by Diahan Southard | Oct 24, 2014 | 01 What's New, Ancestry, DNA, Jewish
 Ancestry.com has improved the ability of AncestryDNA to find good matches for Jewish, Hispanic and other ancestries that maybe weren’t so precise before. Here’s the lowdown, quoted liberally from Ancestry.com’s press release:
Ancestry.com has improved the ability of AncestryDNA to find good matches for Jewish, Hispanic and other ancestries that maybe weren’t so precise before. Here’s the lowdown, quoted liberally from Ancestry.com’s press release:
The problem: Predicting genetic relatives among customers of Jewish and Hispanic descent and some other groups. “In DNA matching, we are looking for pieces of DNA that appear identical between individuals,” says the release. “For genealogy research we’re interested in DNA that’s identical because we’re both descended from a recent common ancestor. We call this identical by descent (IBD). This is what helps us to make new discoveries in finding new relatives, new ancestors, and collaborating on our research.”
“However, we also find pieces of DNA that are identical for another reason. At one extreme we find pieces of DNA that are identical because it is essential for human survival. At the other, we find pieces of DNA that are identical because two people are of the same ethnicity. We call these segments identical by state (IBS) because the piece of DNA is identical for a reason other than a recent common ancestor. This, we have found, often happens in individuals of Jewish descent.”
“The challenge in DNA matching is to tease apart which segments are IBD, and which ones are IBS….Most Jewish customers find that we predict them to be related to nearly every other Jewish customer in the database….Detecting which cousin matches were real and which ones were bogus has always been a challenge for these populations.”
First step toward a solution: “By studying patterns of matches across our more than half a million AncestryDNA customers, we found that in certain places of the genome, thousands of people were being estimated to share DNA with one another–likely a hallmark of a common ethnicity. Our scientific advancements… have allowed us to effectively “pan for gold” in our matches–by throwing out matches that appear to only be IBS, and keeping those that are IBD.”
“While the problem was more pronounced in customers of Jewish and some Hispanic descents, we observed this problem across all ethnic groups. So, all customers will see increased accuracy of their DNA matches, and significantly fewer ‘false’ matches.”
AncestryDNA results with better matches found by this method “will be available in the coming months,” says the release. They plan to email existing customers when results are ready.
by Diahan Southard | Sep 25, 2012 | Genealogy Gems Podcast
In this episode we are pulling back the curtain on the Antiques Roadshow, as well as talking a bit about what to include and not include in your family tree.
I’m just back from Odessa Texas where I presented a full day seminar at the Permian Basin Genealogical Society. I got to enjoy a big dose of Texas hospitality and had an absolutely wonderful time.
Next up I’m heading to Kelowna British Columbia for the Kelowna & District Genealogical Society Harvest Your Family Tree 2012 Conference where I will be again doing four presentations as well as a Meet the Speakers panel.
MAILBOX:
Family Tree Magazine Digital Subscriptions from Kathy: “I subscribe to Family Tree Magazine. Can I download my print subscription to my iPad….as you can with other subscriptions? Or do I need to pay for each issue that I download? Family Chart Masters helped me with my Family Tree Chart. It was beautiful and was a hit at our Family Reunion. Janet was so helpful. Thank you for the recommendation. Love your podcasts.”
Lisa’s Answer: The Family Tree Magazine digital subscription is separate from the print subscription, unless you have purchase their VIP Subscription. So you can either purchase individual digital issues from the Shop Family Tree Store, or you can purchase a separate annual digital subscription. I think they keep it separate because not everyone wants both. Click here for a $10 off coupon for ShopFamilyTree and when you use that link it also supports the free Genealogy Gems Podcast. Thank you!
Get Lisa’s Book Turn Your iPad into a Genealogy Powerhouse
Paperback
Ebook
Replacement for RAOGK
From Mary in Iowa: “In Podcast #139, Ricky asked about a successor to the Random Acts of Genealogical Kindness website. There are actually three Facebook groups (not pages) carrying on the task of looking up genealogy information and other requests. They are RAOGK, RAOGK – USA, and RAOGK – International. You need to be a member of the Facebook group to post a message or request, but most requests for membership are granted quickly.”
Generous Genealogists
Gen Gathering
Scott from Oakland Maine: “I am in need of some advice regarding an un-cooperative family member. My father’s brother wants nothing to do with our family, and in years past once referred to himself as the “black sheep”. He has absolutely no interest in genealogy and is not at all willing to be a part of the family story that I am putting together. My question is, how do I reference this character in my tree.”
Lisa’s Answer: I imagine every family has a tough nut on a branch of the family tree! I’m a firm believer in the truth, and what I would do if it were me is to include basic data (that is publicly available) on him on my private, personal family tree. On trees and other info you make available publicly, (such as an online family tree) I would list him and his immediate family only as “Living” and whether they are male or female. In the end you have to do what seems right for you.
