by Lisa Cooke | Jun 15, 2016 | 01 What's New, Records & databases, Research Skills |
The US Public Records Index can be useful for genealogy–if you understand what it is and how to use it properly. Here’s an example and some tips.
Not long Russ sent in this tip recommending the US Public Records Index for genealogy:
“I was listening to Genealogy Gems Podcast 181 [in which] you were talking about where do we search while we are waiting for the 1950 Census….I recently discovered a wonderful resource, on Ancestry.com, that I have used along with city directories. The name of the record group doesn’t sound interesting but it can be a Gem for you: the US Public Record Index, 1950-1993, Volume 1 and 2. Volume 1 is far more interesting with more data. A search will return a name AND birth date, along with more than one address, zip code and sometimes phone numbers.”
Here’s a sample search result:
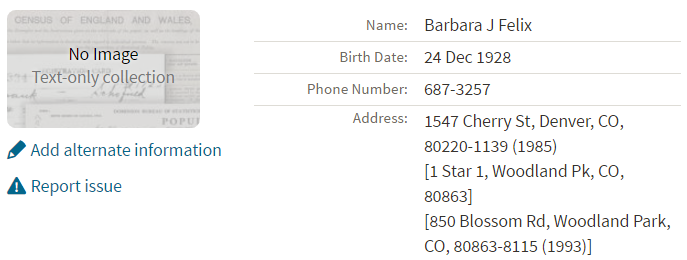
Russ kindly sent me Ancestry’s description of its online database for Volume 1, which says that original data comes from public records spanning all 50 states, such as voter registration lists, public record filings, historical residential records and other household database listings.
Collection Profile
What: U.S. Public Records Index
Where: Ancestry, FamilySearch, MyHeritage
Years Spanned: 1950-2009
Source Type: Lacking original source citations. “Hints to go on and follow up with further research into verifiable sources.”
Then he shared the following example of using the US Public Records Index to find recent relatives that he can’t look up yet in the 1950 census:
“I had a hint for a cousin in a yearbook. I know that she recently lived in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. I didn’t know where she went to college and I know her birthday. The name is not unique, not also not common. At the same time, I had the hint for the Public Record Index. You know those things we can’t use in a proof argument, but there [she] was in Philadelphia. The yearbook had her picture and only her name, not spelled the way I know it, but the Public Record Index puts her in Philadelphia at the right time and place.
I have seen 2 or 3 addresses for folks in the 1980s and 1990s in these indexes. Not all addresses have dates, but some do. I have one cousin with 5 addresses since 1983 and he won’t be in a census until the 1960 Census Records are released.”
Russ blogs about his family history at worthy2be.wordpress.com/. Thanks for the tip!
The U.S. Public Records Index pops up in my search results sometimes, too. Both volume 1 and volume 2 are searchable on Ancestry.com, as Russ says, in separate databases. Each has over 400,000 records in it. There’s also a free partial version of this database for 1970-2009 at FamilySearch.org and yet a third version at MyHeritage, with 816 million records, with nearly the same time frame. The FamilySearch database says its data comes from “telephone directories, property tax assessments, credit applications, and other records available to the public.”
More on the US Public Records Index
Here are a few tips worth mentioning about the US Public Records Index. Some of these points come from the FamilySearch wiki:
- Not everyone who lived in the U.S. appears in the index, and you’re more likely to find birth information for those born between 1900 and 1990. What you’ll find is primarily where someone lived, and often when they lived there.
- It’s rarely possible to positively identify a relative in this index since there’s limited information and it spans the entire country for up to a half-century, and you can’t follow up on the record it comes from because the index doesn’t say where individual records come from. So as Russ says, this is a great resource to use in combination with other records. It’s a similar concept to the way you might consult family trees that lack sources: hints to go on and follow up with further research into verifiable sources.
- When you find more recent listings, you can sometimes find telephone numbers for living distant relatives. If the thought of cold-calling distant relatives seems a little intimidating, listen to my Family History: Genealogy Made Easy podcast, episodes 14-15, for tips–and to get your courage up!
 More Gems on Researching Recent Relatives
More Gems on Researching Recent Relatives
by Lisa Cooke | Jan 6, 2017 | 01 What's New, Records & databases |
With an update to PERSI for genealogy, Pennsylvania birth and death records, and a tidbit or two from the United Kingdom and Scotland, you will start this year off right! It’s a new year and we are ringing in some great new and updated genealogical record collections.

