by Lisa Cooke | May 27, 2016 | 01 What's New
 Here are this week’s collections of new genealogy records online. Included are Scotland mental health records and, in the U.S., WWII draft registrations, WI probate and NY marriages and deaths.
Here are this week’s collections of new genealogy records online. Included are Scotland mental health records and, in the U.S., WWII draft registrations, WI probate and NY marriages and deaths.
SCOTLAND – GLASGOW – MENTAL HEALTH. Arranged by county, the pages contain details of all licensed institutions operating in 1857 when a special report of the Royal Lunacy Commission was being prepared. The Mental Health Institutions Index will give you the information you need to order the entire record.
U.S. – MILITARY. Eight new states have been added to the U.S. World War II Draft cards, 1942 on Fold3.com. New states include North Carolina, Colorado, Arizona, Pennsylvania, Maryland, Delaware, New Mexico, Washington DC, and the U.S. Virgin Islands. These draft cards are a collection of The Fourth Registration, also known as “old man’s registration.” Men participating in this draft were born on or between 28 April 1877 and 16 February 1897.
U.S. – WISCONSIN- PROBATE. Wisconsin, Wills and Probate Records for 1800-1987 have been updated at Ancestry.com. This collection includes images of probate records for approximately 50 percent of Wisconsin counties. Wills, Letters of Administration, Guardianships, Inventories, and Bonds are just a few of the great gems you will buy erectile dysfunction medication online find there!
U.S. – NEW YORK- MARRIAGES. FamilyTree.com is offering a new digital index for New York City marriages, 1908-1938. This index is free and open to the public. Once you have found an ancestor using this index, you can write to the NYC Clerk to request a copy of the full record for $10.00. A full record may inlcude the marriage record, applications, affidavits, and licenses.
U.S. – NEW YORK – DEATHS. Our friend at Extreme Genes let us know about the recent addition of the 1966 deaths for New York State Death Index. Free and available online, this database covers deaths in New York State for 1957 – 1966. Decedents name, sex, date of death, and age at death are given in the index.
 Be sure to check in next week to see what’s new in genealogy collections. Afraid you will miss the post? Sign up for Lisa’s free weekly e-newsletter so you will get future updates. Just enter your email address in the signup box at the top of this webpage. You’ll also receive a free e-book with Lisa Louise Cooke’s Google search strategies for genealogists.
Be sure to check in next week to see what’s new in genealogy collections. Afraid you will miss the post? Sign up for Lisa’s free weekly e-newsletter so you will get future updates. Just enter your email address in the signup box at the top of this webpage. You’ll also receive a free e-book with Lisa Louise Cooke’s Google search strategies for genealogists.
by Lisa Cooke | Sep 29, 2017 | 01 What's New, Australian, British, Irish, Newspaper, Records & databases |
If you’re looking for Irish ancestors, you’ll be delighted by all the new Irish record collections added this week! Also in this week’s new and updated record collections are court records and newspapers for Australia, parish records and more for England, millions of new Dutch records, South African probate records, and digitized newspapers across the United States.
Irish Genealogy: Thousands of New Records

If you have ancestors from Ireland who received an army pension between 1724 and 1924, you’ll want to explore Fold3’s new collection of Royal Hospital Kilmainham Pensioner Discharge Documents. This collection is made up of certificates of pensioners of the Royal Kilmainham Hospital in Ireland. According to the collection: “For each record, details given include, where available: a brief description of the pensioner together with age, place of birth, particulars of service and the reason for discharge.”
New this week at Findmypast are Dublin Electoral Rolls. This new collection contains more than 427,000 transcripts and pertains to eligible voters located in the city of Dublin between 1908 and 1915. (FYI: You can also search Dublin City Electoral Lists 1908-1915 and other records for free from the Dublin City Council’s Civil Records webpage.)
Lastly, Irish records got a big update over at the Irish Genealogical Research Society (IGRS): 5,000 records have been added to IGRS’s Early Irish Birth, Marriage, and Death Indexes. This brings their total number of names to almost 260,000. From the announcement: “This particular update draws from a range material: surviving 19th century census records; marriage licence indexes; pre-1922 abstracts from exchequer and chancery court records; memorial inscriptions; biographical notices from newspapers; a large number of long forgotten published works on particular families and places; and memorials from Ireland’s Registry of Deeds.”
