by Lisa Cooke | Nov 18, 2017 | 01 What's New, Professional Genealogy, Societies
A professional genealogist can help you apply to lineage societies. Joining is a time-honored way to honor your heritage and document your family history research. But it’s not easy! Here’s why even experienced genealogists may want to hire a professional to help with the process.

Thanks to Legacy Tree Genealogists for supplying this guest blog post.
Applying to lineage societies
Do you have an ancestor who lived in Colonial America when the Revolutionary War was fought, or perhaps earlier in Jamestown, Virginia? Does your ancestry extend back to New England when the Mayflower arrived? If so, there are various lineage societies you could consider joining:
 While each organization has different requirements for their lineage society application, most have the same principles: prove a connection from yourself to the person of interest by use of vital records (where available). Where not available, other documentation that proves family connections can be used. (DAR now also accepts DNA evidence.)
While each organization has different requirements for their lineage society application, most have the same principles: prove a connection from yourself to the person of interest by use of vital records (where available). Where not available, other documentation that proves family connections can be used. (DAR now also accepts DNA evidence.)
You may not know that most societies allow you to “piggy-back” on applications they have previously accepted. Let’s say your second cousin Steve already joined a society based on your common patriot (or pioneer) ancestor, Alexander Smith. You would just need to provide documentation proving your connection to your parents, your relevant parent’s connection to his/her parents, and your relevant grandparent’s connection to your common great-grandparents, who were already mentioned in Steve’s application. You may then be able to reference Steve’s application for the remainder of the lineage going back to Alexander Smith.
Overall, this may sound like a simple process. But it often takes quite a bit of work because the records needed to prove each generational link are not always readily available–and sometimes they just don’t exist at all.
Why get help when applying to lineage societies
Below are five ways that a professional genealogist can help you apply to lineage societies:
1. Help you determine how to apply. As we mentioned, each lineage society has different requirements, so you’ll want to be sure you know what they expect in order to be as efficient as possible in gathering documentation. A professional can help you determine exactly what documentation is required and locate contact information for those with whom you need to work to submit your application.
2. Identify where your research should stop and start. There is no need to reinvent the wheel, as the saying goes. If your lineage ties into one that has already been acceptably documented by another member of the society, you should use it! A professional genealogist can help you identify any previous lineage society applications that have already been approved for your lineage. This single step can save you a lot of time and money.
3. Organize your information. A professional genealogist can work with you to determine what documentation you already have and what you will need to order. They can help you order copies of missing vital records or find acceptable substitutes in archives, libraries, and online.
 4. Conduct in-depth research as needed. Many times, at least one ‘problem’ generation requires in-depth research, circumstantial evidence, and a proof summary in order to make the connection. A well-written proof summary explains how all the circumstantial evidence fits together to support the generational link, and often aids the applicant in obtaining membership when not enough concrete documentation is available (or when it conflicts). This often involves delving into land records, tax lists, probate records, and other more obscure sources to find any and all clues and pieces of information that can be used to tie two generations together. It can be a time-consuming task. A professional genealogist can do this efficiently and thoroughly.
4. Conduct in-depth research as needed. Many times, at least one ‘problem’ generation requires in-depth research, circumstantial evidence, and a proof summary in order to make the connection. A well-written proof summary explains how all the circumstantial evidence fits together to support the generational link, and often aids the applicant in obtaining membership when not enough concrete documentation is available (or when it conflicts). This often involves delving into land records, tax lists, probate records, and other more obscure sources to find any and all clues and pieces of information that can be used to tie two generations together. It can be a time-consuming task. A professional genealogist can do this efficiently and thoroughly.
5. Compile and present all records to the lineage society for admittance. You’ll be the one to present or submit your documentation, but professionals can help you get it all ready so that you’ll be as prepared and organized as possible.
Save time and money when applying to lineage societies
A well-prepared lineage society application often shortens the waiting period to be accepted into a society because it is easier to verify and follows the rules of the society. If an application is poorly prepared, it can take several submissions before acceptance into the society is granted. And of course, the lineage society determines what they will and will not accept as proof, so there’s never a guarantee. They may request additional information, and then you have to go back and keep digging! But since professional genealogists have experience working with the various societies and know what types of documentation are usually accepted, working with a pro can make the application process to a lineage easier, more efficient, and in the end, more rewarding.
 If you have an ancestor in your lineage who may qualify you to join a lineage society, experts at Legacy Tree Genealogists can help you gather your documentation and prepare your application. They are the world’s highest client-rated genealogy research firm. Founded in 2004, the company provides full-service genealogical research for clients worldwide, helping them discover their roots and personal history through records, narratives, and DNA. Based near the world’s largest family history library in downtown Salt Lake City, Utah, Legacy Tree has developed a network of professional researchers and archives around the globe.
