by Lisa Cooke | Aug 27, 2015 | 01 What's New, Ancestry, DNA, images, Trees
A new tool at Ancestry DNA is blowing my genealogy mysteries wide open!
is blowing my genealogy mysteries wide open!

I have been up since 5:30 with plenty of goals and ambitions for today. But I got distracted. Distracted by a new tool at AncestryDNA that is blowing my genealogy mysteries wide open.
The new tool AncestryDNA Common Matches tool is hiding between the “Pedigrees and Surnames” filter and the “Map and Locations” filter on your matches’ main match page. The Common Matches tool pulls out the shared 4th cousin or higher matches between two people.
Let’s take a look at how this might work for you.
 Let’s say you have a second cousin, Denise, that you have already identified in the Ancestry database and you know your common ancestral couple is Joseph and Louise Mitchell. You want to gather others who share DNA with both you and Denise. Those individuals then have a high likelihood of being related to Joseph and Louise in some way.
Let’s say you have a second cousin, Denise, that you have already identified in the Ancestry database and you know your common ancestral couple is Joseph and Louise Mitchell. You want to gather others who share DNA with both you and Denise. Those individuals then have a high likelihood of being related to Joseph and Louise in some way.
So we click on the “Shared Matches” button on Denise’s page and find that Mike, Spencer, and Wendy all have DNA in common with you and Denise. After reviewing pedigree charts, you are able to determine that Mike is related through Louise’s sister and Wendy is related through Joseph’s brother. Note that Wendy’s actual relationship to you is not 4th cousin, as it is shown, but she is actually your 3rd cousin once removed. Remember that the relationship given is not always the exact relationship of two people who have been tested.
 But what about Spencer? Spencer, unfortunately has not yet linked his family tree to his Ancestry account or answered any of your queries about his family tree. I am sure he has just been busy. Or he doesn’t know his family tree. Or his computer was captured by aliens or smashed by his two-year-old grandson just as he was about to click “send” and reveal how the two of you were connected. Whatever the case may be, up until this point you haven’t heard a peep from Spencer and therefore had absolutely no way to figure out how Spencer was related to you.
But what about Spencer? Spencer, unfortunately has not yet linked his family tree to his Ancestry account or answered any of your queries about his family tree. I am sure he has just been busy. Or he doesn’t know his family tree. Or his computer was captured by aliens or smashed by his two-year-old grandson just as he was about to click “send” and reveal how the two of you were connected. Whatever the case may be, up until this point you haven’t heard a peep from Spencer and therefore had absolutely no way to figure out how Spencer was related to you.
But now you know that he is somehow associated with the Joseph and Louise Mitchell family because he came up as In Common With (ICW) you and Denise.
We can take this one step further and ask Ancestry to show us who has DNA ICW you and Spencer. You can see here that while Mike still remains, Wendy has dropped off the list. Now there are two possible explanations for this: The first is that Spencer is related through Louise’s parents, John and Sarah, and that is why he is not sharing DNA with Wendy.
The other, less likely, possibility is that Spencer is related through Joseph’s parents Louis and Mary, but doesn’t share enough DNA with Wendy to be detected on this test.
While this information is helpful, it still hasn’t completely solved the case. The first thing you should do with your new-found knowledge is start sending more pointed questions to your matches. Here is an example message you might send to Spencer:
“Dear Spencer,
I was just playing around with the new AncestryDNA Common Matches tool and I see that you are related to a few of my other matches that connect through Joseph and Louise Mitchell. Louise’s parents, John and Sarah Marsh, were both born in Mississippi in the 1840’s and Joseph’s parents Joseph and Mary Mitchell, were born in Tennessee in 1856 and 1863 respectively.
Do any of these names or places sound familiar to you?
I am looking forward to working with you on this connection.
Your DNA Cousin, Diahan”
Assuming this garners a response, you can then work together to find your connection. If his budget is not allowing for a new computer at this time and you never hear from Spencer, the key to figuring out how he is related to you may be in the new match, Beth, who is ICW you and Spencer. If you can figure out how Beth is related to you, you will know Spencer is related in a similar way.
 If you’ve decided you would like to get in the DNA game, start with Ancestry DNA: Genetic Testing – DNA Test
If you’ve decided you would like to get in the DNA game, start with Ancestry DNA: Genetic Testing – DNA Test , and then head over to AncestryDNA and start growing your genetic family tree!
, and then head over to AncestryDNA and start growing your genetic family tree!
