by Lisa Cooke | Jun 23, 2013 | History, Technology
 More than 80% of Americans over the age of three (!) have at least one computer in the house today. Most of us don’t have its predecessor: the typewriter. But the typewriter keyboard was the forerunner of the computer keyboards we all know now. I just wanted to take a moment to wish the keyboard a happy 145th birthday!
More than 80% of Americans over the age of three (!) have at least one computer in the house today. Most of us don’t have its predecessor: the typewriter. But the typewriter keyboard was the forerunner of the computer keyboards we all know now. I just wanted to take a moment to wish the keyboard a happy 145th birthday!
On this date in 1868, an American named Christopher Sholes patented the first usable typewriter with the same “QWERTY” key organization we all know today. The keys were not placed in alphabetical order, but with the most-frequently used keys under and near the fingers of the trained typist (who, if you learned like I did, lines up his her left hand with the pinkie finger on “A” and the right hand with the pinkie finger on the semicolon, and both thumbs on the space bar).
Check out Sholes’ patents at Google Patents
It’s not hard to see how the invention of the typewriter (and later the computer) keyboard has revolutionized our ability to communicate. But it has had interesting “side effects,” too–like giving women ground-floor entrance to the business world. On this the 145th anniversary of the keyboard, think about it for a second–how does this one invention affect your life?
by Lisa Cooke | Sep 8, 2015 | 01 What's New, Book Club, Craft & Displays, images, Listeners & Readers, Records & databases, Writing Family History
 Since featuring Pioneer Girl in the Genealogy Gems Book Club, so many Little House gems have surfaced that we wanted to share this patchwork of Laura Ingalls Wilder documents and stories with you.
Since featuring Pioneer Girl in the Genealogy Gems Book Club, so many Little House gems have surfaced that we wanted to share this patchwork of Laura Ingalls Wilder documents and stories with you.
The Wilder Homestead Claim
A year before he married Laura Ingalls, Almanzo Wilder proved (or secured) his homestead claim to a tract of land he had been steadily improving in Dakota Territory. Click here to read an article about Almanzo’s claim and see a copy of the document. (Find federal land claims for much of the Midwest and West at the Bureau of Land Management General Land Office Records website. Genealogy Gems Premium members can learn more about the Homestead Acts and land claims that may have been filed by their ancestors in Genealogy Gems Premium podcast #33.
Little House-Inspired Fabric Series
Thank you to Barbara from NY who wrote in to say, “Lisa, I know you are very crafty so I wanted to let you know about a new fabric line that is coming in the fall. Andover Fabrics is putting out the Little House on the Prairie fabric line. In their ad it gives a quote from the book, “The attic and the cellar were full of good things once more and Laura and Mary had started to make patchwork quilts. Everything was beginning to be snug and cosy again.” I thought this went well with the book club book for this month.” Thank you, Barbara! We’ll have to look for some heritage projects that will theme well with these fabrics!
Writing and Editing the Little House Series: A Mother-Daughter Effort
Laura Ingalls Wilder’s Little House series didn’t come to press until decades after her childhood. By that time, her daughter Rose Wilder Lane was a freelance writer who knew the market. She saw the value in her mother’s memoirs and wanted to help her shape them into marketable books. This article talks about how stormy their collaboration could be, as they haggled over how best to memorialize Laura’s memories for modern children.
We heard from Chris on the subject of Rose’s editorship. “I also read Pioneer Girl and frankly enjoyed it a lot,” Chris says. But Chris has always wished Rose got more credit for the extensive editing and rewriting she did for her mother’s work, which apparently remained largely unknown. “As genealogists, we want to give all credit where it is due.” She recommends that Little House fans read A Wilder Rose by Susan Wittig Albert, which tells Rose’s story. Knowing Rose’s role doesn’t diminish Chris’ love for the Little House books, just gives her added perspective on the story-telling behind the stories.
Anyone who has ever tried to write a life story (their own or someone else’s) in a format for others to read will be fascinated by the letter shown in that article. Rose is trying to convince her mother of the need to whittle down her stories to the strongest story lines. “It is beyond all human power to tell all the facts. Your whole lifetime spent at nothing else would not tell all the facts of one morning in your life, just any ordinary morning when you get up, dress, get breakfast and wash the dishes.”
Resources
The Genealogy Gems Book Club Selects Pioneer Girl as Featured Book
Interview with Editor of Pioneer Girl: Laura Ingalls Wilder (This is an excerpt from the full interview, which will run in an upcoming Genealogy Gems Premium podcast episode.)
How to Reconstruct Your Early Childhood Memories and Stories
Genealogy Gems Premium Podcast Episode 116 for Life Story Writing Tips with Laura Hedgecock, author of Memories of Me: A Complete Guide to Telling and Sharing the Stories of Your Life (Premium membership required to access)
 The Genealogy Gems Book Club brings you great titles like Pioneer Girl, along with exclusive conversations with the authors. We’ve featured best-selling novels and memoirs, nonfiction books like this one and less-discovered titles we love. Click here to see other books we’ve featured and listen to the author interviews.