PERSI for Genealogy
A monthly PERSI update has been added at Findmypast. With over 67,000 new articles and five new titles, the Periodical Source Index is the go-to source for those looking for stories of their ancestors. The new titles cover the American Historical Society, Chicago, Maryland, and British family histories & heraldry and will allow you to discover articles, photos, and other material you might not find using traditional search methods.
To fully appreciate PERSI as a genealogical tool, read our previous blog post “PERSI for Genealogy: the Periodical Source Index.” And you’ll find more related articles at the bottom of this article.
Pennsylvania – Birth and Death Records
This week, the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania released the 1911 births (105 years old) and 1966 death records (50 years old) to the public. This makes birth records publicly accessible from 1906 through 1911, and deaths 1906 through 1966. This collection index is free through the Pennsylvania Historical and Museum Commission portal.
Ancestry.com offers these records in digital form as well, but there is a subscription cost to use Ancestry. However, Pennsylvania residents can access these records free of charge through Ancestry.com Pennsylvania.
To access the index only, start with the Pennsylvania Historical and Museum Commission page on Vital Statistics for links to the indexes. You need to know the year of the event and the surname. If you do not know the year, you can search several years, one by one. These indexes are not digitized but are PDF files of the ones the State uses. If you locate a state file number for a certificate, you can order it from the State Archives.
However, if you are a Pennsylvania resident, you will be able to access the certificates digitally using the link to Ancestry.com Pennsylvania as mentioned above.
United Kingdom – Huntingdonshire – Marriages
New at Findmypast this week, the Huntingdonshire Marriages 1754-1837 collection contains over 1,000 names taken from 26 volumes of marriage records from the Huntingdonshire district of Cambridgeshire. These records will allow you to discover when and where your ancestor was married.
Scotland – Roxburghshire – Patient Registers
Also at Findmypast, explore the Roxburghshire, Kelso Dispensary Patient Registers 1777-1781. These registers contain over 1,700 names that list the date and outcome of patients’ treatment (such as cured, relieved of symptoms, or died). This may be particularly helpful for those unable to find a death date.
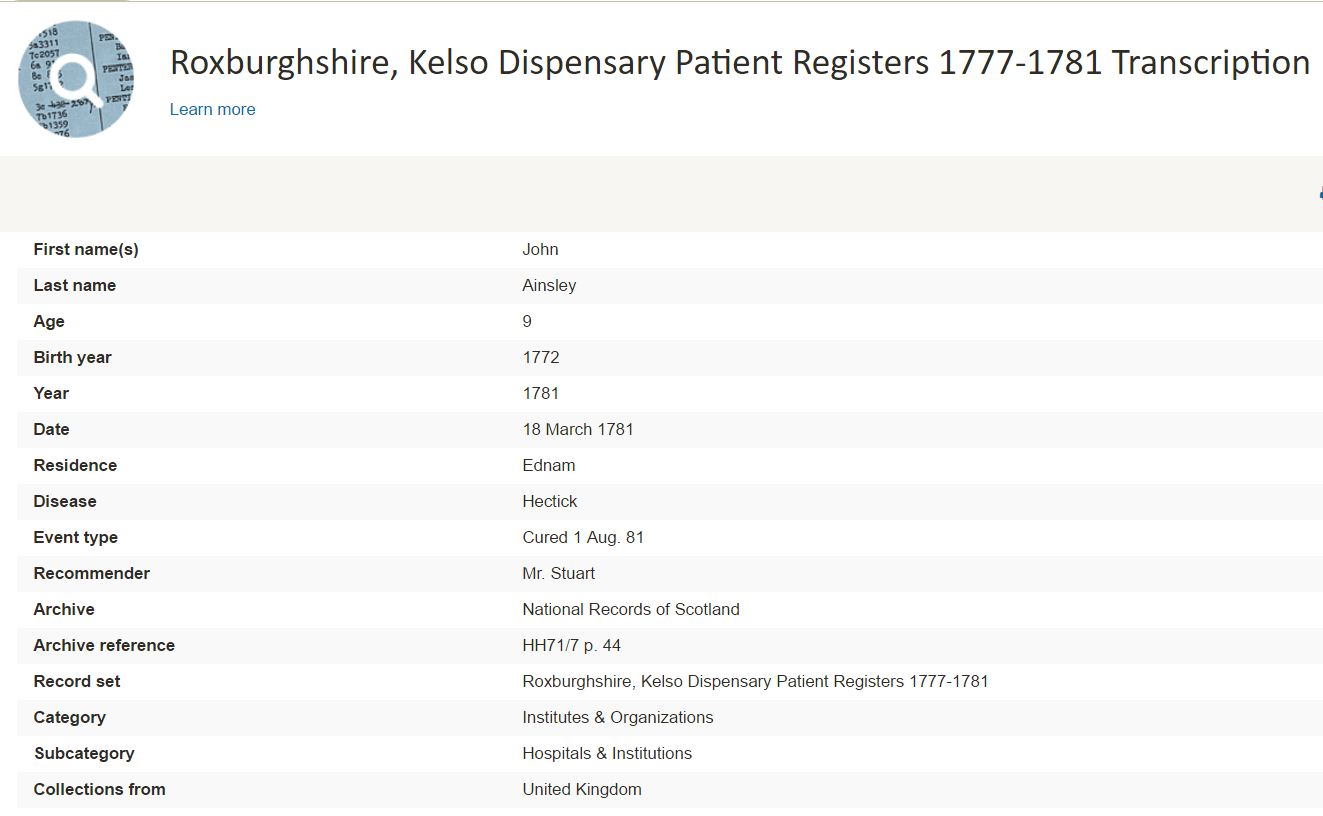
It should be noted that these are transcriptions only and you will not be able to see a digital image of the original.
More PERSI for Genealogy Articles
PERSI Digitized Collections Gaining Ground
New FindMyPast Hints Help Find Records
The Genealogy Gems Podcast Premium Episode 135: Compa rsion of Google Scholar & PERSI (Premium Member Subscription Needed)
rsion of Google Scholar & PERSI (Premium Member Subscription Needed)
