Blog


Video #4 of our 25 Websites for Genealogy – Digital Collections
VIDEO & SHOW NOTES: Video #4 of our 25 Websites for Genealogy Playlist. In this video, my guest presenter Gena Philibert-Ortega covers digital collection websites that are must-haves for family history research. You’ll find plenty of genealogy gems waiting for free at websites #18 through 22.
Websites 18 through 22 of our 25 Websites for Genealogy
Some of these websites will be new to you, and others are going to be very familiar to you. In talking about the familiar websites, I want to get you thinking about them differently, explain a little bit more about what you can do at these websites, and how to get the most out of them.
In this series of 25 Websites for Genealogy, we’re going to be looking at websites in different categories. Our third category is Digital Collection websites (#18 through 22).
Download the ad-free Show Notes cheat sheet for this video here. (Premium Membership required.)
Websites #18: Digital Public Library of America
At the DPLA you can search for public domain research materials that will benefit your genealogy research. It offers a searchable access to millions of items including photographs, manuscripts, books, sounds, moving images, and more from libraries, archives, and museums around the United States.

Use filters to refine your search at DPLA
Website #19: Google Books
According to Lisa Louise Cooke, Google Books is the tool you should use every day for genealogy. It puts 25 million digitized and searchable free books at your fingertips.
Learn much more about how to get the most out of Google Books with these videos by Lisa Louise Cooke:
- Google Books – Getting Started (Premium Membership required)

Log in to watch now
- Google Books – 10 Surprising Finds
- Google Books – New Features
Website #20: FamilySearch Digital Library
https://www.familysearch.org/library/books/
The FamilySearch Digital Library includes over 500,000 genealogy books, family histories, maps, yearbooks, and more.
Website #21: Internet Archive
If you’re looking for new information about your family history, an important website to add to your research list is the Internet Archive. It’s a free website that attempts to archive the web, and that includes a vast array of genealogy materials!
Visit the dedicated Genealogy Collection page: https://archive.org/details/genealogy&tab=about
Learn much more on how to find valuable genealogical records for free with this video by Lisa Louise Cooke: Internet Archive – 10 Records You’ll Love to Find
Website #22: HathiTrust
Founded in 2008, the non-profit HathiTrust provides access to 18+ million digitized items in the HathiTrust Digital Library. Reading access varies depending on the item and whether you belong to a participating organization, but it’s definitely worth a look.
Resources:
Download the ad-free Show Notes cheat sheet for this video here. (Premium Membership required.)
Not a Premium Member yet? Discover the benefits and join today.

Click to learn more about Genealogy Gems Premium Membership.