The Genealogy Gems Book Club brings you great titles like Pioneer Girl, along with exclusive conversations with the authors. We’ve featured best-selling novels and memoirs, nonfiction books like this one and less-discovered titles we love. Click here to see other books we’ve featured and listen to the author interviews.
Who else do you know who might enjoy the Genealogy Gems Book Club? Please share it with them?
by Lisa Cooke | Mar 13, 2017 | 01 What's New, DNA
Do you need help solving your family migration patterns? A groundbreaking new scientific study uses DNA and family trees to map migration routes across North America.

Family Migration Patterns Revealed in Genomes
A new study published in Nature Communications represents a ground-breaking development in using DNA for genealogy. The article from the AncestryDNA Scientific Team is titled Clustering of 770,000 genomes reveals post-colonial population structure of North America. Or, in more understandable terms, “Your DNA can tell us where you came from in America in the last 500 years.”
Wow, right? So, how did they do this?
The power really is in the numbers. In this particular paper, they started with using their autosomal DNA test on 770,000 people. Some of them were AncestryDNA customers who had consented to be part of the research. From these 770,000, they learned quite a bit about the migration patterns of early Americans. As Ancestry analyzes more individuals using these same principles of correlating genetics and genealogy, this data will improve and be able to tell us even more about our heritage. Even though it takes a large data set to figure out the relationship between our DNA and migration patterns, it really comes down to the relationship of two people.
To start, Ancestry determines how just two people are genetically related. Then, they find how those two are related to a third person, again, looking only at pairs of people. This goes on and on until everyone in the group as been compared. They use a graph to plot those relationships, with those more closely related clustering around each other. And then it happens. The point where we see the marriage of genetics and genealogy suddenly appear by adding in the family history information for each of these individuals in the cluster.
What they found was astounding. They have displayed the data in Figure 3 shown below. It is a map of the United States with colored dots scattered across the landscape. The location of the dots corresponds to the genealogy of those tested, while the color of the dots relates to their genetic clustering. Those who cluster closest together are the same color. The result is a nearly perfect rainbow, with buy anti anxiety medication online uk each color holding its respective spot on the map, with very little overlap between groups.
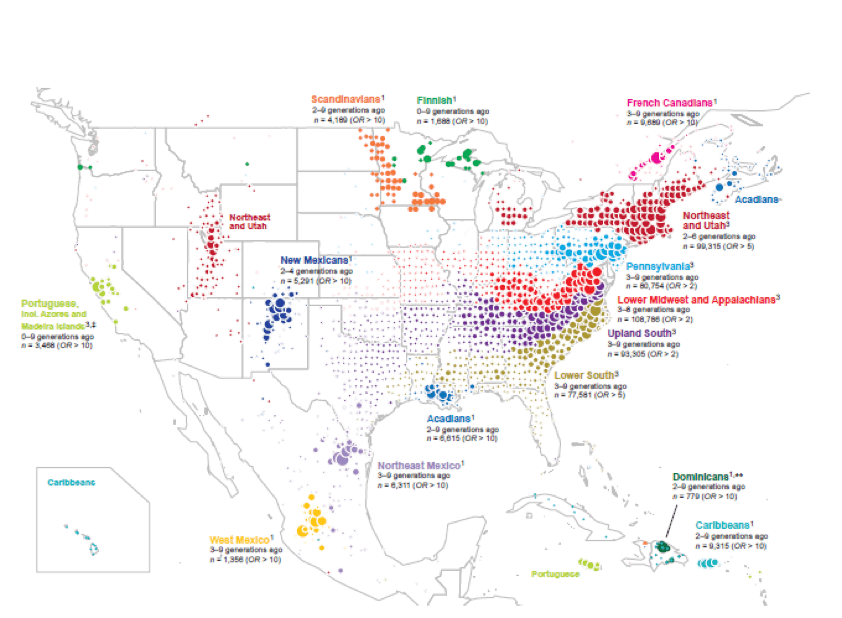
Distribution of ancestral birth locations in North America. Summary map from Nature Communications; click to see article with full explanation of map data. Image used with permission of Ancestry.com.
We might be tempted when looking at the map to think, oh, well, of course there is a large population of European Jews in New York, everyone knows that. But this isn’t their family history, their accent, or their culture telling us this – it is their genetics!
As if that wasn’t exciting enough, the scientists describe how we can trace family migration patterns of different groups over just a few generations. They specifically mention French Canadians and Cajuns/Acadians, but the same principle can theoretically be applied to dozens of other groups.
Family Migration Patterns and Applying these Findings
 So what does this mean for you as a genealogist?
So what does this mean for you as a genealogist?
It means we are getting closer than ever to being able to tell who you are and where you came from using your DNA.
For example, let’s say you have an ancestor in Texas about 4 generations ago, but you aren’t sure where she came from. Your DNA could tell you that you fit into the Lower South group, meaning that your ancestor likely hails from the south. Or, maybe your genetics identify with the Upland South, which means you need to explore records from Arkansas, Tennessee, and North Carolina.