by Lisa Cooke | Aug 9, 2017 | 01 What's New, Interviewing |
Need to contact distant relatives? Got cold feet? Follow these steps and you’ll warm right up–and hopefully, so will those you contact!

Today, online trees, social media, and email make it easier than ever to find relatives you don’t know well (or at all). And there are SO many reasons to contact them: to collaborate on research, swap photos or stories, or even request a DNA sample.
In these cases, you may need to make what salespeople refer to as a “cold call,” or an unexpected contact to someone you don’t know. I’ve done it successfully many times myself, so I can tell you this: it does get easier. Follow these steps to make it a smoother experience.
1. Identify the person you want to call.
Common ways to identify a new relative include:
- Another relative tells you about them
- Family artifact, such as an old greeting card, address book, captioned photograph, letter, etc.
- On a genealogy message board
- In an online family tree (with enough information showing to identify them)
- As the author of a book, article, or blog post with information about your family
2. Locate the person’s phone number, address, and/or email address.
 Here are some great websites for locating people you don’t know, or at least learning more about them (as you can on LinkedIn):
Here are some great websites for locating people you don’t know, or at least learning more about them (as you can on LinkedIn):
TIP: When looking through a geographically-based directory, don’t forget to search the entire metro area, not just one city. Try just searching their first name, particularly if it’s not a really common first name. Try and track down their number through other relatives or researchers.
3. Prepare ahead for making the call.
Every tough job gets just a little easier when you do your homework first!
- Take into account a possible difference in time zones.
- Choose a time when you are not too rushed
- Set yourself up in a quiet place, where there will be minimal background noise or disruptions
- Do a brief review of the family you are researching so it’s fresh in your mind
- Make note of specific questions you would like to ask.
- Have your genealogy software program open or your written notes at your fingertips
4. Adopt a positive mindset.
It’s natural to feel some apprehension when calling someone you don’t know. Before you pick up the phone, give yourself a little pep talk. Remind yourself how valuable this person’s information could be to your research. If he or she is quite elderly, remember that none of us will be around here forever so you need to make the call today! Say to yourself, “I can do this. This is important!” Be positive and remember, all they can do is say, “No thank you.”
5. Introduce yourself.
Give your first and last name and tell them the town and state where you live. Then tell them the family connection that you share. Tell them who referred them to you or how you located them. Cover these basics before launching into why you’re calling or what you want.