New Resources for Australia
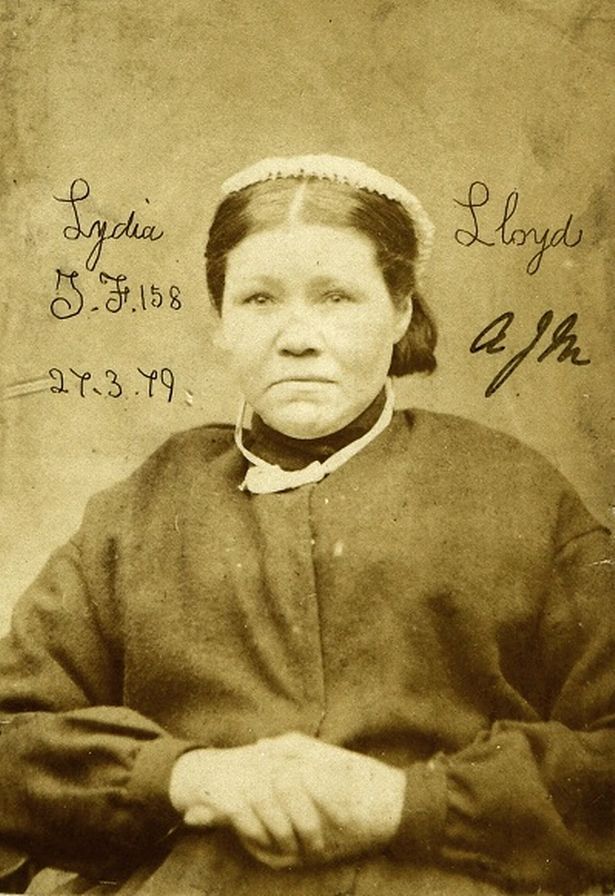 A fascinating new free website, Tracing London Convicts in Britain & Australia, 1780-1925 allows “genealogists and family historians to discover the fate of ancestors convicted of crimes and transported overseas.” This new website allows you to search millions of records from around fifty data sets, relating to the lives of 90,000 convicts from the Old Bailey. Pictured right: Lydia Lloyd, a Victorian era convict. (Image: The National Archives UK ref. PCOM4/71/6 (image 00001))
A fascinating new free website, Tracing London Convicts in Britain & Australia, 1780-1925 allows “genealogists and family historians to discover the fate of ancestors convicted of crimes and transported overseas.” This new website allows you to search millions of records from around fifty data sets, relating to the lives of 90,000 convicts from the Old Bailey. Pictured right: Lydia Lloyd, a Victorian era convict. (Image: The National Archives UK ref. PCOM4/71/6 (image 00001))
From the State Library of New South Wales Australia: The Lone Hand (1907-1921) newspaper has been digitized and made available through Trove. “Modelled on the London Strand and founded by J.F. Archibald and Frank Fox, The Lone Hand was a monthly magazine of literature and poetry, with illustrations by significant Australian artists of the time.”
England: Parish & Court Records
Ancestry.com has two new collections this week for England. Staffordshire Extracted Church of England Parish Records, 1538-1839 includes records for baptisms/christenings, burials, marriages, tombstone inscriptions, obituaries, tax lists, wills, and other miscellaneous types of records for Staffordshire, England. Also included are some records from non-conformist churches. Extracted Parish and Court Records, 1399-1795 is a collection of historical parish registers throughout England.
Also new for England, TheGenealogist has added over 1.1 million individuals to its Sussex County parish record collection. This update includes 717,000 baptisms, 213,000 marriages, and 208,000 burials.
Over at Newspapers.com, The Atlas newspaper has now been digitized. The London area paper operated from 1826 to 1869, and comprised a mixture of national and international social and political news, along with literary, theater, and music reviews. Another new newspaper available online is The Worthington Herald, from 1920-1959 in Worthington, West Sussex, England.
Millions of Dutch Records
FamilySearch has recently published millions of Dutch records (51 million to be exact) from the Netherlands, making it easier than ever to trace your Dutch roots. These new records have increased FamilySearch’s collection of Dutch names from 4,074,736 to over 55 million. From the collection description: “Archives around the Netherlands have contributed indexes which cover many record sources, such as civil registration, church records, emigration lists, military registers, and land and tax records.” Click here to search the collection.
South Africa Probate Records
New at FamilySearch: South Africa, Cape Province, Probate Records of the Master of the High Court, 1834-1989. This impressive collection is comprised of over 155,000 indexed records and 1.1 million digitized images! The original records are located in the Cape Archives Depot, Cape Town.
United States Newspapers
California. The Cal Poly University student newspaper has been digitized in honor of their 100 year celebration. 75,000 pages from 7,138 issues are now fully searchable online, thanks to optical character recognition (OCR) technology. Click here to explore the database.
North Carolina. Saint Mary’s Student School Newspaper, The Belles, is now online. Dating back to 1936 through 1995, the paper gives a good look into the viewpoint of North Carolina teen women over a 60 year period.