From Glenn: “Just wanted to say a quick thanks for both podcasts you produce…I’ve been interested in the Family History for some time…Recently my interest has arisen again, of course I have made classic mistake in not documenting everything, and just collecting names, dates and so forth. So in the last 6 months I’ve been citing sources and updating the database. One of the quandaries I have is when do you stop, not so much vertically, but how wide do you go, in relation to cousins, second cousins and families? Probably the main question I have is trying to decide whether to get a subscription to Ancestry.com or not, I feel I’m at that stage where online document will help out, in filling in the leaves on my branches.”
Lisa’s Answer: Go as wide as you want and are interested in. I would recommend adding basic info for someone you find who you won’t be pursuing, so that if down the road you run in to a brick wall and you need to do some cluster research or reverse genealogy, you will have new leads to follow. RE: Ancestry – I think you will find that Ancestry membership is a very cost effective and time saving way to do your research. Mine has been invaluable. See if you can find a 7 day free trial to check it out and confirm they have the kinds of records you need.
GEM: Diane Haddad Pulls Back the Curtain on The Antiques Roadshow
Music in this segment:
The Antiques Roadshow Remix
By The Elusive MrHatchard
Available on the SoundClick.com website
GEM: Halloween History Tidbits
Halloween Mason Jar Lanterns
Vampire Hunting Kit from the 1800s
GEM: Newspaper Milestones
On September 15, 1982, USA Today began publishing
On September 18, 1851, the New York Times issued its first edition
On September 25, 1690, the first newspaper in America was published for one day in Boston before being shut down by British authorities unhappy with its content.
Check out this episode
by Lisa Cooke | Jul 13, 2015 | 01 What's New, Evernote, images, Technology
 Recently Genealogy Gems Podcast listener Rosie wrote in with an Evernote question:
Recently Genealogy Gems Podcast listener Rosie wrote in with an Evernote question:
“I really enjoy listening to your podcasts. Thanks so much for all your efforts. As a long time researcher I always wondered how the Hunt family got from New England to Ohio around 1800. Not too long ago another researcher found some autobiographical sketches written by Thomas W. Hunt in the Library of Congress. They posted it on Ancestry.com and another researcher sent me the link. I am still trying to figure out Evernote but I am wondering if there is a way to transcribe the sketches from PDF format with this tool.”
Good for Rosie for considering her options for how technology might be able to make the task at hand just a little bit easier!
Currently you must have an Evernote Premium account in order for your PDF documents to be keyword searchable or to annotate PDFs directly. The pdf document that Rosie was hoping to automatically transcribe with optical character recognition (OCR) is in cursive handwriting. Evernote can apply OCR to simple, clear printing, but it can’t read script, especially fancier writing such as this Thomas Hunt sketch or
old German script and handwriting.That would require ICR, or intelligent character recognition, and that technology is still emerging and isn’t widely available to consumers yet.
The Solution: Evernote doesn’t transcribe documents. To get the genealogical content from the sketches into Evernote, Rosie will need to start a new Evernote note and re-type the documents herself. Once that is done, then Evernote can apply OCR to the note and the typed transcription will be keyword-searchable.
A Solution for Type and Printing if you aren’t an Evernote Premium user: If you are fortunate enough to discover a long-sought after genealogical document such as Rosie did, and your PDF document is typed text or simple, neat printing then you are in luck. There are free conversion tools available online that can do the trick. I use
ConvertOnlineFree.com to convert my PDF document to text. I like it because I can use the tool directly from the web without having to download software to my computer.
(As with all tools we discuss here you’ll need to do your own homework and decide if it is right for you.)
I simply:
1. click the Choose File
2. select the PDF file I want to convert from my computer
 3. click the Convert button
3. click the Convert button
4. save the converted file to my computer
5. copy and paste the text into a new note in Evernote, and OCR does the rest.
Resources
How to Use Evernote for Genealogy: The Ultimate Education
Evernote for Genealogy laminated quick reference guide, available for for both Windows and Mac users. This guide is handy for everyday reference, and it’s packed with time saving tips you can use every day in your genealogy research.
How to Add Text to a Web Clipping in Evernote
 It’s nice to share
It’s nice to share
Do you know other genealogists who use Evernote? Why not share this post with them? Use our handy social media buttons at the top of this post, or copy the and paste the URL into an email. Your friends will thank you!
by Lisa Cooke | Jul 23, 2015 | 01 What's New, Ancestry, Census, images, Libraries
 HeritageQuest Online is now even more worth the trip to your local library to access for free, now that its new interface is powered by Ancestry.
HeritageQuest Online is now even more worth the trip to your local library to access for free, now that its new interface is powered by Ancestry.