6. Overcome reluctant relatives.
Be ready to share what you’ve learned, and to share your own memories of a relative that you have in common. Mention something of particular interest in the family tree that might pique their interest. If they are very hesitant or caught off-guard, offer to mail them information and call back once they’ve had a chance to look at it. That way they can get their bearings, too.
 7. Do these things during the call:
7. Do these things during the call:
- Take notes: try a headset or use speakerphone, which will help to free up your hands for writing.
- Ask for new information and confirm what you already have.
If you have a way to record the call, then you won’t have to take notes and you can focus all your attention on the conversation. You can then transcribe the recording later. However, in some places, it’s illegal to record a conversation without telling them first and/or getting a person’s permission (not to mention discourteous). It can be very off-putting to start the first call by asking if you can record them. So, establish a connection first, make your request to record, and then press the record button.
Read more: How to Record a Conversation on your Smartphone or Skype
8. Leave a detailed voice mail message if there’s no answer.
State your name clearly, and that you would like to talk with them about the family history. Leave your phone number and tell them that you will call them back. Consider leaving your email address and suggesting they email you with a convenient time to call back. These days many people are more comfortable with email for the first contact.
9. Ask questions like these:
- “Do you or anyone else in the family have any old family photographs or a family Bible that I could arrange to get copies of? (Reassure them that you are happy to pay for copies and shipping.)
- “Do you know anyone else in the family who has been doing family research?”
- “May I have your permission to cite you as a source in print in the future?”
- “Is it OK with you if I keep in touch from time to time? What is your preferred method of contact?”
10. Wrap up the call.
Offer to give them your address, phone number, and email address. Ask for their mailing address and email address. Repeat or state your desire to share information you have, and tell them how you’ll send it. Let them know you would be pleased to hear from them if they come across any other information, pictures, etc.
11. Document the call.
Keep track in your genealogy database of each time you call someone and the outcome (“left a message” or summary of conversation). Having a log of calls and voice mail messages you’ve left will help you know when it’s time to follow-up with whom—and who wasn’t so interested in chatting again.
After a conversation, sit down at the computer or your notepad right away and make detailed notes about the phone conversation while it’s fresh in your mind. Include the person’s name, address, phone number, and date of the conversation. Make notes regarding any items you think may be questionable to remind you to go back and do more research on those points. Enter their contact information into your genealogy database as well as your email contact list.
12. Enter new information into your genealogy database.
 This is a must. Do it right away while it’s on your mind. Cite the conversation as the source of the information.
This is a must. Do it right away while it’s on your mind. Cite the conversation as the source of the information.
Remember to respect the privacy of those who prefer to remain “off-the-record” by not naming them in sources you post on public online trees.
13. Create an action item list.
Create action items based on what you learned. Ask yourself “What are the logical next steps to take considering what you’ve learned through this interview?” The call is not the end goal. It’s a step in the research process, and it can really help to make this list now, and while it’s fresh in your mind.
Cold Calling:
“The call is not the end goal.”
Lisa Louise Cooke
14. Follow up.
Send the person a written thank-you note or email. Remind them of your willingness to share your information, and acknowledge any willingness they expressed to share theirs (restate your willingness to help with copying expenses, postage etc. and consider including a few dollars). You never know: they might catch the genealogy bug and become your new research partner!
Next, put their birthday on your calendar and send them a card on their next birthday. Try this service: Birthday Alarm. If you don’t know their birthday but do have an address or email, send a greeting card for the next major holiday or on your shared ancestor’s anniversary or birth date. It’s another way of keeping the connection alive and expressing that you really do appreciate their help.
Occasionally make a follow-up call. See how they are doing, share any new family items you’ve come across recently, and ask whether they have they heard or found anything else.
 Resource: Genealogy Gems Premium Members can learn strategies for finding living relatives with their exclusive access to my video class, “Unleash your Inner Private Eye to Find Living Relatives.” Class includes:
Resource: Genealogy Gems Premium Members can learn strategies for finding living relatives with their exclusive access to my video class, “Unleash your Inner Private Eye to Find Living Relatives.” Class includes:
- a handout summarizing 9 strategies and resources
- a resource guide for online public records (U.S.)