For a little more guidance, I suggest you purchase my laminated quick guides, “Understanding AncestryDNA and “Understanding Family Tree DNA.” These are also available as a part of a complete bundle of DNA guides specifically designed to help you navigate your results at the leading genetic genealogy testing companies. Click here to see all our DNA quick guides.
by Lisa Cooke | Oct 5, 2014 | 01 What's New, Australian, DNA
 Recently a group of 100 residents from Wellington, New Zealand assembled together to determine what exactly it was they had in common. Their host? Dr. Spencer Wells, Director of the National Genographic project. Their admittance fee to this party? A cheek swab.
Recently a group of 100 residents from Wellington, New Zealand assembled together to determine what exactly it was they had in common. Their host? Dr. Spencer Wells, Director of the National Genographic project. Their admittance fee to this party? A cheek swab.
What they learned about themselves that evening, has a direct impact on YOU, a genealogist interested in identifying your ancestors.
You see, 800 years ago the first inhabitants of New Zealand were just beginning to explore their new territory. They had arrived from the eastern islands of Polynesia and lived in relative isolation for over 500 years.
While first discovered by the Dutch in 1642, New Zealand wasn’t regularly visited by Europeans until the late 18th century. For Spencer Wells and the National Genographic Project, sampling people of New Zealand would provide a rare opportunity to study the genetic effect of a recent collision of indigenous and outside population groups.
We can think of mixing populations like adding a tablespoon of salt to a glass of water. At first it is easy to see the two different substances co-existing in the same location. But soon the salt becomes part of the water- creating a new substance, with only a small portion of the original substances remaining. This is what happened throughout history as outside groups arrived and intermarried with indigenous populations.
The goal of population genetics as a field of study, and specifically of the National Genographic project, is to look at the modern day population (in our example the salt water), and be able to identify which ancestral populations are present (in our example, determine which parts are salt, and which parts are water. This of course, without knowing beforehand that you were dealing with salt water!).
The National Geneographic project has identified 9 ancestral regions from which they believe all modern populations descend. These nine would be like our salt, and our water. They have then described how 43 reference population groups (our salt water) are comprised of their own unique mix of these 9 groups. They can also describe the origins of your direct maternal line, and if you are male, your direct paternal line.
This information was gathered for the Wellington residents. It was determined that the original Polynesian population and a small East Asian population are certainly the minority among a predominately Western European population group. This information will help groups like the National Genographic Project to determine the possible migration patterns of other peoples and cultures.
What does this mean for genealogy? This kind of research helps fuel the admixture results (the pie charts and percentages) reported to you by a genetic genealogy testing company when you take an autosomal DNA test. It is this research that helps genetic genealogists look at your DNA and pick out the essential, ancestral elements–your salt and your water–and determine how your unique mix reveals information about the origins and migration patterns of your ancestors.
Check out an article on this topic here.
by Lisa Cooke | Dec 6, 2013 | 01 What's New, FamilySearch, RootsTech
The all-star lineup of keynote speakers has been announced for RootsTech 2014. They will inspire everyone to discover and share the stories that connect our families-past, present, and future.
Ree Drummond, blogger and author, The Pioneer Woman
Ree is an award-winning blogger and New York Times bestselling author. Her popular website, The Pioneer Woman, was founded in 2006 and showcases her cooking, photography, and stories about country life.
Annelies van den Belt, CEO, DC Thompson Family History – Annelies is changing the way digital genealogical records are published and organized. Her company hosts 1.8 billion genealogical records across a family of online brands.
Judy Russell, blogger and professional genealogist, The Legal Genealogist – Judy is a certified genealogist with a law degree who enjoys helping others understand the interplay between genealogy and the law. She blogs and maintains The Legal Genealogist website.
Dr. Spencer Wells, project director, National Geographic Genographic Project – The indiana Jones of genetics, Dr. Wells has traveled the world and captured the DNA of more than a half-million people to tell the story of the human journey.
Todd Hansen, TV host, The Story Trek – Behind every door there is a story. This TV series consists of random door-to-door interviews to discover who lives behind those doors and their real stories.
Stephanie Nielsen, blogger and author, NieNie Dialogues – Stephanie’s story of survival and recovery after a plane crash captured the hearts of the nation. She has inspired others through interviews with Oprah Winfrey and on the Today Show.
 The fourth annual RootsTech conference, hosted by FamilySearch, will be held February 6-8, 2014 at the Salt Palace in Salt Lake City, Utah. In addition to renowned keynote speakers, the conference features over 200 classes, hundreds of booths in a huge Expo Hall, and evening events.
The fourth annual RootsTech conference, hosted by FamilySearch, will be held February 6-8, 2014 at the Salt Palace in Salt Lake City, Utah. In addition to renowned keynote speakers, the conference features over 200 classes, hundreds of booths in a huge Expo Hall, and evening events.
by Lisa Cooke | May 28, 2021 | 01 What's New, Newspaper
I used the British Newspaper Archive to make a shocking discovery in my husband’s family history was made with the help of these three powerful strategies. Read on to learn how to find more information on your ancestors in online historical newspapers. (This British Newspaper Archive link is an affiliate link and we will be financially compensated if you make a purchase. This helps support our free content like this. Thank you.)

