by Lisa Cooke | May 14, 2013 | 01 What's New, Newspaper
Spring is in the air, as it was 100 years ago today. On May 14, 1913 the Omaha Daily Bee, the front page sported a comic depicting the eternal struggle of suburban life – fighting weeds in an effort to achieve the perfect lawn.

(Omaha daily bee., May 14, 1913, Weekly Market Review Edition, Image 1 Omaha daily bee. (Omaha [Neb.]) 187?-1922)
You can view the digitized paper featuring “Mr. Suburbs” at the Chronicling America website, along with digitized papers ranging from 1836 – 1922.
To learn more about using newspapers to climb your family tree grab a copy of my book How to Find Your Family History in Newspapers.
by Lisa Cooke | May 23, 2013 | 01 What's New, Military
Here’s the latest from the National Archives:
National Archives Marks 150th Anniversary of U.S. Colored Troops

Sic semper tyrannis – 22th Regt. U.S. Colored Troops, 1864. Bowser, David Bustill, 1820-1900 , artist
Washington, DC. . . Marking (the) 150th anniversary of its creation, the National Archives announces the completion of the United States Colored Troops (USCT) Service Records Digitization Project, in partnership with Fold3. For the first time, this collection – nearly four million images of historic documents with detailed information on former slaves – is available online to anyone, anywhere.
On May 22, 1863, the War Department issued General Orders 143, establishing a Bureau of Colored Troops in the Adjutant General’s Office to recruit and organize African American soldiers to fight for the Union Army. These service records – including those of the men of the famed 54th Massachusetts Infantry featured in the movie Glory – are a treasure trove for genealogists and a rich source of documentation on the black experience in America during the Civil War.
Researchers may be surprised to find that the USCT military service records hold not only muster rolls but also a huge array of personal papers that can include enlistment papers, correspondence, orders, prisoner-of-war memorandums, casualty reports, and final statements. Starting in October 1863, slave owners could enlist their slaves and receive up to $300 upon filing a “manumission” or deed of ownership. Unique to some of the records of the USCT are these deeds of manumission and bills of sale. For genealogists, these records may offer the only source of documentation of an enslaved ancestor in the absence of other vital records.
For the first time, these valuable historical records are available online, thanks to Fold3, and to National Archives staff and volunteers who spent years preparing, preserving, microfilming, and digitizing them. The collection is available free of charge to non-subscribers on www.fold3.com/category_268 today through May 31, and can be accessed for free at any time on computers at National Archives research facilities nationwide.
In total, the USCT consisted of seven cavalry regiments; 13 artillery regiments plus one independent battery; 144 infantry units; two Brigade Bands; and other miscellaneous smaller units. Records are arranged by regiment and then alphabetically by surname of the soldier.
The USCT fought in 39 major engagements and more than 400 other ones. Sixteen African American soldiers received the Medal of Honor. The last USCT regiment was mustered out of Federal service in December 1867.
One soldier chronicled in the records is Edmund Delaney, a slave who served in Company E of the 117th USCT Infantry. Delaney was 25 years old when he enlisted in August 1864. His owner, Harvey C. Graves of Georgetown, Kentucky, filed a compensation claim for Delaney’s military service in December 1866, stating that Delaney was “purchased at private sale when he was quite a small boy.” Graves attached to his “proof of ownership” a rare photo of Delaney, and letters Delaney had written to him while serving in Brownsville, Texas.
Another soldier’s file reads like an ultimate page turner and details the tragic story of Fortune Wright, a free black man before the Civil War who served in the 96th USCT Infantry. Read USCT project manager Jackie Budell’s fascinating Prologue “Pieces of History” blog post.
More information:
by | Jun 29, 2013 | Canadian, Census, Records & databases
 If you have Canadian kin, you’ll be pleased to hear that the 1825 census of Lower Canada is now searchable online, and the 1921 census will soon be available online, too!
If you have Canadian kin, you’ll be pleased to hear that the 1825 census of Lower Canada is now searchable online, and the 1921 census will soon be available online, too!
The 1825 census of Lower Canada counted nearly half a million people. Heads of household were actually named, with other members of the household counted by category. You can search by household name or geographic location.
The 1921 census counted 8.8 million people in thousands of communities across Canada. According to the Library and Archives Canada Blog, the population questionnaire had 35 questions. The census also collected data on “agriculture; animals, animal products, fruits not on farms; manufacturing and trading establishments; and [a] supplemental questionnaire for persons who were blind and deaf. This represents a total of 565 questions.” The census was released this past June 1 from the national Statistics office to the Library and Archives. That office is processing and scanning the nearly 200,000 images for public use. It hopes to have them posted soon.