- a downloadable Living Relatives worksheet you can print (or open in Word) that will help you capture and organize what you learn about them
Click here to learn more about Genealogy Gems Premium website membership.
by Lacey Cooke | Nov 16, 2018 | 01 What's New, Records & databases |
A major announcement from FamilySearch this week, launching the release of over 150 million Italian historical genealogical records online. Search now and learn about how you can help index. Also new this week: the 1901 Ireland Census, a beautiful image collection for...
by Lisa Cooke | Oct 29, 2016 | 01 What's New, Brick Wall, Research Skills |
Another brick wall…busted! We all have trouble spots in our family history research. Sometimes, we just need a little help breaking through. Here’s a tried-and-true method for using the genealogy FAN club principle to overcome brick walls in your family history research from guest author Amie Bowser Tennant.

A FAN club stands for Family, Associates, and Neighbors. Using the FAN club principle is a process in which genealogists identify a list of people (family, associates, and neighbors) that lived and associated with a given ancestor. By researching these other people, you may flesh out some new hints for your own research. Ultimately, identifying our ancestors FAN club is an effective tool for overcoming brick walls in genealogy research.
Renowned genealogist and author Elizabeth Shown Mills, coined the phrase “FAN Club” for genealogical purposes. She points out the significance of not only searching records for an ancestor’s surname, but also paying attention to documents about the ancestor’s “FAN Club” (Friends, Associates, Neighbors). Historical information, she says, is like real estate: the true value of any piece of information is unknown until it is put into community context. Learn more in Elizabeth’s “QuickSheet: The Historical Biographer’s Guide to Cluster Research (the FAN Principle).”
Step 1: “F” Stands for Family
Searching out other family members may prove helpful. Like in the case of Michael Knoop of Miami County, Ohio, I noticed there was another man in the county named Jacob Knoop. What was even more unique is both Michael and Jacob were born in New Brunswick. How unusual, I thought! Two men with the same last name, both born in New Brunswick, living in a small, farming area in Ohio! They had to be related, and they were. Jacob was Michael’s older brother.
Because I was having trouble finding when Michael had come to America, I traced Jacob instead. I located the passenger list with Jacob’s name on it and in doing so, I viewed all the passengers and found Michael, their mother, and lots of siblings!

Image above: Creating a FAN club with Family
In the case of Catherine Fearer Coddington, wife of James Coddington, I was having difficulty finding who her parents were. By searching for other Fearer individuals in the area, I discovered a biographical sketch on a John Fearer, Jr. Historical Encyclopedia of Illinois, Volume 2, reads:
“In 1836[,]John Fearer [Jr.] brought his family to Illinois. From Wheeling, West Va., the journey was made entirely by water. A landing on the Illinois soil was made at Hennepin. James Coddington, from near the Fearer’s old home in Maryland had already settled north of Princeton, in Bureau County, and later married John Fearer’s sister Catherine. The family found a home at Coddington’s until Mr. Fearer rented land near by.”
Catherine had a brother! With this new information, I was able to easily trace John’s father to John Fearer, Sr. of Allegany County, Maryland and finally connect Catherine to her parents through a probate record.
It’s easy to see what a powerful strategy researching the relatives of your ancestors can be!
Step 2: “A” Stands for Associates

Creating a FAN club with Associates
An associate could be a business partner, a witness on a document, a pastor, a lawyer, or the man that bailed Grandpa out of jail! Associates are often related. To create a list of associates, you might start gathering all witnesses to vital events, such as baptismal or christening records, marriage records, probate, land, and affidavits.
Were the courthouse records in your targeted area destroyed? Check the local newspapers for clues for possible associates. As an example, Jacob Trostel was a signee and vouched for Harvey D. Wattles’ tavern license. The license and names of the vouchers were listed in the newspaper, too. Eleven other men of the community appear on that petition. Later, Jacob himself petitions for a tavern license. That petition is signed by twelve men: George Filler, Conrad Slaybaugh, Lebright E. Hartzell, William G. Eicholtz, Isaac Yount, Joseph Dull, Isaac Myers, George W. Rex, Daniel Filler, William Harlan, and John Bream.
In both of these examples, relatives of Jacob Trostel had been vouchers. By tracing them, we were able to find out more about Jacob and his family.
Step 3: “N” Stands for Neighbors
Where can we find a list of our ancestors neighbors? A census, of course! When looking at a census page, we look for other people on the page with the same surname as our targeted ancestor. There’s a good chance those folks could also be related. But, your ancestor’s neighbors may also hold rich clues that can help you in your research. Many neighbors intermarried, sold land to each other, and even migrated to new locations together.