The Research Question
Ever since I first started researching the family of my husband’s grandfather Raymond Harry Cooke, I have been aware that his mother, Mary Ann Susannah Cooke (maiden name Munns), died at a young age, around 40 years old.
What I didn’t know was how she died.

Mary Ann Susannah Cooke
In fact, Mary Ann Susannah Cooke has been one of the most elusive recent direct ancestors I’ve pursued. Up until about a decade ago we had never seen her face.
The image of Mary Ann (above) came to us through one of Bill’s first cousins. I had tracked her down in hopes of learning more about their shared grandfather, Raymond. Once we met I was thrilled to discover that Raymond had lived with her until his death at the age of 93 in 1987.
The cousin brought with her a dusty old box of his belongings. Inside we discovered the first and only known image of Mary Ann. (Genealogy Gems Premium members can learn more about this discovery and the methodology used to find the long-lost distant cousin in the Premium video class 9 Strategies You Need to Find Living Relatives.)
On the back of this cardstock image were notes written in Raymond’s own hand. The handwriting leads me to believe he may have added the notes later in life. This meant that I needed to be especially careful as I analyzed the information as it was likely from childhood memory.

As you can see on the back of the image, Raymond states that Mary Ann died about 1915, and that her birthday was September 3. The birthday was close but incorrect. The actual recorded birth date was September 6.
The date of death was much farther off. Death records from the county of Kent show that Maryann was buried August 20, 1908, a full seven years earlier than Raymond remembered.
It’s not a surprise that his dates were off the mark. Raymond was just 14 years old when Mary Ann died. But the question remained: how did she die?
The Search
About five years ago, after writing a blog post about the British Newspaper Archive, I decided to do some digging in historic newspapers to see if I could find anything about Mary Ann’s death in Tunbridge Wells, England in 1908. With a search of Mary Ann Cooke in the website’s powerful advanced search engine I located the answer within minutes. It was devastating.

The Courier, August 31, 1908:
“Tunbridge Wells Woman’s Sad Death: Drowned in a Water Tank. The Inquest.”
“Mr. Thos. Buss, district coroner, held an inquest at the Town Hall, Tunbridge Wells, on Saturday morning, touching the death of Mary Ann Cooke, aged 41 years, whose body was found in a tank at the roof of her house, 49 Kirkdale road, the previous day.”
Suffering from prolonged depression, Mary Ann had drowned herself upstairs in the family home’s water tank. The newspaper provided a blow-by-blow of the coroner’s inquest, and the heart-breaking testimony of her husband, Harry.
And then came the final shock: Harry and Mary Ann’s 14 year old son Raymond had discovered the body.
After absorbing the story of Mary Ann’s untimely death, I was keen to see if I could learn more about the family. This is where some very powerful search strategies came into play and helped me find MUCH more in the British Newspaper Archive.
3 Powerful Newspaper Search Tips
1. Look for Search Clues in the Articles You Find
Finding an historic article on your ancestors can feel like the end of the research road. But actually, it’s just the beginning!
Go through the article with a fine tooth comb. Make note of every http://laparkan.com/buy-sildenafil/unique detail that could possibly be used in an additional newspaper database search. Here’s a list of what I found in the article about Mary Ann’s inquest. In the following steps I’ll show you how we put some of these into action.
Addresses – The Cooke’s address of 49 Kirkdale Road in Tunbridge Wells, was mentioned twice within the first two sentences of the article.
Name variations – I’m not talking about a variation in spelling, although those are certainly worth noting. In the case of newspaper research I’m referring to the varying ways that people are referred to in the newspaper. In the inquest article, Mary Ann Cooke was also referred to as “Mrs. Cooke.” This got me thinking about other ways that Mary Ann might be referred to, such as Mrs. Mary Ann Cooke, Mrs. M. A. Cooke, etc. In England, a boy Raymond’s age might be referred to as “Master Cooke.” Write down all variations you find, and then continue your list by adding the additional possibilities you can think of.
Neighbors – Mrs. Pout played a vital role on the day of Mary Ann’s death, and she served as a witness at the inquest. This was the first I had heard of her, and her name definitely made it onto my list of “searchables.”
Friends and Acquaintances – The names of Donald Thurkill (an employee of Mary Ann’s husband Harry), and the various doctors (Dr. Abbott, Dr. Grace, and Dr. Nield) were among the names I noted.