Video #3 of our 25 Websites for Genealogy – Newspapers!
VIDEO & SHOW NOTES: Video #3 of our 25 Websites for Genealogy Playlist. In this video, my guest presenter Gena Philibert-Ortega covers digitzed newspaper websites that are must-haves for family history research. Even though some sound specific to a certain area, don’t be fooled. They have resources available for all genealogists including even more than newspapers.
Websites 13 through 17 of our 25 Websites for Genealogy
Some of these websites will be new to you, and others are going to be very familiar to you. In talking about the familiar websites, I want to get you thinking about them differently, explain a little bit more about what you can do at these websites, and how to get the most out of them.
In this series of 25 Websites for Genealogy, we’re going to be looking at websites in different categories. Our third category is the newspaper websites (#13 through 17).
Download the ad-free Show Notes cheat sheet for this video here. (Premium Membership required.)
Websites #13: Newspapers.com
Newspapers.com is a subscription service owned by Ancestry.com. The two websites are connected so that you can attach your Newspapers.com finds to your Ancestry tree. Newspapers.com includes newspapers found at Ancestry but all newly newspaper pages are added to Newspapers.com. They also offer a Publisher’s Extra subscription that expands your access to additional newspaper records.
Learn more:
- Newspapers.com – Finding Family Recipes
- Newspapers.com – Reconstructing Your Ancestor’s Life
- Newspapers.com – Digging Deeper (Premium)
Website #14: GenealogyBank
Website #15: NewspaperArchive
NewspaperArchive includes digitized newspapers from around the world.
Website #16: Chronicling America
Original Website: https://chroniclingamerica.loc.gov
New website: https://www.loc.gov/collections/chronicling-america
The Library of Congress offers this huge free collection of digitized newspapers from across the United States. The papers range from 1756 to 1963. Expand your search with the U.S. Newspaper Directory 1690 to present.
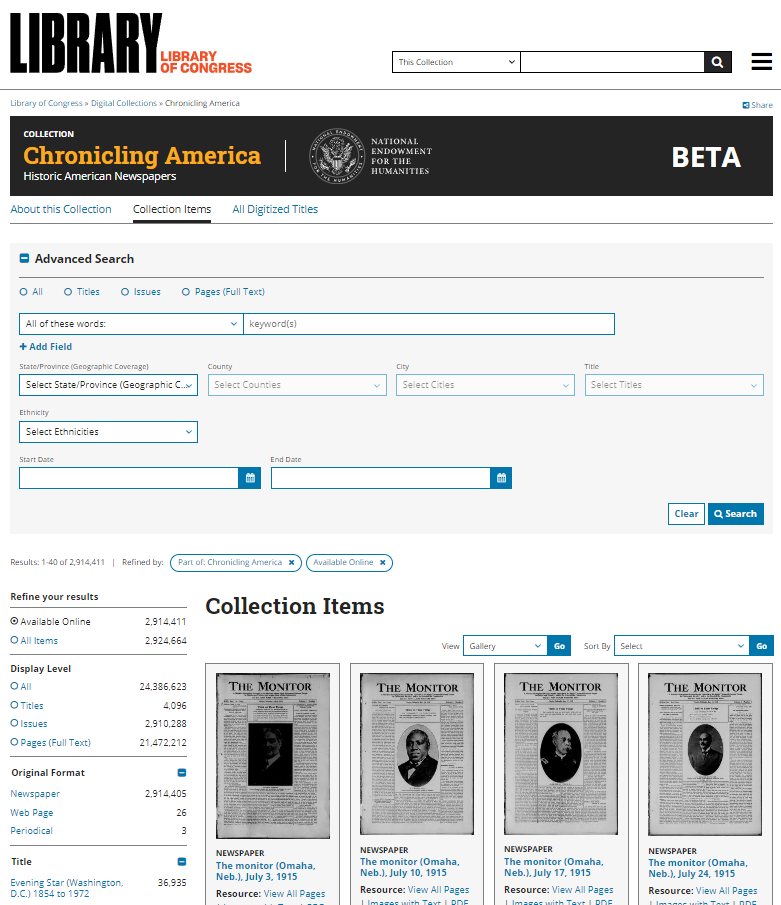
The new user interface at Chronicling America.
Website #17: Fulton History
Fultonhistory.com features over 1,000 New York newspapers, plus newspapers from other states and Canada. It’s a vast free collection curated by one man!
Resources:
Download the ad-free Show Notes cheat sheet for this video here. (Premium Membership required.)
Not a Premium Member yet? Discover the benefits and join today.

Click to learn more about Genealogy Gems Premium Membership.

Find and Identify Old Family Photos at DeadFred – Audio Podcast Episode 281
AUDIO PODCAST SHOW NOTES: Discover more than 100,000 old family photos on Dead Fred. Founder Joe Bott explains how to find photos of your relatives on this free website, as well as how to post your unidentified photos. Who knows, someone else may spot your photo and have the answers.
This interview is also available in video form here on the show notes page (below). And if you’re a Genealogy Gems Premium Member, you can download the show notes as a PDF cheat sheet in the Resources section at the bottom of the page.
Listen to the Podcast Episode
To Listen click the media player below (AUDIO ONLY):
Video & Show Notes
Watch the video version and get the show notes article: The Secret to Finding Old Family Photos
Resources
Downloadable ad-free Show Notes PDF for Premium Members.
Become a Genealogy Gems Premium Member
Premium Members have exclusive access to:
- Our extensive genealogy video classes archive
- The Genealogy Gems Premium Podcast
- Elevenses with Lisa video archive
- downloadable ad-free show notes PDF cheat sheets for all videos and podcasts.
Become a member here. Learn more about Genealogy Gems Premium Membership.

Click to learn more about Genealogy Gems Premium Membership.
Genealogy Gems Podcast App
Don’t miss the Bonus audio for this episode. In the app, tap the gift box icon just under the media player. Get the app here.
Get the Free Genealogy Gems Newsletter
The Genealogy Gems email newsletter is the best way to stay informed about what’s available with your Premium eLearning Membership. Sign up today here.
Our Sponsors:
Get your MyHeritage DNA Test Kit
Archives.com
Archives is an invaluable resource if you want to make your family history research simple and affordable. Visit Archives.com and let your family history journey begin.
Newspapers.com
Get 20% off a Publisher Extra subscription. Click here and use coupon code GenealogyGems
Follow Lisa and Genealogy Gems on Social Media:
- Instagram.com/genealogygemspodcast
- Facebook.com/genealogygems
- Pinterest.com/lisalouisecooke
- YouTube.com/GenealogyGems
Resources
Download the handy PDF show notes that complement this podcast episode.