Besides looking at individuals listed on the same census page as your ancestor, remember to turn the page! Sometimes, a neighbor is not on the same page as your ancestor, but rather the pages before or after. Just because a person appears directly after your ancestor on the census rolls doesn’t necessarily mean they were neighbors. This only indicates the order in which the census taker visited the homes. You might also be able to identify close neighbors by looking at land ownership maps for the area. In this way, you can easily identify who lived near-by.
If you are having difficulty determining where your ancestors came from, researching the neighbors may give the answer. Many neighbors migrated together. Always check at least one page before your ancestor and one page after your ancestor in any given census.
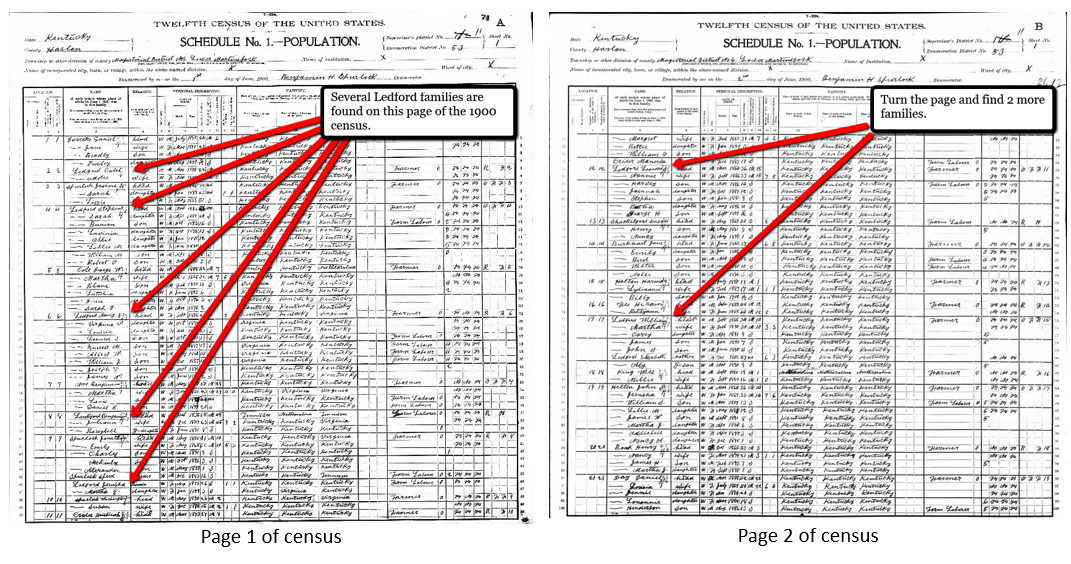
Image above: A FAN Club with Neighbors
Genealogy Fan Club: Comments and More Resources
There are likely dozens of successful ways for creating a FAN club for your ancestor. We would love to hear your examples in the comments below. For even more ways to break through those genealogy brick walls, enjoy these links below.
Read our article Solve Your Genealogy Brick Walls: 3 Tips for Breaking Through!
 Even better: Genealogy Gems Premium Members can watch Lisa’s one hour video class Brick Walls: Cold Case Investigative Techniques. In this video you’ll not only learn how to apply criminal cold case strategies to your brick walls, but you’ll also get loads of fresh and innovative ideas you can try right away. If you are not a Premium Member yet, learn more about becoming a Genealogy Gems Premium Member here.
Even better: Genealogy Gems Premium Members can watch Lisa’s one hour video class Brick Walls: Cold Case Investigative Techniques. In this video you’ll not only learn how to apply criminal cold case strategies to your brick walls, but you’ll also get loads of fresh and innovative ideas you can try right away. If you are not a Premium Member yet, learn more about becoming a Genealogy Gems Premium Member here.

 More Gems on Researching Recent Relatives
More Gems on Researching Recent Relatives




 Here are some great websites for locating people you don’t know, or at least learning more about them (as you can on LinkedIn):
Here are some great websites for locating people you don’t know, or at least learning more about them (as you can on LinkedIn): 7. Do these things during the call:
7. Do these things during the call: This is a must. Do it right away while it’s on your mind. Cite the conversation as the source of the information.
This is a must. Do it right away while it’s on your mind. Cite the conversation as the source of the information.