This is just a glimpse into the advances that genetics are bringing to your genealogy toolbox these days. So it’s high time to go “all in” to learn about genetic genealogy! We recommend The Family Tree Guide to DNA Testing and Genetic Genealogy by Blaine Bettinger. You’ll love this book if:
- You’ve got brick walls that traditional research methods haven’t been able to break down
- You want to take advantage of the hottest tool in genealogy
- You’ve already taken a DNA test and want to know what comes next
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links and Genealogy Gems will be compensated if you make a purchase after clicking on these links (at no additional cost to you). Thank you for supporting Genealogy Gems!
by Lisa Cooke | Jan 14, 2015 | 01 What's New, Apps, Canadian, Google Earth, Listeners & Readers
 Awhile back, Barbara from Courtenay, British Columbia, sent me an excellent question about using Google Earth for Canadian genealogy. Then she sent me an excellent answer before I had a chance to answer it myself! Here’s what they were:
Awhile back, Barbara from Courtenay, British Columbia, sent me an excellent question about using Google Earth for Canadian genealogy. Then she sent me an excellent answer before I had a chance to answer it myself! Here’s what they were:
Question: “I live in Canada and a lot of the Google Earth articles involving land plats can’t be applied in Canada. The prairie provinces do have a similar land survey system, with townships, ranges and meridians. I found a website where these can be converted to coordinates that Google Earth will recognize. However, this particular website would like to be paid for providing this information (legallandconverter.com). Do you know of any way these numbers can be converted without paying?”
Answer: “I have some good news! My very smart son found a free website,
prairielocator.com, which will give you the coordinates of Section, Township, Range and Meridian for the Canadian prairie provinces. It doesn’t cover quarter sections, but that’s okay if you know which one your ancestor was on. Please pass this along to your Canadian fans or Americans who have Canadian ancestors (there are many, I know).”

Thank you, Barbara–and a special shout-out to your son for finding that resource to help genealogists use Google Earth for Canada research!
Here’s my two-cent’s worth: I just peeked at PrairieLocator.com and I see the site also has an app for the iPhone: Prairie Locator Mobile – for iPhone, by Lisa Cooke | Jul 20, 2015 | 01 What's New, FamilySearch, images, Volunteer
The FamilySearch Worldwide Indexing Event: It’s like a big, happy relay race for family historians: a display of skill with record-setting accomplishments and the coming together of a community for a cause.
Last year, 66,511 FamilySearch indexers helped set a new record for the most people indexing in a 24-hour period. Their efforts resulted in more than 5.7 million records being processed in a single day!
This year, we encourage you to participate in FamilySearch’s Worldwide Indexing Event from August 7-14, 2015. “You have one week to participate by indexing at least one batch in the language of your choice,” said FamilySearch in an invitation to current indexers. “If you are fluent in French, Italian, Portuguese, or Spanish-our focus languages for 2015-please help index records in one of those languages. Let’s help our friends in other countries to find their ancestors too! All it takes is one batch indexed sometime during the week to be counted.” (Special training is available.)
I’ve learned that indexing for others feels great, but I get something out of it, too. I use indexing to become more familiar with different record types, like naturalization records, border crossings or church registers (my favorite record type) from different places or time periods. I become better at reading old handwriting and picking out genealogical details from old documents–great skills that help me in my own research!
Last year, more than 18,000 new indexers joined the fun during the 24-hour challenge. Why not do the same this year? Click here to learn more about FamilySearch volunteer indexing or read the articles below to learn about other indexing opportunities out there.
Resources:
Find Your Ancestor in Freedmen’s Bureau Records–Or Help Others Do the Same
Want to Help Index De-Classified CIA Records?
Volunteer Gem: He Indexed Milwaukee Journal Obituaries Himself
 More than 80% of Americans over the age of three (!) have at least one computer in the house today. Most of us don’t have its predecessor: the typewriter. But the typewriter keyboard was the forerunner of the computer keyboards we all know now. I just wanted to take a moment to wish the keyboard a happy 145th birthday!
More than 80% of Americans over the age of three (!) have at least one computer in the house today. Most of us don’t have its predecessor: the typewriter. But the typewriter keyboard was the forerunner of the computer keyboards we all know now. I just wanted to take a moment to wish the keyboard a happy 145th birthday!




 So what does this mean for you as a genealogist?
So what does this mean for you as a genealogist?
 Thank you, Barbara–and a special shout-out to your son for finding that resource to help genealogists use Google Earth for Canada research! Here’s my two-cent’s worth: I just peeked at PrairieLocator.com and I see the site also has an app for the iPhone:
Thank you, Barbara–and a special shout-out to your son for finding that resource to help genealogists use Google Earth for Canada research! Here’s my two-cent’s worth: I just peeked at PrairieLocator.com and I see the site also has an app for the iPhone: 
