by Lisa Cooke | Sep 1, 2017 | 01 What's New, British, Records & databases
English genealogy records abound in this week’s roundup of new family history records online. Find England BMD, parish records, newspapers, and more. Also: an important addition to the British Newspaper Archive’s Irish newspaper collection, over 1,000 years of Chinese documents and records, German vital records, parish records for Italy and Sweden, and new US collections for VA, OH and NY.
English Genealogy Records Now Online
Ancestry.com subscribers can now search these English genealogy record collections:
-
-
-
-
- Bedfordshire Petty Sessions 1854-1915 This collection includes details of over 100,000 individuals involved in petty session hearings in Befordshire. Details for each individual may include name, role in the case, date of the hearing, location of the court, and even the fines or punishments given to the defendant(s).
- Bedfordshire Valuation Records 1838-1929 These records deal solely with the value of properties in Bedfordshire county. The volumes name the proprietor or tenant, describe or name the property and give an annual rental value. It will also sometimes give an acreage for the property.
- Bedfordshire Land Tax Records 1797-1832 Details found within this collection include may include year of residence, name of occupier, name of owner, and parish of residence.
- Shropshire Extracted Church of England Parish Records, 1538-1812. This collection of indexes is taken from various published versions of parish and probate records from Shropshire, England dating from the early 1500s (with some non-parish records earlier) to the late 1800s. “The records include baptisms/christenings, burials, marriages, tombstone inscriptions, obituaries, tax lists, wills, and other miscellaneous types of records,” states the collection description. “Also included are some records from non-conformist churches.”
At FamilySearch.org, you can now search a free collection of Staffordshire Church Records. In partnership with Findmypast’s expansion of Staffordshire records, this collection provides church records from 1538-1944. Nearly 5 million indexed records and over 278,000 images are included.
Over at Findmypast, subscribers can now search extensive new collections for Buckinghamshire. (The original records are held at the Buckinghamshire Archives.) New databases include:
-
-
-
-
- Buckinghamshire Baptism Index 870,000 transcripts created from original records held at the Buckinghamshire Archives. You will also discover your ancestor’s birthplace, the date of the baptism, their father’s occupation and residence.
- Buckinghamshire Banns Index Explore 101,000 records created from original parish registers and bishop’s transcripts. “Each transcript will reveal the name of your ancestor’s intended spouse, the couple’s residence, the dates the announcements were read and their intended date of marriage.”
- Buckinghamshire Marriage Index Over 485,000 transcripts “will reveal the couple’s birth years, marital status, occupation, date of marriage, place of marriage, residence, occupation, father’s names, father’s occupations and the names of any witnesses.”
- Buckinghamshire Burial Index More than 662,000 transcripts are included, created from original parish registers and bishop’s transcripts. “Each record will reveal your ancestor’s birth year, age at death, burial date, and residence. An archive reference is also included, allowing you to locate a copy of the original document.”
 British and Irish Newspapers Now Online
British and Irish Newspapers Now Online
Over 2.3 million new articles and 7 brand new titles have been added to the British Newspaper Archive’s collection of historic newspapers this month. New titles now available to search include:
- Tenby Observer
- Brechin Herald
- Milngavie and Bearsden Herald
- Alcester Chronicle
- Abergavenny Chronicle
- Ripley and Heanor News and Ilkeston Division Free Press
- Eastern Daily Press and the Colchester Gazette
Click here to explore these and other historic British Newspapers.
More than 5,000 pages from the Leitrim Advertiser have been added to Irish newspapers at the British Newspaper Archive. From the description: “The paper was originally published in Mohill, Leitrim and known in later years and The Leitrim and Longford Advertiser.” The earliest issue dates back to 1886, through 1916. With this addition, the British Newspaper Archive now has a newspaper for every county in Ireland!
German Births and Deaths: Bischofswerda
Ancestry.com has added new collections for Bischofswerda births (1876-1902) and deaths (1876-1951). Bischofswerda is located about 22 miles east of Dresden at the edge of Upper Lusatia in the German state of Saxony. To local residents, it is also known as “Schiebock” and known for its large historic market square and town hall.
