellishments, but in a beautifully orderly fashion.
Recently, Genealogy Gems Premium member Mary Ann shared some beautiful family history crafts with us. One is this exquisite family history photo display she made for a cousins’ gift exchange. It’s a collage concept that incorporates pictures with mementos and meaningful embellishments, but in a beautifully orderly fashion.
“This was so easy to make,” Mary Ann wrote. “The hardest part was rounding up the photos I wanted to use, then sizing them to fit the appropriate little openings. I use Photoshop Elements for my photos and digital scrapbooking so I cropped and sized the photos there, put them all into one larger page so I could print all at once, printed a draft on printer paper to make sure the photos were the correct size then printed my good version on photo paper.
“When I made the photo tray a few years ago, I found the tray in my local Archiver’s scrapbooking store. Archiver’s has since closed their retail stores but they sell online. I was looking at their site last night and found the same item for sale that I used in my project. Here is the link to the item.
“I cut out my photos, some of which filled the entire little opening, but if they didn’t, I added some scrapbook paper as a background to those. The “generations” and “ancestry” tags, as well as the ovals, flowers and key, are all scrapbooking embellishments. I used little pieces of ribbon under the outhouse photo, as a bow on the key and to cover the “handle” of the tray. I had some leftover lace I used to trim the bottom of the box. I copied a piece of a census record that showed my grandparents’ names and some of my aunts and uncles. I used acid-free double sided tape made for scrapbooking to attach it all. And I found the little frame to put on my grandfather’s photo.”
Mary Ann also hopes to create a photo tray like this for her son’s school photos (she saw the idea online) but hasn’t gotten to it yet. But she got a lot of mileage out of the one she did finish. “I made a total of 6 of these, all alike, and gave the remainders later as Christmas gifts to my mom, an aunt and a couple cousins,” she tells us. “And I was even clever enough to keep on for myself. My aunt told me she cried when she opened it and saw what it was.”
I remember little display trays like this being popular in the 1970s or 1980s, too. I’ve seen them at resale and antique shops, and tucked away in friends’ basements and attics. You may be able to find vintage trays that are less-expensive than the new ones. This inspiring idea made me wonder what mementos, tiny memorabilia, embellishments and even photocopied genealogy records I would tuck into my own version of this project.
 We’ve got more beautiful ideas like this on our Pinterest boards! Check them out: Family History Craft Projects, Legacy Displays and Heritage Scrapbooking for Family History.
We’ve got more beautiful ideas like this on our Pinterest boards! Check them out: Family History Craft Projects, Legacy Displays and Heritage Scrapbooking for Family History.
by Diahan Southard | Jul 16, 2014 | 01 What's New, Digital Archives, German, History, Newspaper
 Do you have German roots in the U.S.? Have you ever looked for them in newspapers?
Do you have German roots in the U.S.? Have you ever looked for them in newspapers?
The folks who run Chronicling America, the most comprehensive free collection of digitized U.S. newspapers, have published a new article on historical German newspapers. Here’s an excerpt:
“For decades, Germans were the largest non-English-speaking immigrant group in America. Between 1820 and 1924, over 5.5 million German immigrants arrived in the United States, many of them middle class, urban, and working in the skilled trades, and others establishing farming communities in the West. Their numbers and dedication to maintaining their language and culture made Germans the most influential force in the American foreign-language press in the 1880s – the 800 German-language newspapers accounted for about 4/5 of non-English publications, and by 1890, more than 1,000 German newspapers were being published in the United States.” (Click here to read the whole article, which includes fascinating facts about how they retooled OCR technology to read Fraktur.)
Chronicling America currently includes 23 German-language titles from 9 states. You can search German newspapers in America (or other foreign languages) by going to the Advanced Search page. Under Language, select German (or another language):

Are you interested in learning more about newspaper research, online or offline? Read Lisa’s How to Find Your Family History in Newspapers, available as an e-book or in print. Or ask for it at your local library (if they don’t have it, they may be willing to purchase it–librarians are always looking for new titles their patrons want).
by Lisa Cooke | Jun 22, 2015 | 01 What's New, African-American, Brick Wall, FamilySearch, images, Records & databases, School Records, United States, Volunteer
 The more I learn about U.S. history and records, the more I appreciate the challenges faced by those researching their African-American roots. In addition to the emotional toll of learning about their ancestors’ hardships, today’s researchers face the practical challenges of finding kin in records that mostly ignored their existence.
The more I learn about U.S. history and records, the more I appreciate the challenges faced by those researching their African-American roots. In addition to the emotional toll of learning about their ancestors’ hardships, today’s researchers face the practical challenges of finding kin in records that mostly ignored their existence.