Here’s a sample page from the 1921 census population schedule:
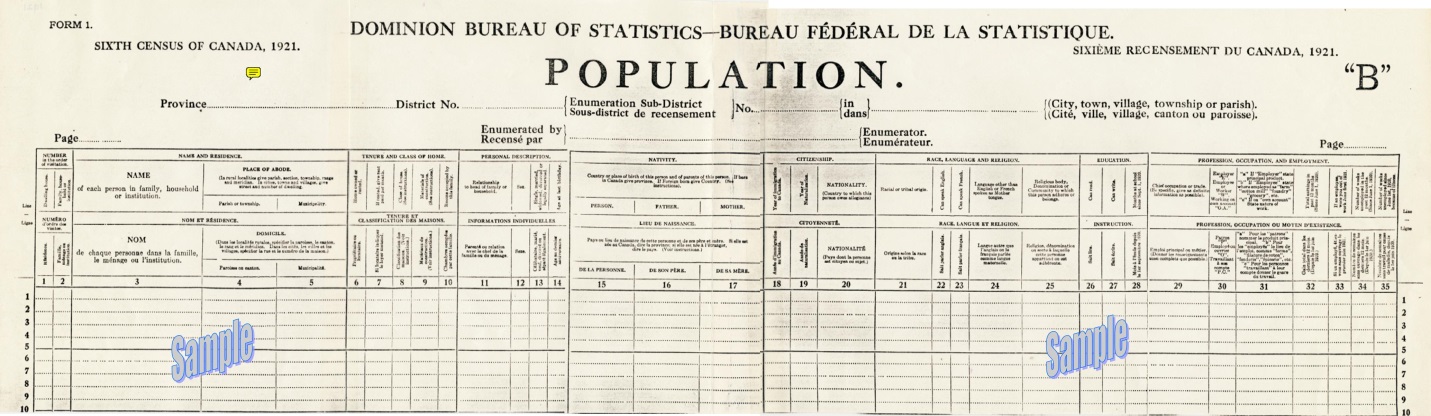
We think of Canada as a real melting pot today—or salad bowl, as they prefer. That wasn’t always the case. The 1825 census of Lower Canada counted mostly Europeans of French extraction. In 1901, 70% of Canadians claimed either British or French heritage. But in the first two decades of the 1900s, a huge immigration boom occurred that reached well beyond England and France. So the folks who show up on the 1921 census represented a newly multicultural Canada!
Start looking for your Canadian ancestors in the Library and Archives Canada’s popular Census Indexes, which include that 1825 census and a new version of the 1891 census, too. Watch the website for the 1921 census.
If your family arrived in Canada after the 1921 census, check out the website for The Canadian Museum of Immigration at Pier 21, where a million immigrants landed between 1928-1971.
by Lisa Cooke | Aug 15, 2013 | 01 What's New, Newspaper
Have you already searched for your relatives’ names at Chronicling America, the the Library of Congress’ web collection of digitized American newspapers? Well, search again!
Recently the the Library of Congress added more than 600,000 historic newspaper pages to its enormous collection. According to a press release, these pages include “first-time contributions from Iowa, Michigan, and West Virginia. Other new additions include content from Hawaii, Indiana, Illinois, Kansas, Kentucky, Louisiana, Minnesota, Montana, North Dakota, Oklahoma, Oregon, South Carolina, Tennessee, and Texas.” The site now has over 6.6 million searchable newspaper pages from over 1100 newspaper titles, published in 30 states and Washington, D.C. between 1836 and 1922.
 What are the chances your family will appear on one of those pages? Pretty good, actually. Here’s a list of the kinds of articles they may show up in from my book How to Find Your Family History in Newspapers:
What are the chances your family will appear on one of those pages? Pretty good, actually. Here’s a list of the kinds of articles they may show up in from my book How to Find Your Family History in Newspapers:
- Advertising: classifieds, companies your ancestor worked for or owned, grocery or dry goods stores ads (for historical context), runaway slaves search and reward, ship departures.
- Births & deaths: birth announcements, card of thanks printed by the family, obituary and death notices, “Community Pioneer” article upon passing, funeral notice, reporting of the event that lead to the death, or the funeral.
- Legal notices and public announcements: auctions, bankruptcies, city council meetings, divorce filings, estate sales, executions and punishments, lawsuits, marriage licenses, probate notices tax seizures, sheriff’s sale lists.
- Lists: disaster victims, hotel registrations, juror’s and judicial reporting, letters left in the post office, military lists, newly naturalized citizens, passenger lists (immigrants and travelers), unclaimed mail notices.
- News articles: accidents, fires, etc. featuring your ancestor; front page (for the big picture); industry news (related to occupations); natural disasters in the area; shipping news; social history articles.
- Community and social events like school graduations, honor rolls, sporting and theater events; social news like anniversaries, church events, clubs, engagements, family reunions, visiting relatives, parties, travel, gossip columns, illnesses, weddings and marriage announcements.
Learn more about researching family history with my book, available in both print and e-book format. And don’t forget to keep checking Chronicling America for stories and clues about your ancestors’ lives.