Italian civil registration: Padova
FamilySearch has published 42,000 newly indexed records and images in its free collection,
Civil Registration Records: Padova 1621 – 1914. From the collection description: “Civil registration of births, marriages, and deaths within the custody of the State Archive of Padova. Includes supplemental documents, residency records, ten-year indexes, and marriage banns. Availability of records is largely dependent on time period and locality.”
Swedish Household Examination Books
Also at FamilySearch are 1 million indexed records and images for
Swedish Household Examination Books 1880-1920. According to the collection, “Each year until 1894 the Parish Priest would visit each home in the parish and test each individual’s knowledge of the catechisms. In addition, they would collect birth, death, and marriage dates as well as where families had moved to or from and when, etc. The priest would then come back each year and update or edit the information from the previous year and note any changes in the population of the home.” (These are also online at
MyHeritage.com.)
Click here to read a great article for getting started on your Swedish genealogy.
Chinese Records at the Library of Congress
An exciting announcement from the Library of Congress this week! “The contents of the Asian Division’s Pre-1958 Chinese Collection, totaling more than 42,000 items, are now fully searchable through the Library’s online catalog in both Chinese characters and Romanized script. This rich and diverse collection has served researchers and general audiences for nearly 90 years; until now, however, bibliographic records for these materials were only available through a card catalog.”
United States
New York. The Vassar College Digital Newspaper Archive is now available online. Provided by the Vassar College Libraries, this archive provides access to newspapers published by Vassar College students. Earliest issues date back to 1872, and cover a wide range of topics and events on and off campus. This collection currently contains over 85,000 pages.
Ohio. New at Ancestry this week are Ohio Soldier Grave Registrations, 1804-1958. This database contains grave registration cards for soldiers from Ohio who served in the armed forces, mainly from the time of the War of 1812 up through the 1950s. Records may contain an individual’s name, date and place of birth, date and cause of death, location of burial, next of kin, military service information, and more.
Also in Ohio, Kent State University has completed the digital Daily Kent Stater Archive. It contains 90 years of Kent State student publications, dated from Feb 1926 to Dec 2016. According to the
press release, “it covers several historic events as well as some great memories for the Kent State alumnae.” Check out the introductory video!
Did you know? You can search the Genealogy Gems website for articles about your favorite genealogy categories–including records and research tips for several countries and ethnicities. Go to our home page and click on the dropdown menu under What do you want to learn about? Scroll down to see the various categories or start typing a few letters to jump down to that part of the alphabetical list.
Disclosure: This post contains affiliate links and Genealogy Gems will be compensated if you make a purchase after clicking on these links. Thank you for supporting Genealogy Gems!
by Lisa Cooke | Oct 21, 2015 | 01 What's New, Canadian, Immigration, Records & databases
Library and Archives Canada, the Canadian national archive, holds original passenger arrival records. You can search a massive index to them on their website for free.

Canadian Passenger Arrival Lists: The Good and Bad News
There’s good news and bad news for those searching for Canadian passenger arrival lists.
The Bad News:
You won’t find a lot of Canadian passenger arrival lists before 1865. There are no comprehensive nominal lists of immigrants arriving prior to 1865 in Canada according to the Library and Archives Canada. Unfortunately, those lists didn’t generally survive.
Those that have can be scattered amongst various French and British collections.

“Les passagers du Saint-André : la recrue de 1659” is among the French resources at the Library and Archives Canada.
Visit the Passenger Lists page at the Library and Archives Canada here for details lists, years and microfilm numbers.
Good news:
You will be able to find a lot of records after 1865.
And the news gets even better. These records can easily be found online!
“The passenger lists are the sole surviving official records of the arrival of the majority of people accepted as immigrants in Canada,” says a Library Archives Canada webpage. “The passenger list is a list of immigrants arriving at an official port of entry on a particular ship on a given date.