If you have an ancestor in your lineage who may qualify you to join a lineage society, experts at Legacy Tree Genealogists can help you gather your documentation and prepare your application. They are the world’s highest client-rated genealogy research firm. Founded in 2004, the company provides full-service genealogical research for clients worldwide, helping them discover their roots and personal history through records, narratives, and DNA. Based near the world’s largest family history library in downtown Salt Lake City, Utah, Legacy Tree has developed a network of professional researchers and archives around the globe.
Contact them today to discuss your options–and your ancestors. EXCLUSIVE OFFER for Genealogy Gems readers! Receive $100 off a 20-hour+ research project from Legacy Tree Genealogists with code GEMS100. Offer good through December 31, 2017.
by Diahan Southard | Nov 10, 2014 | 01 What's New, Digital Archives, Military, Photographs
Recently listener Stacy sent us links to two fabulous collections of historical photos. The stories they tell–and the back story of one of the photographers–are just stunning.
Civil War Soldiers
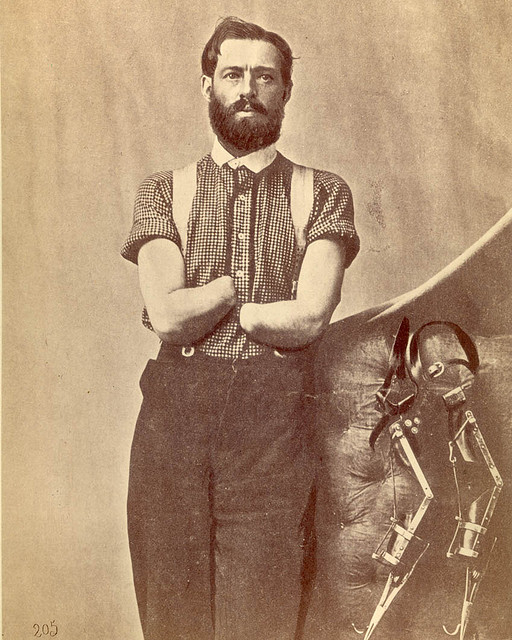

Pvt. Samuel Decker, SP 205, National Museum of Health and Medicine. Pvt. Samuel H. Decker, Company I, 4th US artillery. Double amputation of the forearms for injury caused by the premature explosion of a gun on 8 October 1862, at the Battle of Perryville, KY. Shown with self-designed prosthetics. Photo ID: SP 205. Source Collection: OHA 82 — Surgical Photographs. Repository: National Museum of Health and Medicine, Otis Historical Archives.
The first collection is a sobering visual record of wounded Civil War soldiers. The National Museum of Health and Medicine has posted this collection online.
“From missing fingers and hands to completely amputated legs, the portraits show solemn soldiers posing with what remains of their bodies,” writes Gannon Burgett, the author of this article about the collection. “Some of the portraits were captured by hospitals, as a way of showing how their surgical procedures had turned out; others were commissioned by the soldiers themselves as a memorabilia of sorts.”
It struck me how young some of these soldiers were, and how for many of them, their injuries would have made them unable to earn a living.
Settlers of the American West
In the late 1800s-early 1900s, Solomon Butcher photographed settlers of the Great Plains of the American West. Aware that he was capturing history in the making, he posed settlers in front of their sod homes, with their tools or livestock (and one family with their pump organ). The wide expanse of sky and sun behind these sun-hardened settlers places them squarely in their harsh natural environment.
About 3000 Butcher photographs are now online at the Library of Congress’ American Memory site, one of the only visual records of the settling of the Great Plains, mostly thanks to the generous land ownership terms of the Homestead Act. Most of the photographs are labeled–was your ancestor among them?
The story of the man behind the camera mirrors the outright failures and delayed success of the settling of the West itself. Read his story here and see if you agree with me that the time he knocked himself out trying to save his burning home sort of epitomizes his entire life.
These really are photographs you don’t see every day! Some are grim–but they illustrate the realities of our ancestors’ lives in ways that sometimes the most vivid written descriptions can’t capture. Thanks for sending these links, Stacy!
by Lisa Cooke | Jun 22, 2015 | 01 What's New, African-American, Brick Wall, FamilySearch, images, Records & databases, School Records, United States, Volunteer
 The more I learn about U.S. history and records, the more I appreciate the challenges faced by those researching their African-American roots. In addition to the emotional toll of learning about their ancestors’ hardships, today’s researchers face the practical challenges of finding kin in records that mostly ignored their existence.