New Mexico. Now available at Newspapers.com is the Albuquerque Journal, with issues dating back to 1882. Almost 2 million pages are available to browse by date.

There’s a wealth of information about your ancestors in newspapers! Lisa’s book, How to Find Your Family History in Newspapers, provides you with a foolproof research process for discovering them, and is stuffed with everything you need for genealogical success. Available in both print and ebook formats, you’ll get step-by-step instructions, worksheets, tons of free online resources, case studies, and more!
Disclosure: This post contains affiliate links and Genealogy Gems will be compensated if you make a purchase after clicking on these links (at no additional cost to you). Thank you for supporting Genealogy Gems!
by Lisa Cooke | May 6, 2014 | 01 What's New, Family History Podcast, Immigration
Family History: Genealogy Made Easy Podcast
with Lisa Louise Cooke
Republished May 6, 2014
Listen to the Family History: Genealogy Made Easy podcast by Lisa Louise Cooke. It’s a great series for learning the research ropes and well as refreshing your skills.
https://lisalouisecooke.com/familyhistorypodcast/audio/fh30.mp3
Download the Show Notes for this Episode
Welcome to this step-by-step series for beginning genealogists—and more experienced ones who want to brush up or learn something new. I first ran this series in 2008-09. So many people have asked about it, I’m bringing it back in weekly segments.
Episode 30: Immigration and Naturalization Records for Family History, Part 2
This episode continues last episode’s conversation about immigration and naturalization records. With me again is Stephen Danko, PhD, a genealogy lecturer and a very popular blogger. In today’s show Steve and I talk more about passenger lists, and some of the ramifications of an immigrant being detained or deported. We cover the multi-step naturalization process and you’ll hear about a fantastic find in naturalization papers–so fantastic that other researchers at the Family History Library in Salt Lake City wanted a copy!
Here are my favorite take-away points from this episode:
There were no requirements to keep passenger lists in the U.S. before 1820, or in Canada before 1867. (Many people originally arrived in one or the other of these countries, then migrated across the border, which was essentially unregulated before the 1890s.) There may have been records kept, but you’re not going to find them easily.
The passenger lists we’re most familiar with were filled out in the port of departure, then surrendered to U.S. government officials upon arrival. But other records were maintained at the port of departure. Departure information from European ports is often available on microfilm at the Family History Library, on Ancestry.com or other websites. Some of the passenger steamship lines themselves kept departure lists, like the White Star Line or the Red Star Line, and these are on microfilm. Here’s an excellent article on Passenger Departure Lists of German Emigrants, 1709-1914. Look for resources specific to other countries in genealogical guides under the headings “emigration” or “departure lists.”
Immigrants who were deported or even detained for further investigation, the steamship line had to pay the bill. If they were detained or they went back, the date and ship of deportation may be indicated on the passenger manifests.
Naturalization was a multistep process. The “first paper” is the declaration of intent. After a certain period of time, they applied for their petition for naturalization (“second papers”). Eventually they received their certificate of naturalization. After 1926, there may also be a certificate of arrival. (See Episode 29.)
Naturalization records may be at the county level or may be in federal court. Increasingly these are coming online. Meanwhile, some are easier to track down than others. Most Massachusetts naturalizations are available on microfilm and at the Massachusetts State Library. Some books
Many 20th-century naturalizations are packed with family information. Steve shared an example for one of his relatives. Her naturalization had her name, birthdate and birthplace, name of her husband and date of her marriage, her husband’s birthplace and date, the names of all her children, her date of arrival and the ship she came on! Some later naturalizations also have photographs. Microfilmed files may also have the certificate of arrival.
Updates and Links
About 70 million immigration and naturalization records have been indexed in recent years through an enormous community indexing project led by FamilySearch. Check out their site (below) to see what records are searchable now.
Ancestry.com
Ellis Island.org
FamilySearch.org Immigration and Naturalization Online Resources
One-Step Webpages by Stephen P. Morse (Ellis Island Search Tool)
Timeline of U.S. Immigration Laws
by Lisa Cooke | Feb 12, 2016 | 01 What's New, Records & databases
Each week we scour announcements of new genealogy records online and share those we think our readers most want to know about. This week, it’s all about Irish and US records!
IRELAND CENSUS RECORDS. MyHeritage.com has added to its site “over 8.7 million Irish census records from the 1901 and 1911 censuses [which record every household member]. Both collections are completely free and contain images.”