Occupations – Harry Cooke is described as a “coach builder.” Future searches of “coach builder” and “Cooke” together could prove fruitful in the future.
After assembling a comprehensive list of additional searchable words and phrases, I headed back to the British Newspaper Archive to search those leads.
2. Look Beyond Known Names
All of the naming variations I made note of in step number one could now be put to work. But before doing so, I realized that each option I came up with could actually be searched in two ways: Cooke with an “e” and Cook without an “e”. And I knew it was worth doing, because unfortunately my own name is misspelled in print on a regular basis.
Searching both “Mrs. Cooke” and “Mrs. Cook” resulted in even more articles. And in the article about “Mrs. Cooke,” Raymond was referred to as “Master Cooke.” Indeed, even more articles existed under that name as well. In the following example, I found Raymond’s name displayed three different ways!

3. Go Beyond People
While finding your ancestor’s name in print in the newspaper is exciting, don’t underestimate the power of searching for other bits of information. Searching for addresses where they lived can put you in the middle of a wealth of new information about your family.
It isn’t necessary to include the surname of your family. In fact, I highly recommend that you don’t. The property where they lived has a history of it’s own. Simply searching the address can give you a kind of “house history” set of search results. These articles can potentially reveal who lived there before your family, descriptions of the home and its contents, and who your family sold the property to. In both the buying and selling of the property there is the potential to learn more about your family and possible further connections to others in the transactions.
In my case, I located an article about the Cooke home by searching the address 49 Kirkdale Road.
In the search results I discovered an article about the home being put up for sale several years before the Cooke family owned it. It was interesting to note that the previous owner had also been a coach builder, so it was a logical purchase for Harry Cooke when he decided to start up a coach building and horseless carriage mechanic shop of his own.
The final article I found in the British newspapers was also found only by address. The Cooke name was never mentioned, but indeed it did provide the slightest mention of the family: “Owner going abroad.” This article advertised the family home being put up for sale in 1912 in anticipation of their emigration.
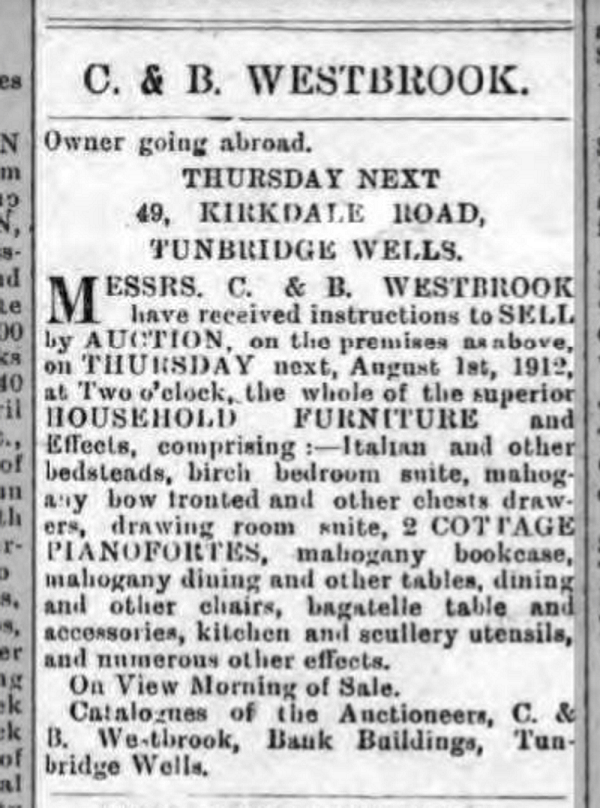
I admit I got a lump in my throat as I read of Mary Ann’s beloved pianofortes being sold. She was a skilled and talented musician who often played violin at the Tunbridge Wells Opera House and at garden parties around the countryside, and clearly she enjoyed playing the piano at home as she owned not one, but two “pianofortes.”
With the description of the inside of the home in the inquest article, the outside of the home in the “house for sale” newspaper advertisement that Harry first responded to, and now this article describing their possessions as they prepare to move to Canada, my newspaper research painted a much more complete picture of the Cooke’s life in Tunbridge Wells, England.
You can hear more about my search for Mary Ann’s story in the free Genealogy Gems Podcast episode #174.
More Resources from Genealogy Gems:
I’ve written additional article here at Genealogy Gems that I think you will benefit from and enjoy:
And if you’re a Genealogy Gems Premium member you have access to my video class Getting the Scoop on Your Ancestors in Newspapers.
If you’re not yet a member, you can learn more here.
Did these tips help you find your ancestors in old newspapers? Please leave a comment below. We all learn from hearing each other’s successes!