Newspaper advertising was used to attract immigrants to Canada
Information Found in Canadian Passenger Lists
Generally speaking, each manifest provides the following information:
- the name of the ship
- port(s)
- date(s) of departure and arrival in Canada
- names
- ages
- sex
- professions or occupations
- nationalities
- destinations
The earlier lists aren’t always so detailed. But in some cases, other lists have information about the travelers’:
- health
- religion
- previous travels to Canada
- family members
- and how much they carried in their wallets.
Where to Search for Canadian Passenger Lists 1865-1922
Start your search for free in the Passenger Lists, 1865-1922 collection at the Library and Archives Canada website.
The city of Quebec, the major arrival port for many years, is covered for nearly that entire time span.
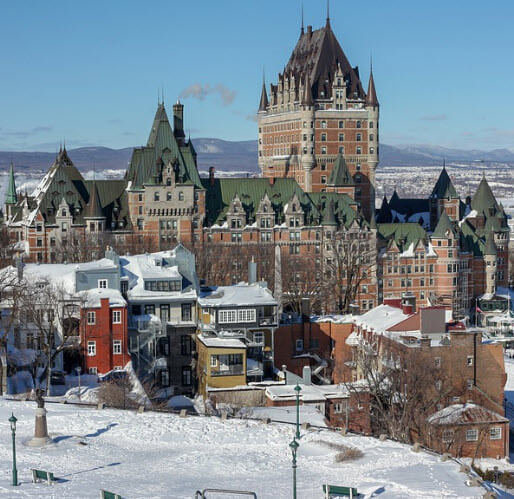

Quebec: Major Arrival Port in Canada
If you find it easier to search for these records in genealogy websites (so you can attach them to individuals in your tree), or if you’re specifically looking for passengers whose final destination was the U.S., check out these databases:
Canadian Passenger lists, 1881-1922 at FamilySearch.
The database includes records for Canadian ports:
- Quebec City,
- Halifax,
- St. John,
- North Sydney,
- Vancouver
- Victoria
- U.S. ports for passengers who reported Canada as their final destination.
Canadian Passenger Lists, 1865-1935 at Ancestry.
Quebec ports are included for these time periods:
- May 1865–Jun 1908,
- Jun 1919–Jul 1921,
- Apr 1925–Nov 1935.
U.S., Passenger and Crew Lists for U.S.-Bound Vessels Arriving in Canada, 1912-1939 and 1953-1962 at Ancestry.
Nearly 100,000 records of travelers to the U.S. via Canada are recorded for the ports of:
- Montreal
- Quebec
- Saint John
- New Brunswick
- Halifax
- Nova Scotia
- Vancouver
- British Columbia
- Victoria
- British Columbia
- Toronto
- Ontario
- Quebec
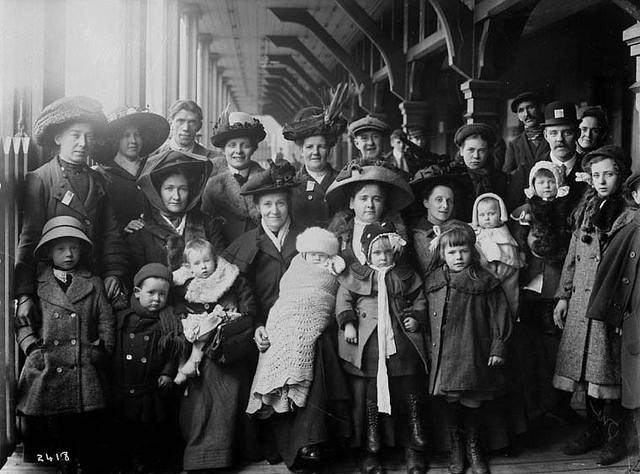

Mixed group immigrants, Quebec
More Great Canada Genealogy Resources
We have several more resources to assist you in your Canadian family history research.
- Click here to learn why Quebec Church Records are a Great Place to Look for Ancestors.