For the past few months, library patrons have been getting used to a new version of HeritageQuest Online. This online genealogy resource, available only at libraries or through their websites, “has a new interface powered by Ancestry, enriching the search experience and streamlining the research process,” as described by a company press release a few months ago.
“The intuitive interface provides a fresh user experience that will be familiar to Ancestry.com users,” states the release. “A new Image Viewer offers basic and advanced capabilities without any plug-in, making it easy to share images with family and friends. Image resolution…is significantly improved with the addition of greyscale and color. The Research Aids resources for learning opportunities for novice, intermediate, and advanced searchers.”
Other bloggers have commented on the improved user interface, but what caught my eye was a more detailed, mouthwatering description of all the census extras and other new HeritageQuest Online content (from its site):
- “Now available for searching is the entire U.S. Federal Census collection from Ancestry.com including supplements (e.g., 1940 Enumeration District Maps) and several schedules (e.g., non-population schedules) previously not included for searching.
- 20,000 city directories have been added to the existing city directories in the Book collection, increasing the size of the Books collection to more than 45,000 titles.
- Expanded content in the Revolutionary War Collection. The entirety of the NARA Series M804 is now included here, providing access not only to the previously available “Selected Records” (Series M805) but now also to the “Non-Selected” records of each file.”
Finally, four of the six HeritageQuest Online data collections (Census, Books, Revolutionary War, and Freedman’s Bank) have “brand new search pages with limits, exact matching options, and additional fields for searching.”
Resources:
5 Genealogy Resources to Look for at YOUR Public Library
WorldCat for Genealogy: 40 Million Records and Digital Gateway
 Genealogy Gems Premium members can learn more about using HeritageQuest Online and other fantastic resources in Genealogy Gems Premium Podcast Episode 125. (Premium membership required: learn more about that here.)
Genealogy Gems Premium members can learn more about using HeritageQuest Online and other fantastic resources in Genealogy Gems Premium Podcast Episode 125. (Premium membership required: learn more about that here.)
by Lisa Cooke | Oct 15, 2015 | 01 What's New, Adoption, African-American, DNA, Health History
Two cousins recently chatted after learning that they share DNA. The first asked whether the second is white. “No,” she answered. The response: “Are you sure?”
In our modern society, families are defined in a myriad of different ways. Using DNA for genealogy is certainly contributing to these
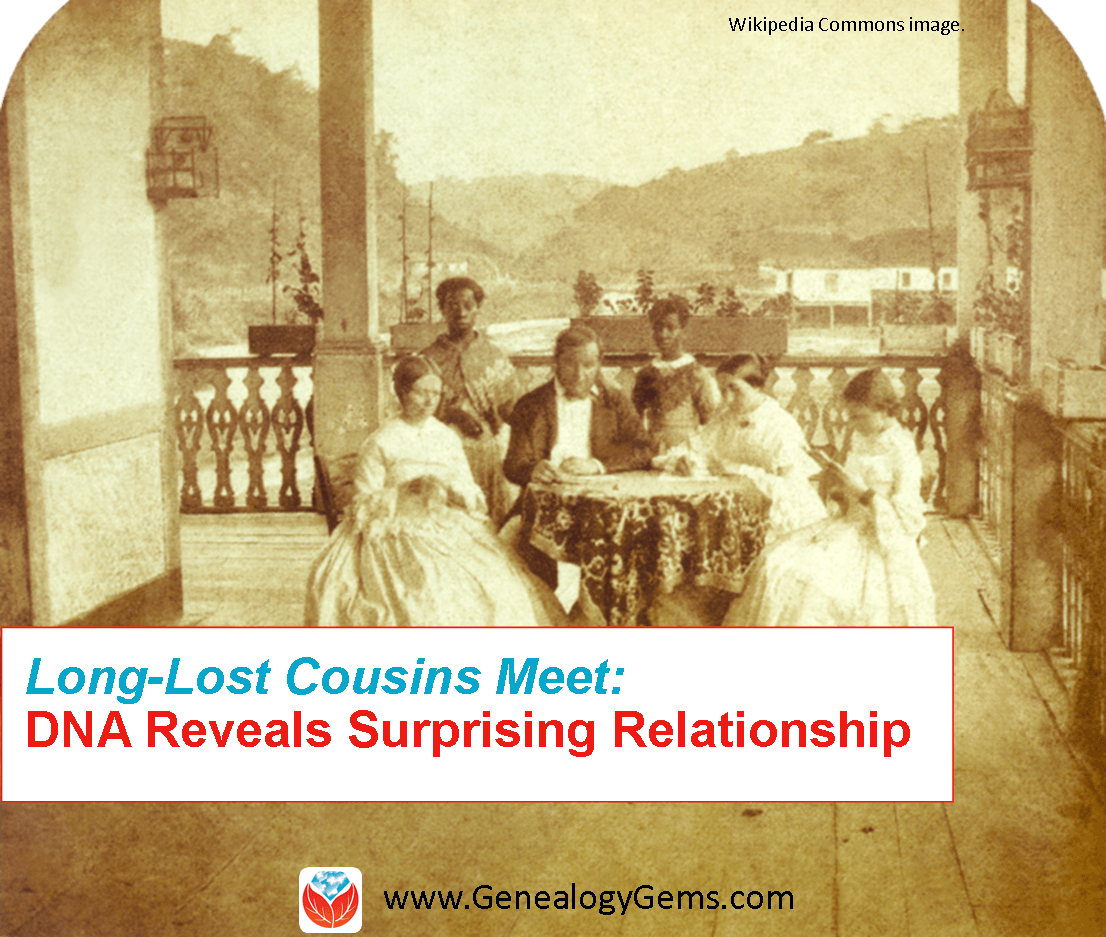
A family and its female slave house servants in Brazil, c.1860. Wikimedia Commons image. Click to view full source citation.