IRELAND PARISH RECORDS. Findmypast.com subscribers now have access to an exclusive index to the National Library of Ireland’s free online collection of digitized-but-not-indexed registers from 1000 parishes, with over 10 million baptisms and marriages. According to a FMP press release, “This is the first time that the collection has been indexed with the images linked online, making the search much easier and the records more accessible. As a result, family historians will now be able to make all important links between generations with the baptism records and between families with the marriage registers. These essential records cover the entire island of Ireland, both Northern Ireland and the Irish Republic.”
(US) DUTCH REFORMED CHURCH RECORDS. Ancestry.com has added a new collection of Dutch Reformed Church records (1701-1995)  from 14 states and has updated a separate but similar collection of Dutch Reformed Records
from 14 states and has updated a separate but similar collection of Dutch Reformed Records (1639-1989).
(1639-1989).
US MARRIAGES. Findmypast has just released an enormous collection of marriage records from across the United States. “Containing over 450 million names from 1650 to 2010…the US Marriages collection will, when complete, include over 100 million records, 60% of which have never been published online before.” A third of the data (about 33 million names) are already online.
 More Irish Research Gems
More Irish Research Gems
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links and Genealogy Gems will be compensated if you make a purchase after clicking on these links (at no additional cost to you). Thank you for supporting Genealogy Gems!
by Lisa Cooke | Sep 30, 2014 | 01 What's New, Ancestry, Census, Collaborate
 There are lots of ways to find historical records about your ancestors online. Did you know there are also ways to learn who else has added that record to their trees–or who else is researching the same people you are? Here are two ways:
There are lots of ways to find historical records about your ancestors online. Did you know there are also ways to learn who else has added that record to their trees–or who else is researching the same people you are? Here are two ways:
1. On Ancestry.com, when you are looking at an image of a record, there’s a sidebar to your right called “Related Content.” Click on it. Below other suggested records you will see a list showing anyone who has saved this record to their trees. You’ll see a link to that username and you can contact them. This is what it looks like: 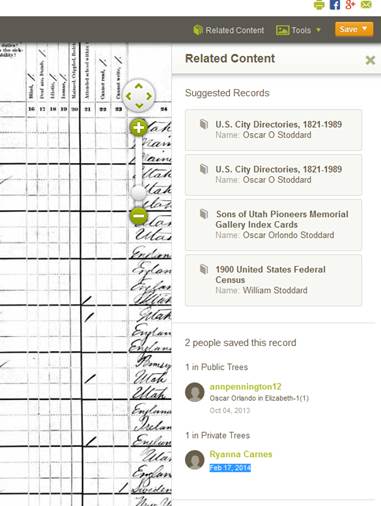 2. On LostCousins.com, you can enter the names of relatives whose names appear on specific censuses. Their database will search for others who are looking for the same people. This is a great resource for people with British Isles roots, as the site originates from there. Here are the censuses they support:
2. On LostCousins.com, you can enter the names of relatives whose names appear on specific censuses. Their database will search for others who are looking for the same people. This is a great resource for people with British Isles roots, as the site originates from there. Here are the censuses they support:
- England and Wales, 1841, 1881, 1911
- Scotland, 1881
- United States, 1880, 1940
- Canada, 1881
- Ireland, 1991.
Basic membership at LostCousins.com is free, but has limited functionality. You can only contact new people during certain windows of time during the year. With a £10 annual subscription, you can make new contacts anytime.  Looking for more ways to find living relatives? Genealogy Gems Premium members can click here to access my full-length video class, Unleash Your Inner Private Eye to Find Living Relatives. Not a member? Click here to join.
Looking for more ways to find living relatives? Genealogy Gems Premium members can click here to access my full-length video class, Unleash Your Inner Private Eye to Find Living Relatives. Not a member? Click here to join.
 Here are this week’s collections of new genealogy records online. Included are Scotland mental health records and, in the U.S., WWII draft registrations, WI probate and NY marriages and deaths.
Here are this week’s collections of new genealogy records online. Included are Scotland mental health records and, in the U.S., WWII draft registrations, WI probate and NY marriages and deaths.  Be sure to check in next week to see what’s new in genealogy collections. Afraid you will miss the post? Sign up for Lisa’s free weekly e-newsletter so you will get future updates. Just enter your email address in the signup box at the top of this webpage. You’ll also receive a free e-book with Lisa Louise Cooke’s Google search strategies for genealogists.
Be sure to check in next week to see what’s new in genealogy collections. Afraid you will miss the post? Sign up for Lisa’s free weekly e-newsletter so you will get future updates. Just enter your email address in the signup box at the top of this webpage. You’ll also receive a free e-book with Lisa Louise Cooke’s Google search strategies for genealogists.


 A fascinating new free website,
A fascinating new free website, 

 More Irish Research Gems
More Irish Research Gems