The more I learn about U.S. history and records, the more I appreciate the challenges faced by those researching their African-American roots. In addition to the emotional toll of learning about their ancestors’ hardships, today’s researchers face the practical challenges of finding kin in records that mostly ignored their existence.
That’s why I’m super excited that the Freedmen’s Bureau records are finally being fully indexed. Scattered records are already transcribed (see the Freedmen’s Bureau Online). But there hasn’t been a comprehensive index of its 1.5 million state field agency documents. These include military pensions, marriage records, property claims, hospital records, trial summaries, labor contracts, school rolls, registers and censuses. Many of the four million African-Americans freed from slavery are mentioned, as are many white Southerners.
FamilySearch indexers began quietly indexing Freedmen’s Bureau records in 2009: the state of Virginia’s records are already searchable. Last week, in observance of the Juneteenth holiday (which celebrates emancipation), FamilySearch issued a call to action. They asked for help indexing the rest of the Freedmen’s Bureau within the year.
“Records, histories and stories will be available on DiscoverFreedmen.org,” says a release. “Additionally, the records will be showcased in the Smithsonian’s National Museum of African American History and Culture, which is currently under construction on the National Mall in Washington, D.C., and expected to open in late 2016.”
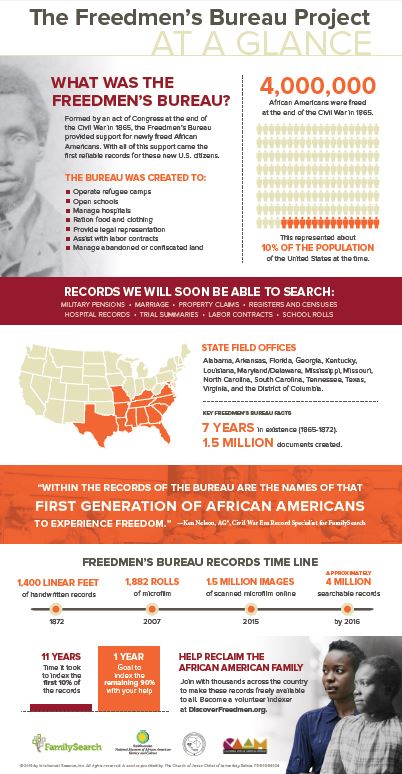 Here’s a quick history lesson: The Freedmen’s Bureau was organized after the Civil War to aid newly-freed slaves in 15 states and Washington, DC. For several years it gathered “handwritten, personal information on freed men, women and children, including marriage and family information, military service, banking, school, hospital and property records,” according to FamilySearch.
Here’s a quick history lesson: The Freedmen’s Bureau was organized after the Civil War to aid newly-freed slaves in 15 states and Washington, DC. For several years it gathered “handwritten, personal information on freed men, women and children, including marriage and family information, military service, banking, school, hospital and property records,” according to FamilySearch.
The richest genealogical records of the Freedmen’s Bureau are in the field office records of each state. Click here to download a PDF from the National Archives about these original records.
Find more tips on finding African-American and other Southern U.S. ancestors here on the Genealogy Gems website. Recent posts include:
 Receive a heads-up about posts like these–and get a free e-book on Google searching for genealogy–when you subscribe to the free Genealogy Gems newsletter in the upper right corner of this webpage or our home page.
Receive a heads-up about posts like these–and get a free e-book on Google searching for genealogy–when you subscribe to the free Genealogy Gems newsletter in the upper right corner of this webpage or our home page.
by Lisa Cooke | Jul 19, 2015 | 01 What's New, Brick Wall, images, Photographs, Research Skills, Technology
 The forensic investigator pulls up to the crime scene and snaps a fresh set of rubber gloves. She props open the trunk of the car and carefully, slowly, sweeps a tube of florescent light back and forth inside the trunk, watching with an eagle eye for the glimmer of something that shouldn’t be there.
The forensic investigator pulls up to the crime scene and snaps a fresh set of rubber gloves. She props open the trunk of the car and carefully, slowly, sweeps a tube of florescent light back and forth inside the trunk, watching with an eagle eye for the glimmer of something that shouldn’t be there.
It’s a familiar scenario – well, that is, if you watch Court TV or CSI or one of the other of myriad of television shows featuring forensics. If you’re like me, you’re fascinated by this type of investigation. Criminal investigators are not all that different from genealogists: they are looking for dead people and trying to find out what happened to dead people.
So it will be be no surprise that this recent news item grabbed my attention:

Image from the National Library of Wales website. Click to view.