changing definitions, as families find themselves genetically linked across social and cultural boundaries to kin they never expected.
Such is the case for a Bartow, Florida resident who submitted a DNA test out of curiosity and found more than she expected. Through a combination of DNA testing and social media, Mary McPherson, who is white, met one of her cousins, Dolores Washington-Fleming, who is black.

Peter Williams’ entry in 1850 U.S. Census Slave Schedule, St Bartholomews Parish, Colleton, South Carolina. Image from Ancestry.com.
According to an article on The Ledger, the two women share a great-great-grandfather, Peter Edward Williams, who was born in South Carolina two centuries ago. Peter was a slaveholder. The 1850 census slave schedule shows that he held a female slave who was a few years younger than she was. Dolores believes that’s her grandmother’s grandmother.
The two finally met this past May for the first time and enjoyed this new definition of family. I think what I like most is what Dolores’ son said about the situation: “My mom and I are fascinated by history, and this is history. We represent what the times were like back then.” It still boggles my mind just a little that we are able to use the DNA of living people today to resurrect the past, and bring depth and meaning to the present, and possibly even prepare us for the future.
I find myself in a similar situation to Dolores and Mary. My mom was adopted, and even though we have had DNA testing completed for several years, we didn’t have any close matches, and honestly, we weren’t looking. Though she did have a passing interest in her health history, my mom did not feel the need to seek out her biological family. But then over the last few months various pieces of her puzzle have started to fall into place. This is much because of a key DNA match that popped up in March.
With that one match and subsequent correspondence, our interest in my mom’s biological family has skyrocketed. Why? I think it is because our DNA match, sisters from Texas, have shown us genuine kindness and interest. They have truly shown us what it means to be family. Even though we are unexpected, even though we aren’t sure yet how exactly we are connected, they have embraced us without reservation without hesitation.
To me, this is what family is. They accept you in whatever condition you come in and do their best to make you feel like you belong. Now, that kind of welcome isn’t felt by everyone who meets their genetic cousins, and people should carefully consider whether they’re ready for unforeseen results or unanticipated reactions from DNA matches before they get started.
But what about you? If you’ve started down the genetics path, how has DNA testing expanded or strengthened your definition of family?
Learn more about DNA testing for genealogy–how to get started or how to make sense of testing you’ve already had–with my quick guides available at the Genealogy Gems store, and then contact me at YourDNAGuide.com to arrange your own personal DNA consultation.
Resources for DNA for Genealogy
DNA Quick Guides for Genealogy (Bundle them for savings!): Getting Started, Autosomal DNA, Y Chromosome DNA, Mitochondrial DNA, Understanding Ancestry,  Understanding Family Tree DNA
Understanding Family Tree DNA
New AncestryDNA Common Matches Tool: Love It!
Confused by Your AncestryDNA Matches?
 Thank you for sharing this article with others by email or on your favorite social media site. You’re a gem!
Thank you for sharing this article with others by email or on your favorite social media site. You’re a gem!
 Ancestry.com has improved the ability of AncestryDNA to find good matches for Jewish, Hispanic and other ancestries that maybe weren’t so precise before. Here’s the lowdown, quoted liberally from Ancestry.com’s press release:
Ancestry.com has improved the ability of AncestryDNA to find good matches for Jewish, Hispanic and other ancestries that maybe weren’t so precise before. Here’s the lowdown, quoted liberally from Ancestry.com’s press release:







 Understanding Family Tree DNA
Understanding Family Tree DNA Thank you for sharing this article with others by email or on your favorite social media site.
Thank you for sharing this article with others by email or on your favorite social media site.