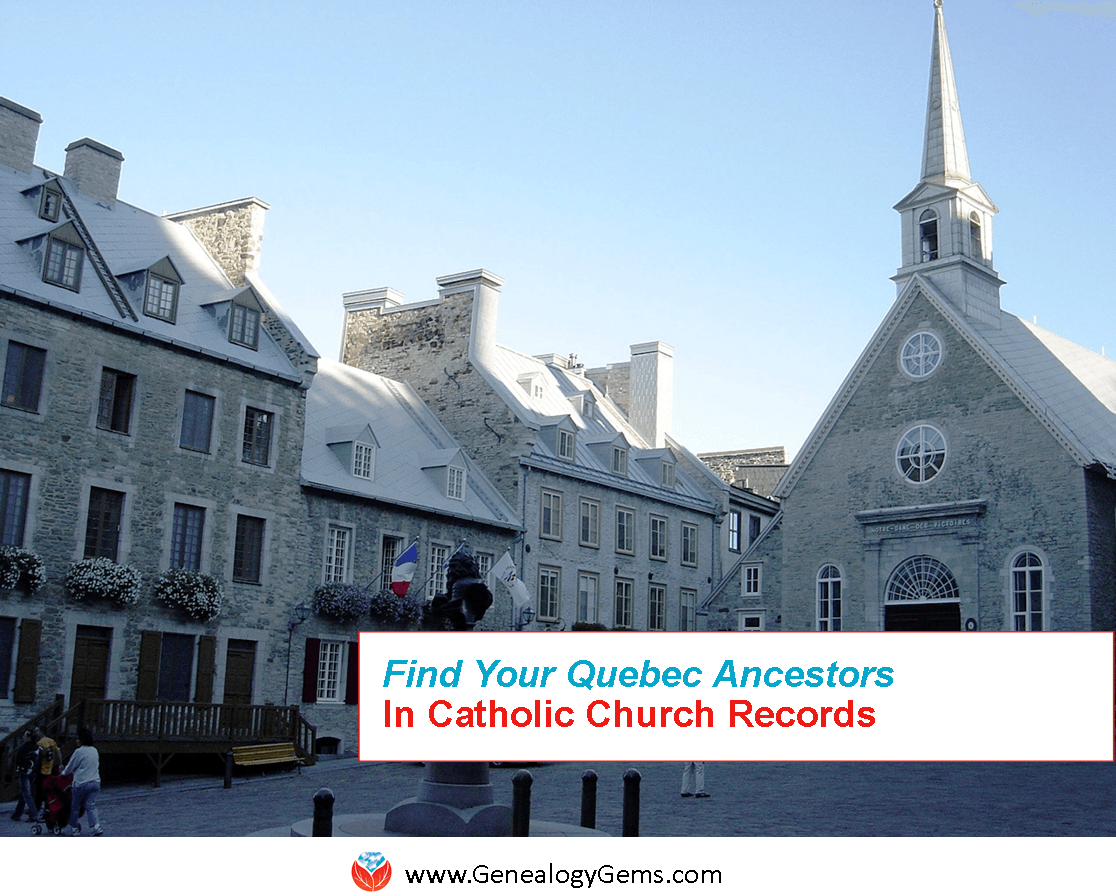
Notre-Dame-des-Victoires Church, Basse-Ville (Lower Town). Wikimedia Commons image; click to view.
by Sunny | Jul 27, 2018 | 01 What's New, Newspaper, Records & databases
The New Jersey Death Index tops this week’s list of new and updated U.S. genealogy records online. Along with a Native American census collection, our list includes family history records for Georgia, Illinois, New York, North Carolina, Tennessee and Virginia. Among...
by Lacey Cooke | Jan 2, 2019 | 01 What's New, Military
Military ephemera outside of photographs are abundant and located at many research libraries and other facilities across the United States. Familiarizing yourself with historical collections and the finding aids online at many places can make all the difference in...

 British and Irish Newspapers Now Online
British and Irish Newspapers Now Online






