Here are the step-by-step instructions you need to know to effectively navigate the Dawes Applications for Native American research. Many American families have a tradition of Native American ancestry. Now through Nov. 15, 2016 Fold3 has made access to their Native American records collections free. Read on to gain a thorough knowledge of how to properly use these records and achieve research success! And sign up for our free Genealogy Gems newsletter for our upcoming posts on this important subject.

Dawes Applications for Native American Research
In 1893, an act of Congress approved the establishment of a commission to negotiate agreements with the Choctaw, Creek, Chickasaw, Seminole, and Cherokee Indian tribes. The commission became known as the Dawes commission. The commission was to divide tribal land into plots, which were then divided among the members of the tribe. The Commission either accepted or rejected applicants for tribal membership based on whether the tribal government had previously recognized the applicant as a member of the tribe. Applicants were categorized as Citizens by Blood, Citizens by Marriage, Minor Citizens by Blood, New Born Citizens by Blood, Freedmen (African Americans formerly enslaved by tribal members,) New Born Freedmen, and Minor Freedman.
Researching the Dawes Packets is tricky. One problem arises when researchers find their family members in an index and assume that means their family was a legitimate member of a tribe. That is not the case. You will find doubtful or even rejected applications as well.
The good news is that in applying, our ancestors provided lots of genealogically valuable details of their birth, residences, and family ties.
Let’s see how to use this special collection.
Dawes Packets are Listed By Application Number
It would take forever to go through the applications one by one to find your ancestor. You really need to check an index first, but Fold3 doesn’t have the index for the Dawes Packets collection available…at least as far as I have found.
Instead, I would suggest going over to Ancestry.com. There, click on Search and choose Card Catalog from the pull-down menu. In the keyword search at the card catalog, type in Five Civilized Tribes. This will give you the option of several databases, but the one we want to check first is the one titled “U.S., Native American Applications for Enrollment in Five Civilized Tribes, 1898-1914.”
Now, search for your targeted ancestor by name. In my example, I am going to search for David O. Scott.

The results indicate that David O. Scott appears in two entries. One entry gives the number of #9446 and the other is #616. I can view each of these records directly from Ancestry. The first image you see is a jacket cover, so just click the right arrow key to scroll through the digital pages contained in David’s file.
Remember, if you don’t have access to Ancestry.com, many local libraries and family history centers have free access for patrons. But, we are talking about using Fold3, so let’s pop back over there.
Go back to Fold3.com to access their Native American records. You will do this by clicking on Browse at the top of the Fold3 homepage. Next, scroll through the options and choose Non-Military Records. A new list of options will appear and you will click on Native American Collections, then Dawes Packets. The Dawes Packets that appear here on Fold3.com are first broke down into tribe, then by number.

David O. Scott’s search on Ancestry listed him as Cherokee, so I want to choose that tribe. One of his numbers was #616.

Did you notice the numbers have a “D” in front of them? These are the applications deemed “doubtful.” If you scroll down, the letter changes to “R.” These applications were rejected. We don’t know if David’s number 616 is in the doubtful category or the rejected category, so we will check both.
David’s #616 matches the D616 and now I know that his application was marked doubtful. David’s pages of information were packed with genealogical detail like family names, dates, and residences.
The 1896 Applications
Here’s another tip: Your ancestor may have applied in the first wave of applications submitted in 1896. Those applications were later deemed invalid and thrown out, but wow…you don’t want to overlook them! Whether your ancestor applied again in 1898 and you already found their Dawes Packet on Fold3, try looking at this collection as well.
The research center at the Oklahoma Historical Society webpage allows you to search the 1896 overturned applications index for free. I typed in the name of my third great-grandfather, Jacob Cole.