That’s why I’m super excited that the Freedmen’s Bureau records are finally being fully indexed. Scattered records are already transcribed (see the Freedmen’s Bureau Online). But there hasn’t been a comprehensive index of its 1.5 million state field agency documents. These include military pensions, marriage records, property claims, hospital records, trial summaries, labor contracts, school rolls, registers and censuses. Many of the four million African-Americans freed from slavery are mentioned, as are many white Southerners.
FamilySearch indexers began quietly indexing Freedmen’s Bureau records in 2009: the state of Virginia’s records are already searchable. Last week, in observance of the Juneteenth holiday (which celebrates emancipation), FamilySearch issued a call to action. They asked for help indexing the rest of the Freedmen’s Bureau within the year.
“Records, histories and stories will be available on DiscoverFreedmen.org,” says a release. “Additionally, the records will be showcased in the Smithsonian’s National Museum of African American History and Culture, which is currently under construction on the National Mall in Washington, D.C., and expected to open in late 2016.”
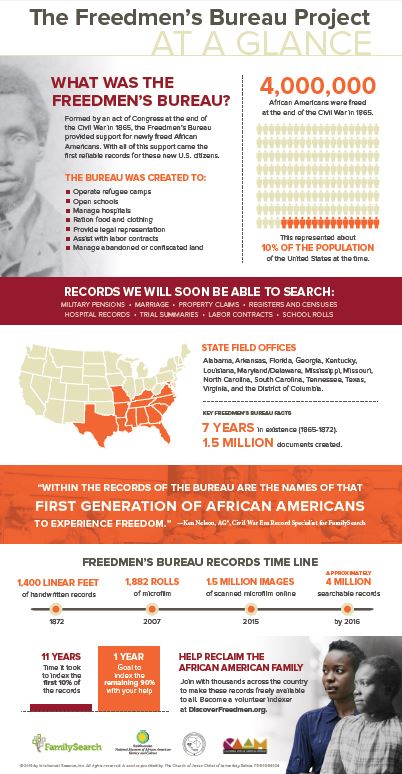 Here’s a quick history lesson: The Freedmen’s Bureau was organized after the Civil War to aid newly-freed slaves in 15 states and Washington, DC. For several years it gathered “handwritten, personal information on freed men, women and children, including marriage and family information, military service, banking, school, hospital and property records,” according to FamilySearch.
Here’s a quick history lesson: The Freedmen’s Bureau was organized after the Civil War to aid newly-freed slaves in 15 states and Washington, DC. For several years it gathered “handwritten, personal information on freed men, women and children, including marriage and family information, military service, banking, school, hospital and property records,” according to FamilySearch.
The richest genealogical records of the Freedmen’s Bureau are in the field office records of each state. Click here to download a PDF from the National Archives about these original records.
Find more tips on finding African-American and other Southern U.S. ancestors here on the Genealogy Gems website. Recent posts include:
 Receive a heads-up about posts like these–and get a free e-book on Google searching for genealogy–when you subscribe to the free Genealogy Gems newsletter in the upper right corner of this webpage or our home page.
Receive a heads-up about posts like these–and get a free e-book on Google searching for genealogy–when you subscribe to the free Genealogy Gems newsletter in the upper right corner of this webpage or our home page.
by Lisa Cooke | Oct 27, 2014 | 01 What's New, Inspiration, Listeners & Readers
Recently I heard from Emily, a mom of younger children who is feeling inspired to take her love for family history in a more professional direction. Have you considered becoming a professional genealogist yourself? You’ll want to check out an interview I told her about (see below). Anyone can take their life’s experiences and channel them into their career path!
“Dear Lisa,
I was at the Midwestern Roots conference today and I just wanted to say ‘thanks’ for something you said at your opening session this morning. You were talking about when your daughters gave you the iPod and how you were at a point in your life when you were trying to figure out what to do, and I think you even used the expression ‘just a mom.’
I really related to what you said. I am a mom to two younger kids, I love my family history research, and I’m trying to find a new professional direction in life. So, you’ve given me some hope that maybe I can use my love of genealogy to (somehow) help and teach other people.
Probably not the typical type of ‘thank you’ note you usually receive, but I just wanted you to know.”
Hi Emily,
You are very welcome and how sweet of you to take the time to write. Believe me when I say that “just a mom” was a reference to the fact moms often get that sort of response from the culture these days. (I know that other moms know what I mean.) Being a mom is the highest calling possible, and remains my first priority. And the great news is that technology makes it possible more than ever to pursue additional dreams!
I think you might enjoy a special interview I gave recently to the Genealogy Professional Podcast. It was for folks just like you. You’ll also find additional interviews at the bottom of my About page on my website.
Wishing you great success as you pursue your dreams!!
Lisa