Poetry and pictures drawn in the margins of a medieval manuscript–and then erased–have been rediscovered using modern imaging techniques. The Black Book of Carmarthen is the oldest known surviving Welsh language manuscript. Written in 1250, it’s now “throwing up ghosts from the past after new research and imaging work revealed eerie faces and lines of verse which had previously been erased from history,” according to a National Library of Wales blog post.
“A combination of ultraviolet light and photo editing software” were used to better see ancient doodles that had been erased from the margins. The process revealed “images, and snatches of poetry which are previously unrecorded in the canon of Welsh verse.”
We’ve featured several types of forensic analysis as applied to genealogy over the years. In fact, forensic genealogy principles inspired my popular presentation, How to Reopen and Work a Genealogical Cold Case (if you’re a Premium Member of this website you can sign in right now and watch it under Premium Videos).
Criminal investigators are not all that different from genealogists:
they are looking for dead people and trying to find out what happened to dead people.
Genealogy Gems Podcast Episodes 89 and 90 features Dr. Robert Leonard, a forensic linguist featured on an episode of Forensic Files on TV. It was such a riveting interview that I brought him back for Premium episode 48 where his brother Dr. George Leonard joined us. And way back in the pioneer days of this podcast (2008) Episode 18 featured “Vehicular Forensics.”
 It was my genealogical take on using alternative light sources on not the trunks of cars, but rather their faded license plates as they appear in old photos. That episode has been “retired” but will soon be
It was my genealogical take on using alternative light sources on not the trunks of cars, but rather their faded license plates as they appear in old photos. That episode has been “retired” but will soon be  remastered and available for listening (stay tuned to the free Genealogy Gems email newsletter for the publication announcement.) In the meantime you can read about it in depth in my very first book Genealogy Gems: Ultimate Research Strategies.
remastered and available for listening (stay tuned to the free Genealogy Gems email newsletter for the publication announcement.) In the meantime you can read about it in depth in my very first book Genealogy Gems: Ultimate Research Strategies.
Have you looked to see what lurks on the pages and photos of your ancestors? Email me and we may share it in an upcoming blog post or episode.

 While each organization has different requirements for their lineage society application, most have the same principles: prove a connection from yourself to the person of interest by use of vital records (where available). Where not available, other documentation that proves family connections can be used. (DAR now also accepts DNA evidence.)
While each organization has different requirements for their lineage society application, most have the same principles: prove a connection from yourself to the person of interest by use of vital records (where available). Where not available, other documentation that proves family connections can be used. (DAR now also accepts DNA evidence.) 4. Conduct in-depth research as needed. Many times, at least one ‘problem’ generation requires in-depth research, circumstantial evidence, and a proof summary in order to make the connection. A well-written proof summary explains how all the circumstantial evidence fits together to support the generational link, and often aids the applicant in obtaining membership when not enough concrete documentation is available (or when it conflicts). This often involves delving into land records, tax lists, probate records, and other more obscure sources to find any and all clues and pieces of information that can be used to tie two generations together. It can be a time-consuming task. A professional genealogist can do this efficiently and thoroughly.
4. Conduct in-depth research as needed. Many times, at least one ‘problem’ generation requires in-depth research, circumstantial evidence, and a proof summary in order to make the connection. A well-written proof summary explains how all the circumstantial evidence fits together to support the generational link, and often aids the applicant in obtaining membership when not enough concrete documentation is available (or when it conflicts). This often involves delving into land records, tax lists, probate records, and other more obscure sources to find any and all clues and pieces of information that can be used to tie two generations together. It can be a time-consuming task. A professional genealogist can do this efficiently and thoroughly. If you have an ancestor in your lineage who may qualify you to join a lineage society, experts at Legacy Tree Genealogists can help you gather your documentation and prepare your application. They are the world’s highest client-rated genealogy research firm. Founded in 2004, the company provides full-service genealogical research for clients worldwide, helping them discover their roots and personal history through records, narratives, and DNA. Based near the world’s largest family history library in downtown Salt Lake City, Utah, Legacy Tree has developed a network of professional researchers and archives around the globe.
If you have an ancestor in your lineage who may qualify you to join a lineage society, experts at Legacy Tree Genealogists can help you gather your documentation and prepare your application. They are the world’s highest client-rated genealogy research firm. Founded in 2004, the company provides full-service genealogical research for clients worldwide, helping them discover their roots and personal history through records, narratives, and DNA. Based near the world’s largest family history library in downtown Salt Lake City, Utah, Legacy Tree has developed a network of professional researchers and archives around the globe.