You can also search by tribe, however, I suggest you do not do that. Sometimes, individuals actually applied to more than one tribe because they were not sure which tribe they might belong to. By adding that criteria, you may miss your ancestor’s application all together.
Only one result appeared for Jacob Cole. On this result, you notice the tribe affiliation as Cherokee and the case/application number of 639. I will need that tribe and number to find the application at Fold3. [Note: As I mentioned earlier, this index does not tell me if Jacob’s application was accepted or rejected, but it really doesn’t matter because these applications were deemed invalid anyway.]
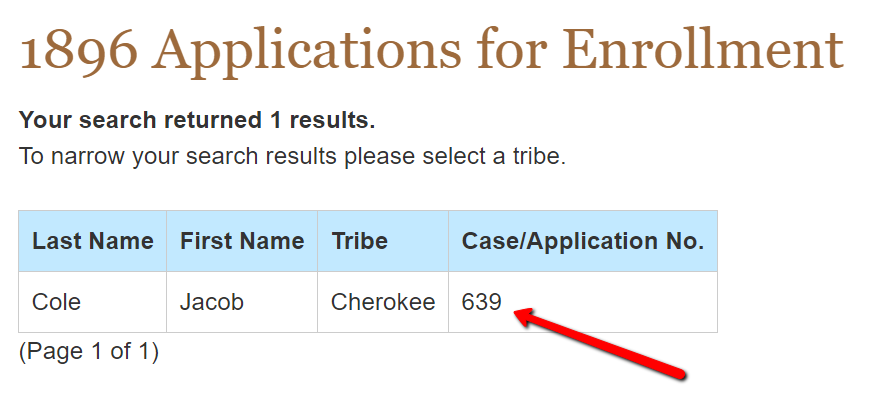
You won’t find Jacob’s overturned application of 1896 on Fold3 at this time, but it is available at Ancestry.
Where Can I find Overturned Applications for 1896?
Overturned applications from 1896 are still very valuable records. They can be found at the National Archives and Records Administration in Washington D.C., or at Ancestry.com.
Let’s look at Ancestry. Once at the homepage, click Search at the top, then choose Card Catalog from the pull-down options.
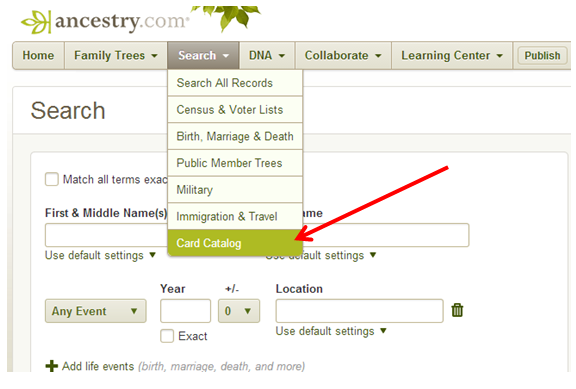 In the keyword field on the right, type in Five civilized tribes. You will see many options, but you want to click on the collection titled “U.S. Native American Applications for Enrollment in Five Civilized Tribes (overturned,) 1896.”
In the keyword field on the right, type in Five civilized tribes. You will see many options, but you want to click on the collection titled “U.S. Native American Applications for Enrollment in Five Civilized Tribes (overturned,) 1896.”

This next step is a bit tricky. You will be directed to a page that allows you to seemingly search for your targeted ancestor’s application. But, the search only searches an index for the applications. To find the entire application packet, you need to browse the microfilm by hand.
To do that, look over to the far right where it says Browse this collection. Choose from the drop-down menu which tribe your ancestor applied to…so, I will choose Cherokee Applications. Then, choose the roll number based on the application number of the packet. I can determine the correct roll number because Jacob’s application number was 639 and Roll 25 includes all applications between the numbers of 486 and 681.

Click ALL and a digital image of the microfilm pops up. You will need to browse image-by-image until you find your ancestor’s application number. Be patient. With more than 1800 images, it will take some time.
[Special Note: On the very last roll of microfilm, Roll 54, there are some miscellaneous files and applications that were received past the application deadline. These records were not included in the Master Index. If you did not find your targeted ancestor in the Master Index, check these miscellaneous records.]
I found Jacob’s application on digital image number 1405. His application packet was nine pages long. I learned the ages and names of his current wife and children, how he believes he is Cherokee through the blood of his grandfather, Hawk Bowman, and I read two witness statements about Jacob and his family.
In particular, because this record was made in the 1890s, I was able to learn of two daughters that I had never known about. Martha had been born after the 1880 census and married before 1900, never having appeared with her father in a census. The second daughter, Mary J., had been born in 1895 and died before 1900, also never appearing with her family in a census record.
More on Native American Research
We will be creating further blog posts regarding each of the Native American collection sets at Fold3.com. We want you to be able to take advantage of this awesome opportunity to view the records for free for this limited time. In the meantime, be sure to read this how-to post on using Eastern Cherokee Applications: Eastern Cherokee Applications for Native American Research







 In the keyword field on the right, type in Five civilized tribes. You will see many options, but you want to click on the collection titled “
In the keyword field on the right, type in Five civilized tribes. You will see many options, but you want to click on the collection titled “


 In honor of our Genealogy Gems Book Club featured author
In honor of our Genealogy Gems Book Club featured author 
 Ingredients:
Ingredients: